这篇文章主要为大家分析了Android自定义recyclerView怎么实现时光轴效果的相关知识点,内容详细易懂,操作细节合理,具有一定参考价值。如果感兴趣的话,不妨跟着跟随小编一起来看看,下面跟着小编一起深入学习“Android自定义recyclerView怎么实现时光轴效果”的知识吧。
时光轴效果在很多app上都有出现,例如淘宝中快递的跟踪,下面将使用recyclerView实现时光轴效果,我们会到自定义控件,首先先看一下效果图:
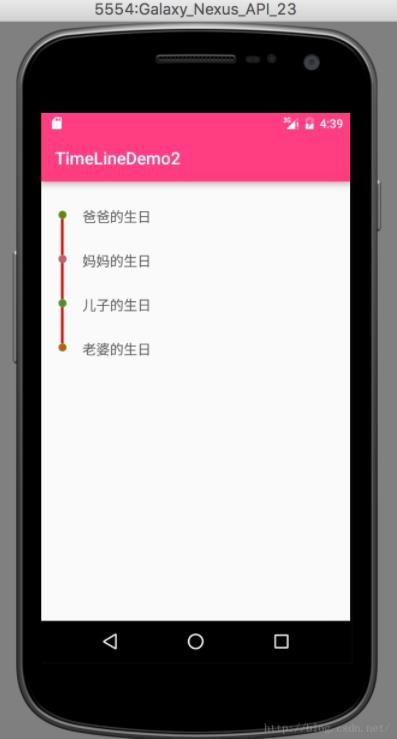
接下来是步骤分析
1自定义属性
这个大家应该都了解了,根据我们之前的分析,直接在attrs.xml中进行声明
<declare-styleable name="TimeLine"> <attr name="beginLine" format="reference|color"></attr> <attr name="endLine" format="reference|color"></attr> <attr name="lineWidth" format="dimension"></attr> <attr name="timeLineImage" format="color|reference"></attr> <attr name="timeLineImageSize" format="dimension"></attr></declare-styleable>进行一下各个属性的声明
• beginLine:开始的线条
• endLine:下面的线条
• lineWidth:线条的宽度
• timeLineImage:中间的圆形
• timeLineImageSize:中间的圆形的大小,这里默认他的宽高一致
2.自定义TimeLine继承View,构造方法如下
private int lineWidth;private Drawable mBeginLine;private Drawable mEndLine;private Drawable mTimeLineImage;private int mTimeLineImageSize; public TimeLine(Context context) { this(context,null);} public TimeLine(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context,attrs,0);} public TimeLine(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.TimeLine); lineWidth = a.getDimensionPixelOffset(R.styleable.TimeLine_lineWidth,15); mBeginLine = a.getDrawable(R.styleable.TimeLine_beginLine); mEndLine = a.getDrawable(R.styleable.TimeLine_endLine); mTimeLineImage = a.getDrawable(R.styleable.TimeLine_timeLineImage); mTimeLineImageSize = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.TimeLine_timeLineImageSize,25); a.recycle(); }3.复写onMeasure方法
我们都知道自定义控件,一般需要重写onMeasure,onDraw,onLayout方法,这里onMeasure需要对wrap_content的情况进行特殊处理,具体原因请看源码
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); int w = timeLineMarkerSize + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight(); int h = timeLineMarkerSize + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom(); int widthSize = resolveSizeAndState(w, widthMeasureSpec, 0); int heightSize = resolveSizeAndState(h, heightMeasureSpec, 0); int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); int heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); // 处理宽高都为 wrap_content 的情况 if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { setMeasuredDimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } // 处理宽为 wrap_content 的情况 else if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { setMeasuredDimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, widthSize); } // 处理高为 wrap_content 的情况 else if (heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { setMeasuredDimension(heightSize, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } }看过View源码的同学应该知道,在控件进行测量的时候,需要根据
specMode来进行具体的操作,View中提供了resolveSizeAndState方法来进行判断,该方法源码如下:
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState) { int result = size; int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec); int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec); switch (specMode) { case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: result = size; break; case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: if (specSize < size) { result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL; } else { result = size; } break; case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: result = specSize; break; } return result | (childMeasuredState&MEASURED_STATE_MASK); }4.onDraw方法
