字符串
1.字符串的常见构造方法
主要有三种,一种是直接使用常量去构造,要么使用new String来构造,或者还可以使用字符数组的形式。
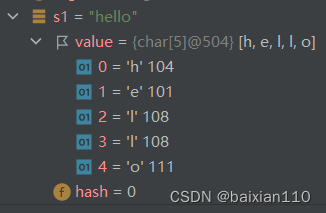
public static void main(String[] args) {// 使用常量串构造String s1 = "hello";System.out.println(s1);// 直接newString对象String s2 = new String("hello");System.out.println(s1);// 使用字符数组进行构造char[] array = {'h','e','l','l','o'};String s3 = new String(array);//将字符数组构造成一个字符串System.out.println(s1);}String 类型本身并不存储数据,而是存储指向该字符串的引用,所以字符串类型是一个类,s1是一个引用,指向这个类。而这个类有两个成员变量,一个名称为value,这也是一个引用类型,指向一个字符数组,与C++类似,但是java中的字符数组是没有\0的。此外,字符串类型还有一个成员变量hash,这个暂时知道就行了。
2.常见的String类的方法
求长度
String.length()
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "hello"; String str2 = ""; char[] arr = {'h','e','l','l','o'}; System.out.println(str1.length());//求字符串度,打印5 System.out.println(str2.length());//求字符串度。打印0 System.out.println(arr.length);//主要数组求长度和字符串求长度的区别,一个调用方法,一个调用属性 }}
判空
String isEmpty
判断是不是空字符串
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str2 = ""; System.out.println(str2.isEmpty());//返回的是true }}主要空字符串和空引用的区别
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str2 = ""; System.out.println(str2.isEmpty());//返回的是true String str3 = null; System.out.println(str3.isEmpty());//报错 NullPointerException }}一个代表指向空字符串,一个代表不指向任何空间。
String对象的比较
queals方法
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "hello"; String str2 = "hello"; System.out.println(str1 == str2);//实际比较的是两个字符串所在的地址,结果是false System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));//实际比较的是两个字符串的内容,结果是true }}eques方法在java中定义是这样的
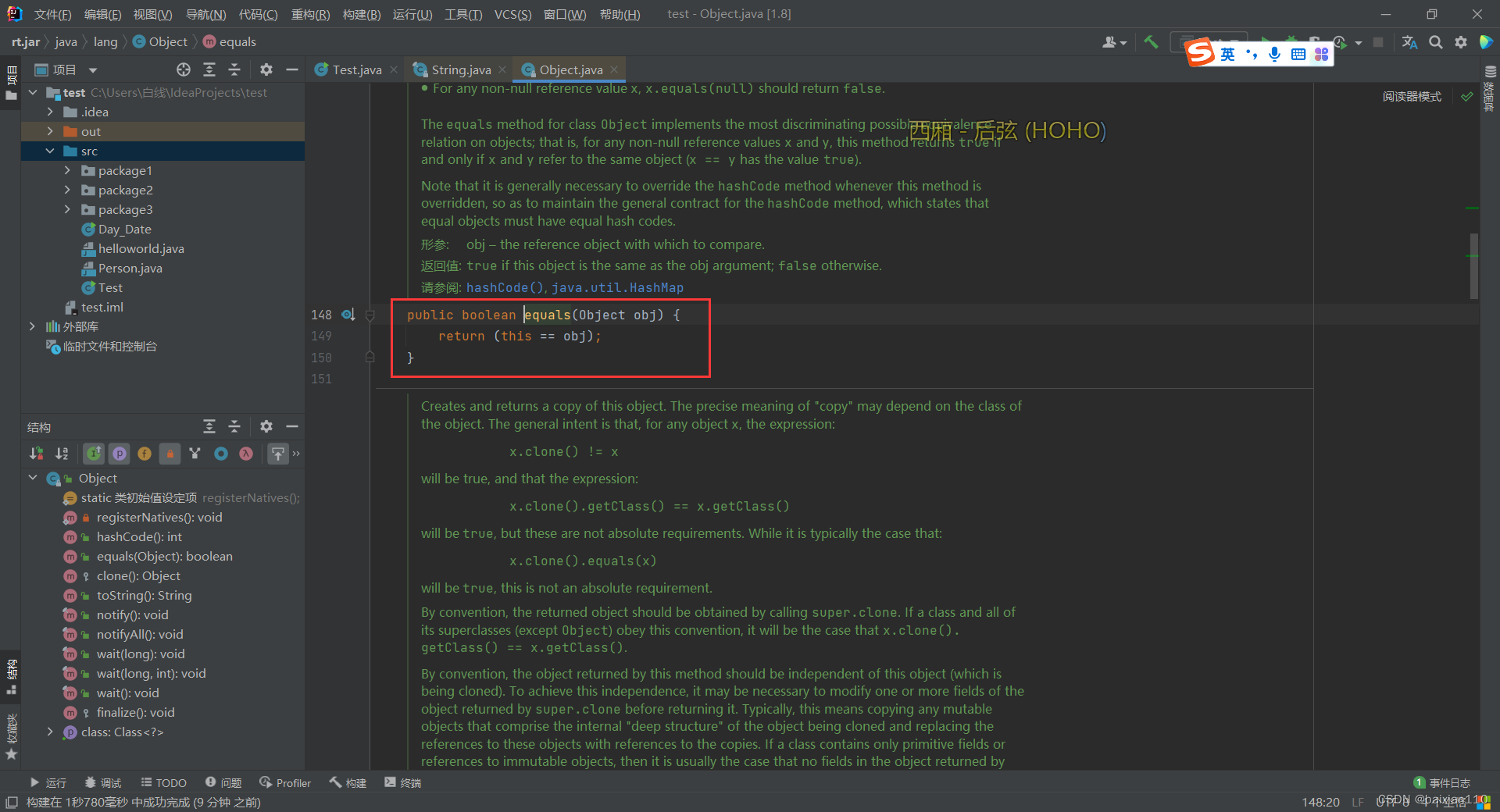 Object类里有一个equals方法,然后String类继承,并进行重写,重写后的equals方法如下
Object类里有一个equals方法,然后String类继承,并进行重写,重写后的equals方法如下
public boolean equals(Object anObject) { if (this == anObject) {//如果两个指向的是同一个字符串 return true; } if (anObject instanceof String) {//instanceof 关键字判断一个对象是否为一个类(或接口、抽象类、父类)的实例 String anotherString = (String)anObject; int n = value.length; if (n == anotherString.value.length) { char v1[] = value; char v2[] = anotherString.value; int i = 0; while (n-- != 0) { if (v1[i] != v2[i]) return false; i++; } return true; } } return false; }public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)函数比较方法与equals是一样的,但是会忽略大小写。
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = new String("abc"); String s2 = new String("ac"); String s3 = new String("ABc"); String s4 = new String("abcdef"); System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)); // 不同字母,输出false System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3)); // 相同字母,忽略大小写。输出true System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s4)); // 字符串不同,输出false }}String对象的比较
