本篇内容主要讲解“react中context传值和生命周期源码分析”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“react中context传值和生命周期源码分析”吧!
假设:
项目中存在复杂组件树:
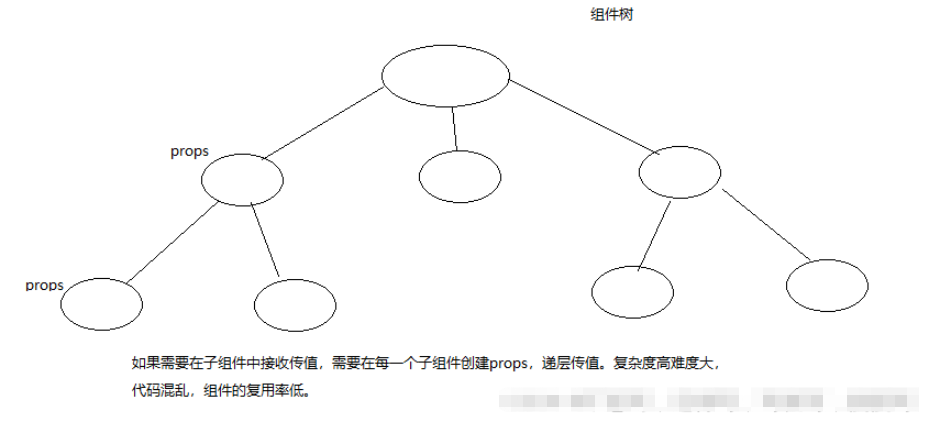
context传值用途
数据是通过 props 属性自上而下(由父及子)进行传递的,但这种做法对于某些类型的属性而言是极其繁琐的(例如:地区偏好,UI 主题),这些属性是应用程序中许多组件都需要的。
Context传值优点
Context 提供了一种在组件之间共享此类值的方式,而不必显式地通过组件树的逐层传递 props。
何时使用 Context
Context 设计目的是为了共享那些对于一个组件树而言是“全局”的数据,例如当前认证的用户、主题或首选语言。
ContextAPI
1.React.createContext API 功能:创建一个 Context 对象。//代码//创建context对象的import React from 'react'let context=React.createContext();export default context; 2.Context.Provider API功能:Provider 是context对象提供的内置组件 限定在某个作用域中使用context传值。限定作用域传值。 3.Context.Consumercontext对象的内置组件<MyContext.Consumer> {value => }</MyContext.Consumer>作用:监听订阅的context变更, 这个函数接收当前的 context 值,返回一个 React 节点。项目案例:主题色切换。
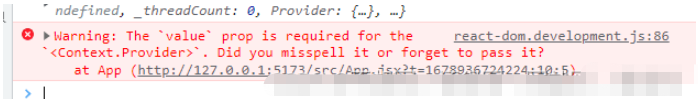
1.创建context.js文件 创建context对象 用来做context传值。//创建context对象的import React from 'react'export default React.createContext();2。使用context找到限定范围使用内置组件Provider {} {} <ThemeContext.Provider> <div className="Admin"> <div className="LeftMenu"> <LeftMenu></LeftMenu> </div> <div className="RightContent"> <div className="RightContent-top"> <TopHeader></TopHeader> </div> <div className="RightContent-bottom"> <Dashborder></Dashborder> </div> </div></ThemeContext.Provider>浏览器报错:
3.在使用context的组件中进行订阅左侧菜单组件import React, { Component } from "react";console.log(Component);//引入context对象import ThemeContext from "../components/context";class LeftMenu extends Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = {}; } render() { return ( <> <div>左侧菜单</div> </> ); }}//class类组件存在contextType 绑定context对象LeftMenu.contextType = ThemeContext;组件中绑定context之后使用:
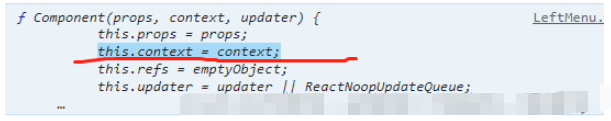
意味着订阅context组件的内部使用this.context获取。
render() { //获取context let theme = this.context; return ( <> <div className={theme}>左侧菜单</div> </> ); }固定主体修改为动态主体