@Overrideprotected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); if (mBeginLine != null) { mBeginLine.draw(canvas); } if (mEndLine != null) { mEndLine.draw(canvas); } if (mTimeLineImage!=null){ mTimeLineImage.draw(canvas); }}5.onSizeChange
@Overrideprotected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) { int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft(); int paddingRight = getPaddingRight(); int paddingTop = getPaddingTop(); int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom(); //父容器的宽高 int width = getWidth(); int height = getHeight(); int childWidth = width - paddingLeft - paddingRight; int childHeight = height - paddingTop - paddingBottom; mTimeLineImageSize = Math.min(mTimeLineImageSize, Math.min(childHeight, childWidth)); if (mTimeLineImage != null) { mTimeLineImage.setBounds(paddingLeft, paddingTop, paddingLeft + mTimeLineImageSize, paddingTop + mTimeLineImageSize); bounds = mTimeLineImage.getBounds(); } else { bounds = new Rect(paddingLeft, paddingTop, paddingLeft + childWidth, paddingTop + childHeight); } if (mBeginLine != null) { int lineLeft = mTimeLineImage.getBounds().centerX() - (lineWidth >> 1); mBeginLine.setBounds(lineLeft, 0, lineLeft + lineWidth, mTimeLineImage.getBounds().top); } if (mEndLine != null) { int lineLeft = mTimeLineImage.getBounds().centerX() - (lineWidth >> 1); mEndLine.setBounds(lineLeft, mTimeLineImage.getBounds().bottom, lineLeft + lineWidth, height); }}这里需要说明的是,我们的mBeginLine的长度,其实是我们自定义控件的paddingTop高度,同理mEndLine的长度是paddingBottom高度,所以我们在使用这个控件时,一般都会设置paddingTop和paddingBottom
6.使用TimeLine控件
以下是recyclerView中一个item的布局,多个item拼接起来就是一条时光轴,这里需要说明的是,我们的 LinearLayout使用的高度模式是wrap_content,这里我的TextView设置了android:paddingTop="30dp",如果不对TextView设置android:paddingTop,会发现TimeLineView控件是看不见的,这是由于父控件wrap_content,那么父控件包裹TextView的内容,那么父控件的高度就是TextView的高度,这样TimeLineView设置了android:paddingTop="34dp",这个高度是大于父控件的高度的,所以就看不到TimeLineView了,除非我们给LinearLayout的android:layout_height="wrap_content",修改成固定的高度
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" android:paddingLeft="16dp" android:paddingRight="16dp"> <com.example.jikeyoujikeyou.timelinedemo2.TimeLineView android:id="@+id/timeLineView" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:clickable="true" android:focusable="true" android:focusableInTouchMode="true" android:paddingBottom="8dp" android:paddingLeft="4dp" android:paddingRight="4dp" android:paddingTop="34dp" app:beginLine="#ff0000" app:endLine="#ff0000" app:lineWidth="3dp" app:timeLineMarker="@drawable/timeline_marker" app:timeLineMarkerSize="24dp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/timeLineName" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:ellipsize="end" android:paddingTop="30dp" android:singleLine="true" android:text="name" android:textColor="@color/grey_700" android:textSize="16sp" /></LinearLayout>7.最后就是recyclerView的使用
recyclerView的使用大家应该都很熟悉了,无非就是设置adapter,viewHolder等,这里不再赘述,还有一点需要强调的是ItemViewType有四种情况,第一个,最后一个,中间,还有只有一个四种情况情况,根据这几种情况,有选择设置mBeginLine与 mEndLine是否进行绘制
TimeLineAdapter代码:
package com.example.jikeyoujikeyou.timelinedemo; import android.annotation.TargetApi;import android.content.Context;import android.graphics.drawable.Drawable;import android.os.Build;import android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView;import android.view.LayoutInflater;import android.view.View;import android.view.ViewGroup;import android.widget.TextView; import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import java.util.Random; public class TimeLineAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<TimeLineAdapter.ViewHolder> { private