compare方法
与equals不同的是,equals返回的是boolean类型,而compareTo返回的是int类型。具体比较方式:
- 先按照字典次序大小比较,如果出现不等的字符,直接返回这两个字符的大小差值
- 如果前k个字符相等(k为两个字符长度最小值),返回值两个字符串长度差值
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "hello"; String str2 = "hello"; String str3 = "word"; System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2)); System.out.println(str3.compareTo(str2));//w的ASCIIz值为119,h的ASCII值是104 ;15= 1119-104 }}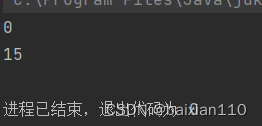
String.java是这样重写compareTo函数的
public int compareTo(String anotherString) { int len1 = value.length;//本字符串的长度 int len2 = anotherString.value.length;//另外一个字符串长度 int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);//去最小值 char v1[] = value;//将字符串转化为数组 char v2[] = anotherString.value; int k = 0; while (k < lim) { char c1 = v1[k]; char c2 = v2[k]; if (c1 != c2) { return c1 - c2;//返回的是首个不同字符的ASCII相减值 } k++; } return len1 - len2; }int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) 方法:与compareTo方式相同,但是忽略大小写比较
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = new String("abc"); String s2 = new String("ac"); String s3 = new String("ABc"); String s4 = new String("abcdef"); System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1 System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s3)); // 相同输出 0 System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s4)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3 }}字符串查找
1char charAt(int index)
返回index位置上字符,如果index为负数或者越界,抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException异常
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String name = "baixian"; for (int i = 0; i < name.length(); i++) { System.out.println(name.charAt(i));//下标从0开始 } }}结果是
b
a
i
x
i
a
n
String.java中对该方法定义如下
public char charAt(int index) { if ((index < 0) || (index >= value.length)) { throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);//越界,扔出警告 } return value[index];//如果没错,就返回字符数组对应下标的元素 }2.int indexOf()
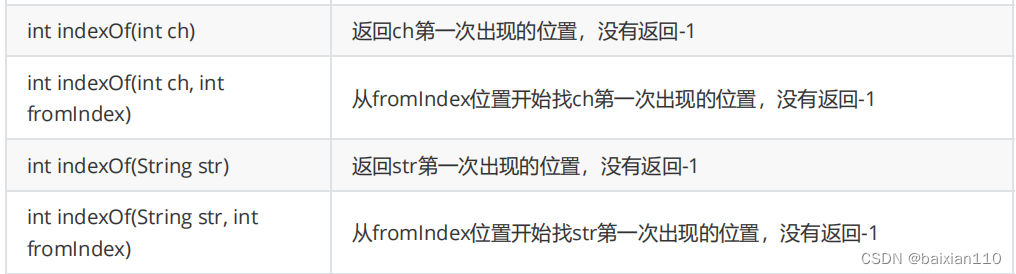
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String name = "baixian"; System.out.println(name.indexOf('a'));//打印值为1 System.out.println(name.indexOf('a',2));//从下标2的位置开始遍历,打印值为5 System.out.println(name.indexOf("ai"));//在"baixian"主串中寻找子串(默认从0下标开始),返回子串的首字母所在的下标,打印值为1 System.out.println(name.indexOf("ai",3));//在"baixian"主串中从3下标开始寻找子串,返回子串的首字母所在的下标,打印值为-1 }}String.java中对该方法定义如下
