这篇文章主要讲解了“怎么使用Shell脚本实现监测文件变化”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“怎么使用Shell脚本实现监测文件变化”吧!
代码
完整的shell脚本如下,可以直接使用。本示例中,脚本文件名为fileTracer.sh。
#!/bin/bash# ------------------------------------------# Filename : fileTracer.sh# Version : 1.1# Date : 2022-5-22 00:52:23# Author : 农民工老王@CSDN# Email : scwja@qq.com# Website : https://blog.csdn.net/monarch91# Description : 用于追踪文件变化的脚本# ------------------------------------------time=$1sleepNum=$2filePath=$3fileName=`basename ${filePath}`whileNum=$(echo "scale=0;${time}*60/${sleepNum}"|bc)flag=0historyDir=./fileHistorytimeStr=""detection_log() { timeStr=$(date "+%H:%M:%S.%N") timeStr=${timeStr:0:12} echo -e "\033[35m${timeStr}\033[0m \033[36m[DEBUG]\033[0m :$1"}existNotice=0deleteNotice=0md5StrLast=""mkdir -p $historyDirwhile [ $flag -lt $whileNum ]; do if [ -f "${filePath}" ]; then if [ $existNotice -eq 1 ] || [ $flag -eq 0 ] ; then if [ $flag -eq 0 ]; then detection_log "文件已存在。" else detection_log "文件被创建。" fi md5StrLast=`md5sum ${filePath} | awk '{ print $1 }'` cp -fr ${filePath} ${historyDir}/${timeStr}_${fileName} else md5StrNow=`md5sum ${filePath} | awk '{ print $1 }'` >/dev/null 2>&1 if [ "lw${md5StrNow}" != "lw" ] && [ "lw${md5StrNow}" != "lw${md5StrLast}" ]; then detection_log "文件被修改。" cp -fr ${filePath} ${historyDir}/${timeStr}_${fileName} md5StrLast=${md5StrNow} fi fi existNotice=0 deleteNotice=1 else if [ $flag -eq 0 ]; then detection_log "文件未创建。" elif [ $deleteNotice -eq 1 ]; then detection_log "文件被删除。" fi deleteNotice=0 existNotice=1 fi flag=$((flag+1)) sleep ${sleepNum}done使用方法
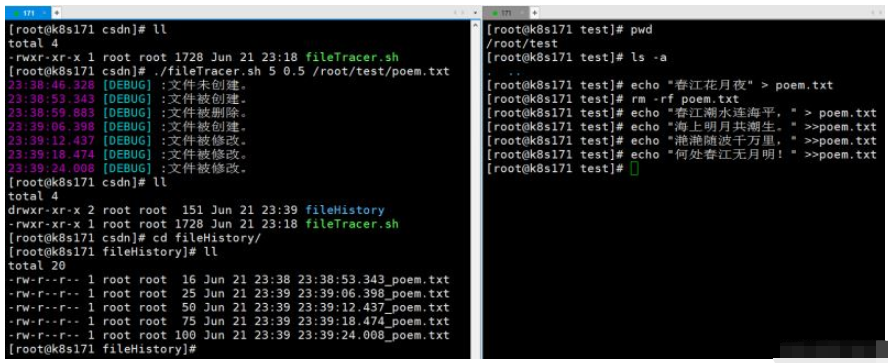
在脚本所在文件夹运行:./fileTracer.sh ${监测时长} ${监测间隔} ${被监测文件的绝对路径}
其中 监测时长 的单位为 分钟,检测间隔的单位为 秒,以上两个参数均可以为小数。如:./fileTracer.sh 5 0.5 /root/test/poem.txt ,此指令表示在未来的5分钟内,每隔0.5秒监测一次 /root/test/poem.txt的文件变化。
感谢各位的阅读,以上就是“怎么使用Shell脚本实现监测文件变化”的内容了,经过本文的学习后,相信大家对怎么使用Shell脚本实现监测文件变化这一问题有了更深刻的体会,具体使用情况还需要大家实践验证。这里是编程网,小编将为大家推送更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注!