修改了context文件代码//定义默认主体色 export const themes = { dark: { backgroundColor: "#000", color: "#fff", }, light: { backgroundColor: "#fff", color: "#000", },}; //创建context对象的import React from "react";export const ThemeContext = React.createContext();app.js文件中获取主题,动态切换主题。使用主题变量constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { //将固定的主体设置为state状态 themeType: "dark",//控制主体切换 nowTheme: themes["dark"],//获取当前默认主体 }; } render() { //解构获取 let { nowTheme } = this.state; return ( <> {} {} <ThemeContext.Provider value={nowTheme}>订阅组件中使用this.context获取订阅
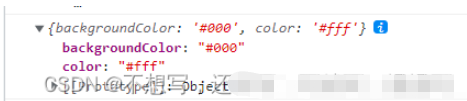
render() { //获取context let { backgroundColor, color } = this.context; return ( <> //直接绑定行内css <div style={{ backgroundColor: backgroundColor, color: color }}> 左侧菜单 </div> </> ); }
用户点击其他组件修改主题的按钮来变更主题
注意:不能直接使用this.context修改变量值//可以在provider组件上 value中携带修改函数传递。在订阅组件中获取修改方法,执行反向传递值。//修改主题变量方法 changeTheme(type) { console.log("测试", type); this.setState({ themeType: type, nowTheme: themes[type] }); } render() { //解构获取 let { nowTheme } = this.state; return ( <> {} {} <ThemeContext.Provider value={{ ...nowTheme, handler: this.changeTheme.bind(this) }} > <div className="Admin"> <div className="LeftMenu"> <LeftMenu></LeftMenu> </div> <div className="RightContent"> <div className="RightContent-top"> <TopHeader></TopHeader> </div> <div className="RightContent-bottom"> <Dashborder></Dashborder> </div> </div> </div> </ThemeContext.Provider> </> ); //在订阅组件中直接使用 //修改主题的方法 change(themeType) { console.log(themeType); //获取provider传递方法 let { handler } = this.context; handler(themeType); } render() { let { themeButton } = this.state; return ( <> <div> <span>主题色:</span> <div> {} {themeButton.map((item, index) => { return ( <button key={index} onClick={this.change.bind(this, item.type)}> {item.name} </button> ); })} </div> </div> </> );添加自定义颜色
{} 背景色: <input type="color" name="selectbgColor" value={selectbgColor} onChange={this.changeColor.bind(this)} /> 字体色: <input type="color" name="selectColor" value={selectColor} onChange={this.changeColor.bind(this)} /> <button onClick={this.yesHandler.bind(this)}>确认</button> //代码区域操作事件向父级传递参数 //确认修改 yesHandler() { let { myhandler } = this.context; let { selectbgColor, selectColor } = this.state; console.log(selectbgColor, selectColor); myhandler(selectbgColor, selectColor); }添加监听context变化