public int indexOf(int ch) { return indexOf(ch, 0); }public int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) {//fromInde表示起始下标 final int max = value.length; if (fromIndex < 0) {//起始下标小于0默认从从0开始 fromIndex = 0; } else if (fromIndex >= max) {//起始下标大于字符串长度,返回-1 // Note: fromIndex might be near -1>>>1. return -1; } if (ch < Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT) { // handle most cases here (ch is a BMP code point or a // negative value (invalid code point)) final char[] value = this.value; for (int i = fromIndex; i < max; i++) {//遍历寻找 if (value[i] == ch) { return i; } } return -1; } else { return indexOfSupplementary(ch, fromIndex); } }public int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) { return indexOf(value, 0, value.length, str.value, 0, str.value.length, fromIndex); }当然还有,这里就不一一列举出来了。
3.int lastIndexOf()
int lastIndexOf(int ch) 从后往前找,返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
int lastIndexOf(String str) 从后往前找,返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
int lastIndexOf(String str, intfromIndex)从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找str第一次出现的位置,没有返
回-1
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String name = "baixian"; System.out.println(name.lastIndexOf('a')); System.out.println(name.lastIndexOf('a',6)); System.out.println(name.lastIndexOf("ai")); System.out.println(name.lastIndexOf("ai",4)); }}
字符串的转换
1.数值转字符串
注意:这里的转换并不是按照ASCII进行转换,而是直接变成字符形式

public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = String.valueOf(1234); String str2 = String.valueOf(12.34f); String str3 = String.valueOf(false); String str4 = String.valueOf('1'); String str5 = String.valueOf("1234"); String str6 = String.valueOf(12.34); char[] arr = {'a','b'}; String str7 = String.valueOf(arr); System.out.println(str1); System.out.println(str2); System.out.println(str3); System.out.println(str4); System.out.println(str5); System.out.println(str6); System.out.println(str7); }}
2.字符串转数字
// 字符串转数字// 注意:Integer、Double等是Java中的包装类型,这个后面会讲到int data1 = Integer.parseInt("1234");double data2 = Double.parseDouble("12.34");System.out.println(data1);System.out.println(data2);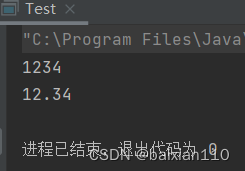
注:有关包装类的知识,可以去看https://blog.csdn.net/qq_53312143/article/details/126124615这位博主的博客
3.大小写转换
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "HELLO,你好"; String str2 = "hello,你好"; String str3 = "HEllo"; System.out.println(str2.toLowerCase());//转换成小写 System.out.println(str2.toUpperCase());//转换成大写 System.out.println(str3.toLowerCase()); }}4.字符串转数组
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "hello";// 字符串转数组 char[] ch = s.toCharArray();//toCharArray()字符串转化为字符数组 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ch)); System.out.println();// 数组转字符串 System.out.println(s+"");//可以使用变量名+““的形式,将这个变量输出为字符型 String s2 = new String(ch); System.out.println(s2);//或者用String方法,转换 }}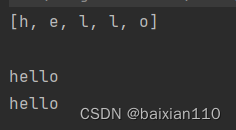