List<TimeLineItem> datas ; public TimeLineAdapter(List<TimeLineItem> datas) { super(); this.datas = datas; } @Override public ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) { LayoutInflater layoutInflater = LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()); View view = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.item_timeline, null); return new ViewHolder(view, parent.getContext(), viewType); } @Override public void onBindViewHolder(ViewHolder holder, int position) { TimeLineItem timeLineItem = datas.get(position); holder.tv_name.setText(timeLineItem.getTimeLineName()); } @Override public int getItemCount() { return datas.size(); } @Override public int getItemViewType(int position) { int size = datas.size() - 1; if (size == 0) { return TimeLineItemType.ATOM; } else if (position == 0) { return TimeLineItemType.START; } else if (position == size) { return TimeLineItemType.END; } else { return TimeLineItemType.NORMAL; } } class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder { private TextView tv_name; private TimeLine timeLine; public ViewHolder(View itemView, Context context, int viewType) { super(itemView); tv_name = (TextView) itemView.findViewById(R.id.name); timeLine = (TimeLine) itemView.findViewById(R.id.timeLineView); Drawable drawable = context.getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.timeline_marker); Drawable drawable2 = context.getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.timeline_marker2); Drawable drawable3 = context.getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.timeline_marker3); Drawable drawable4 = context.getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.timeline_marker4); Drawable drawable5 = context.getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.timeline_marker5); Random random = new Random(); final int i = random.nextInt(5); final Drawable drawables[] = {drawable, drawable2, drawable3, drawable4, drawable5}; timeLine.setTimeLineImage(drawables[i]); if (viewType == TimeLineItemType.START) { timeLine.setBeginLine(null); } else if (viewType == TimeLineItemType.END) { timeLine.setEndLine(null); } else if (viewType == TimeLineItemType.ATOM) { timeLine.setBeginLine(null); timeLine.setEndLine(null); } } } class TimeLineItemType { //正常 public final static int NORMAL = 0; //开始 public final static int START = 1; //结束 public final static int END = 2; //只有一条数据,那么beginLine和endLine都没有 public final static int ATOM = 3; } }MainActivity代码:<pre name="code" class="java">public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private List<TimeLineItem> mDatas; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); initData(); RecyclerView recyclerView = (RecyclerView) findViewById(R.id.recyclerview); LinearLayoutManager linearLayoutManager = new LinearLayoutManager(this); linearLayoutManager.setOrientation(LinearLayoutManager.VERTICAL); recyclerView.setLayoutManager(linearLayoutManager); TimeLineAdapter adapter = new TimeLineAdapter(mDatas); recyclerView.setAdapter(adapter); } private void initData() { mDatas = new ArrayList<>(); mDatas.add(new TimeLineItem("爸爸生日")); mDatas.add(new TimeLineItem("妈妈生日")); mDatas.add(new TimeLineItem("姐姐生日")); mDatas.add(new TimeLineItem("女神生日")); mDatas.add(new TimeLineItem("前任生日")); }}运行项目,就会呈现本文一开始的效果。
Android是什么
Android是一种基于Linux内核的自由及开放源代码的操作系统,主要使用于移动设备,如智能手机和平板电脑,由美国Google公司和开放手机联盟领导及开发。
关于“Android自定义recyclerView怎么实现时光轴效果”就介绍到这了,更多相关内容可以搜索编程网以前的文章,希望能够帮助大家答疑解惑,请多多支持编程网网站!