{} <ThemeContext.Consumer> {(value) => { let { backgroundColor, color } = value; return ( <> <span>背景色:{backgroundColor}</span> <span>文字色:{color}</span> </> ); }} </ThemeContext.Consumer>
类组件的生命周期
组件生命周期解释:组件初始化到销毁整个过程。
生命周期三类:
Mounting(挂载):已插入真实 DOM
Updating(更新):正在被重新渲染
Unmounting(卸载):已移出真实 DOM
第一个阶段:代码演示第一个阶段初始化挂载阶段import React, { Component } from "react"; class App extends Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = {}; console.log("初始化"); } componentDidMount() { console.log("挂载完成"); } render() { console.log("渲染"); return ( <> <div>测试</div> </> ); }} export default App;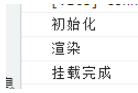
添加了挂载之前周期
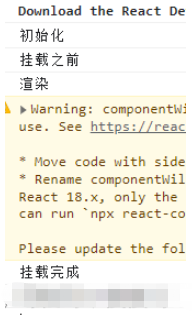
UNSAFE_componentWillMount() { console.log("挂载之前"); } //18.x 版本中UNSAFE_ 前缀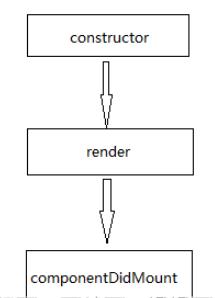
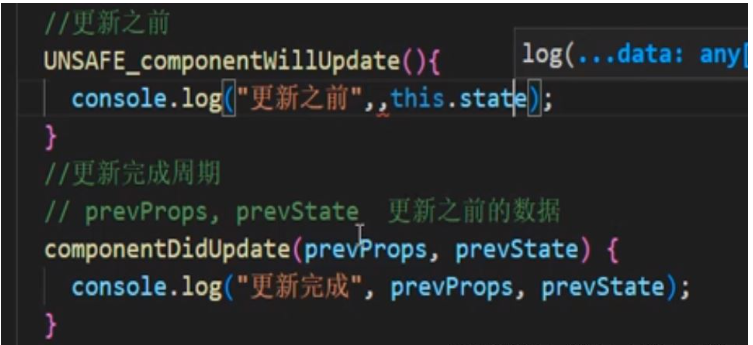
第二个阶段:更新阶段能触发类组件更新 props state添加了更新之前周期
componentWillUpdate() { console.log("更新之前");}第三阶段卸载:
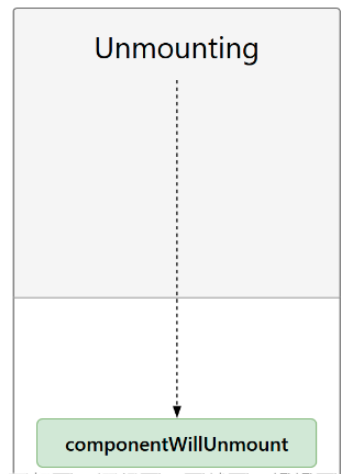
//卸载周期 componentWillUnmount() { console.log("组件卸载"); }常用周期:
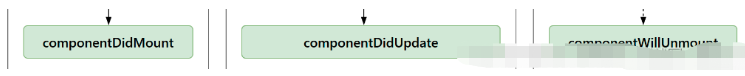
测试完成之后:18版本直接使用周期以上三个。
react推荐网络请求在componentDidMount卸载清除副作用 componentWillUnmount确认当前组件是否更新周期
//确认是否更新周期 //必须带返回值 true false //提升性能 shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState, nextContext) { console.log(nextProps); if (nextProps.name == this.props.name) return false; else return true; } 不写该周期默认是执行更新1.componentWillMount() - 在染之前执行,在客户端和服务器端都会执行.2.componentDidMount() - 是挂在完成之后执行一次3.componentWillReceiveProps() - 当从父类接收到 props 并且在调用另一个渲染器器之前调用。4.shouldComponentUpdatel) -根据特定条件返回 true 或 false如果你希望更新组件,请返回true 否则返它返回 false。5.componentWillUpdate() - 是当前组件state和props发生变化之前执行6.componentDidUpdate()-是当前组件state和props发生变化执行7.componentWillUnmount0) - 从 DOM 卸载组件后调用。用于清理内存空间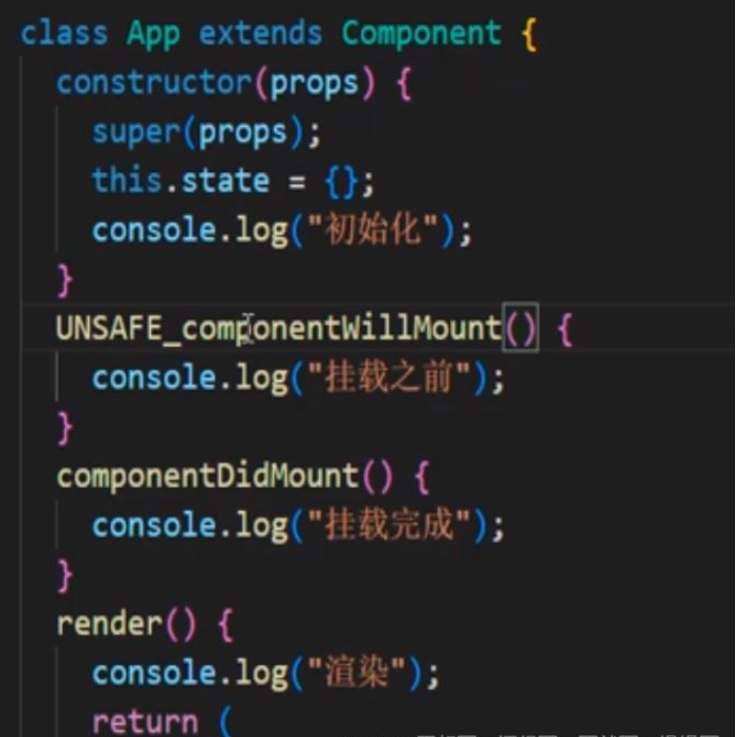
到此,相信大家对“react中context传值和生命周期源码分析”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是编程网网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!