格式化
一般用于输出打印上
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = String.format("%d-%d-%d",2019,9,14); System.out.println(str1); }}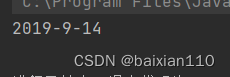
字符替换
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "aabbabbaa"; String ret1 = str1.replace('a','b');//将字符串中所有a替换为b System.out.println(ret1); String ret2 = str1.replace("ab","cc");//将字符串中所有ab替换为cc System.out.println(ret2); String ret3 = str1.replaceAll("a","b");//将所有字符都替换为b System.out.println(ret3); String ret4 = str1.replaceAll("a","ab");//将所有字符都替换为ab System.out.println(ret4); String ret5 = str1.replaceAll("a","b");//将第一个字符a替换为b System.out.println(ret5); }}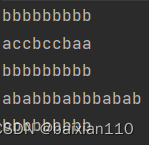
注意事项: 由于字符串是不可变对象, 替换不修改当前字符串, 而是产生一个新的字符串.
字符串拆分
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "hello bai xian"; String[] ret1 = str1.split(" ");//以空格为界限,分组,并存入字符串数组中 String[] ret2 = str1.split(" ",2);///以空格为界限,分组,最多分两组 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ret1)); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ret2)); }}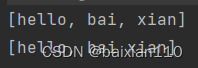
但是需要注意
由于regex正则表达式的特殊性,所以一定要注意正则表达式在遇到转义字时的特殊情况
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "hello.bai.xian"; String str2 = "hello.bai*xian"; String[] ret1 = str1.split(".");//以.为分隔符需要注意,单独的.在正则表达式中表示所有字符,所以打印出来会是空字符数组 String[] ret2 = str1.split("\\. ",2);//java中以\\代表一个\,所以\\.才表示真正的. System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ret1)); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ret2)); String [] ret3 = str2.split("\\.|\\*");//用|表示或,表示两个不同的分隔符都可以分割 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ret3)); }}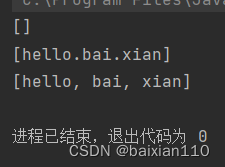
有关正则表达式,可以看这位博主的博客
https://blog.csdn.net/senxu_/article/details/126109760
多次拆分
public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "name=zhangsan&age=18" ; String[] result = str.split("&") ; for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) { String[] temp = result[i].split("=") ; System.out.println(temp[0]+" = "+temp[1]); } }}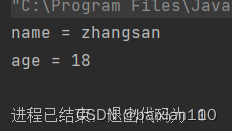
字符串的截取
String substring(int beginIndex) 从指定索引截取到结尾
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) 截取部分内容(左闭右开)
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "abcdef"; System.out.println(str.substring(5));//从下标5开始截取一直到字符末尾 System.out.println(str.substring(0, 5));//从下标0开始到下标4结束 }}删除空格
String trim() 会去掉字符串开头和结尾的空白字符(空格, 换行, 制表符等).
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = " hello world "; System.out.println("["+str1+"]"); System.out.println("["+str1.trim()+"]"); }}字符串的不可变性
首先先看一个代码
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "abcde"; String str2 = "abcde"; String str3 = new String("abcde"); System.out.println(str1 == str2); System.out.println(str1 == str3); }}结果
truefalse整个程序执行过程是这样的,执行String str1 = "abcde";系统会在内存空间方法区中一块叫常量池的地方,这个里面存的是“abcde”这样一个字符数组,这个字符数组的地址假设为0x7,在栈中系统会创建一个名为str1的变量来,存储0x7。当进行第二行代码String str2 = "abcde";系统不会再在常量池里创建另外一个字符数组“abcde”了,而是依旧使用唯一的那一个"abcde",对str2进行实例化,所以str2中依旧存放的是0x7,所以第一个打印true;但是第三句代码执行了new()操作,实际在底层,他在堆区开辟了一块存储空间,用以存储常量池里面“abcde”的地址,然后再在栈区创建str3变量存储堆区的堆区的地址。所以第二行打印是false.
这里建议去看一下这篇博客,再去理解一下
//blog.csdn.net/liuyong1992/article/details/113835447
从上层定义上去看String的不可变性
在Java,jdk8中Sring类的部分定义如下图
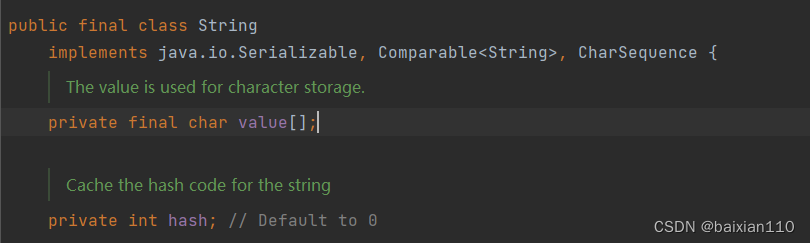 我们可以看到Sring类本身被
我们可以看到Sring类本身被final修饰,而Sring类里面的字符数组value,是被private final修饰的
final修饰类表明该类不想被继承,final修饰引用类型表明该引用变量不能引用其他对象,但是其引用对象中的内
容是可以修改的。
我们常说的String不能被修改是指String类里面的value数组不能更改,而不能更改的原因并不是因为final,而是因为private,这是一个私有变量,要想更改必须通过调用set方法,但是原生String类中并没有提供setvalue 方法,所以没有办法更改。
字符串的修改
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "abcde"; str1 += "abc"; System.out.println(str1); }}不要认为这里是对str1这个对象改变了,本质上创建了一个新的对象abcdeabc,将这个对象重新命str1,而不是将abcde这个对象进行了更改。
我们可以反汇编去看一下
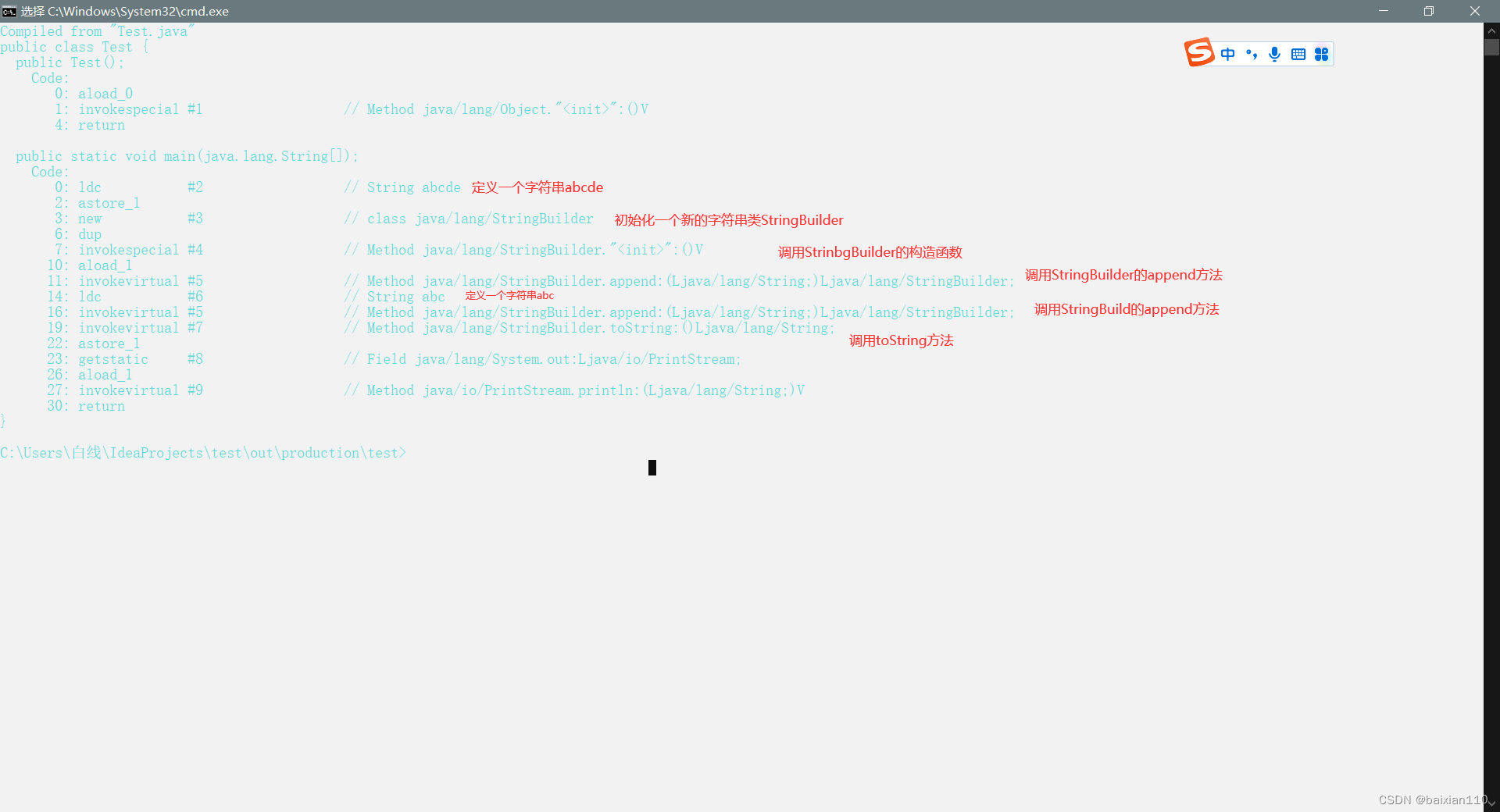
实际上上述代码可以改为
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "abcde"; StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); stringBuilder.append(str); stringBuilder.append("abc"); str = stringBuilder.toString(); System.out.println(str); }}注意:只要两个字符串相加就会调用toSting函数,并不是说println函数调用才会调用toString
可以看出在对String类进行修改时,效率是非常慢的,因此:尽量避免对String的直接需要,如果要修改建议尽量
使用StringBuffer或者StringBuilder。
StringBuilder和StringBuffer
由于String的不可更改特性,为了方便字符串的修改,Java中又提供StringBuilder和StringBuffer类。这两个类大
部分功能是相同的,这里介绍 StringBuilder常用的一些方法
StringBuff append(String str)在尾部追加,相当于String的+=,可以追加:boolean、char、char[]、double、float、int、long、Object、String、StringBuff的变量
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) {// StringBuilder stringBuilder = "abc";//注意,这样是不成立的,因为"abc"默认是String类型,并不是 StringBuilder类型 StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("abc"); stringBuilder.append("abc"); stringBuilder.append(10).append(19.5);//所有方法都是返回一个this 所以不会有那么多临时变量 System.out.println(stringBuilder); }}下面看一个题目
String str = new String("ab"); // 会创建多少个对象String str = new String("a") + new String("b"); // 会创建多少个对象上面这个代码创建了多少对象
首先常量池里就会创建“ab”这样一个String对象,然后堆区里new了一个String对象,第二行代码,常量池里面创建两个String对象“a”和“b”,然后在堆区又new了两个String对象.然后两个字符串相加在底层是创建了StringBuilder对象,此外还要注意,调用toString 函数的时候,返回值里面,也会new一个String对象
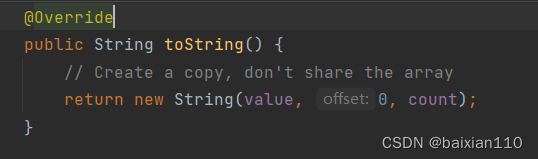
至此,String 就讲解到这里
来源地址:https://blog.csdn.net/baixian110/article/details/130533505







