这篇文章主要为大家展示了“Python面向对象和类的示例分析”,内容简而易懂,条理清晰,希望能够帮助大家解决疑惑,下面让小编带领大家一起研究并学习一下“Python面向对象和类的示例分析”这篇文章吧。
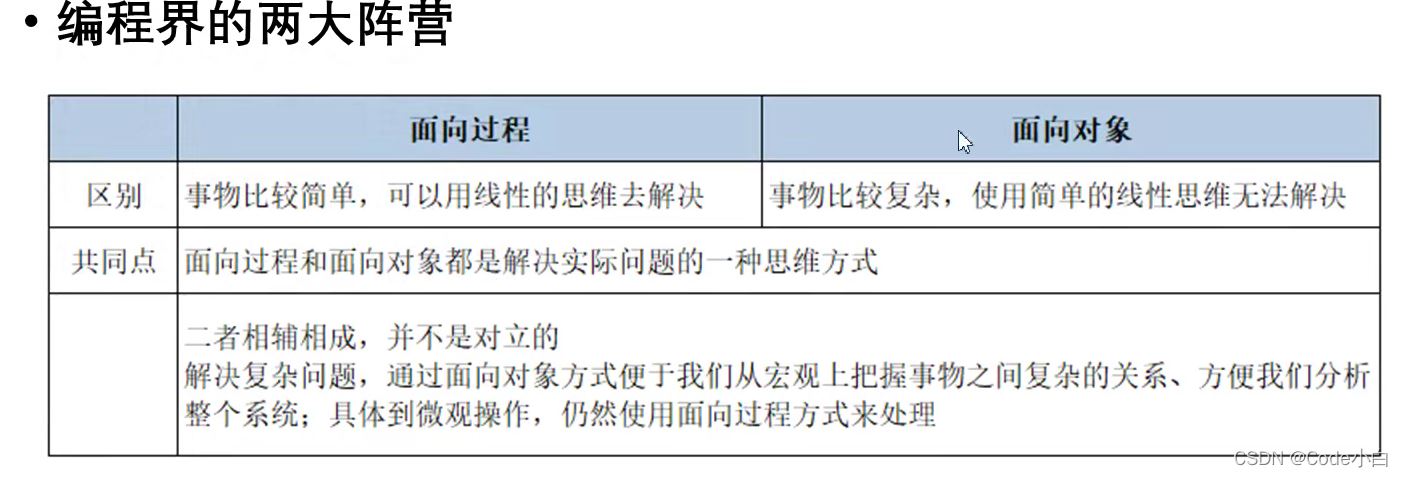
一、两大编程思想
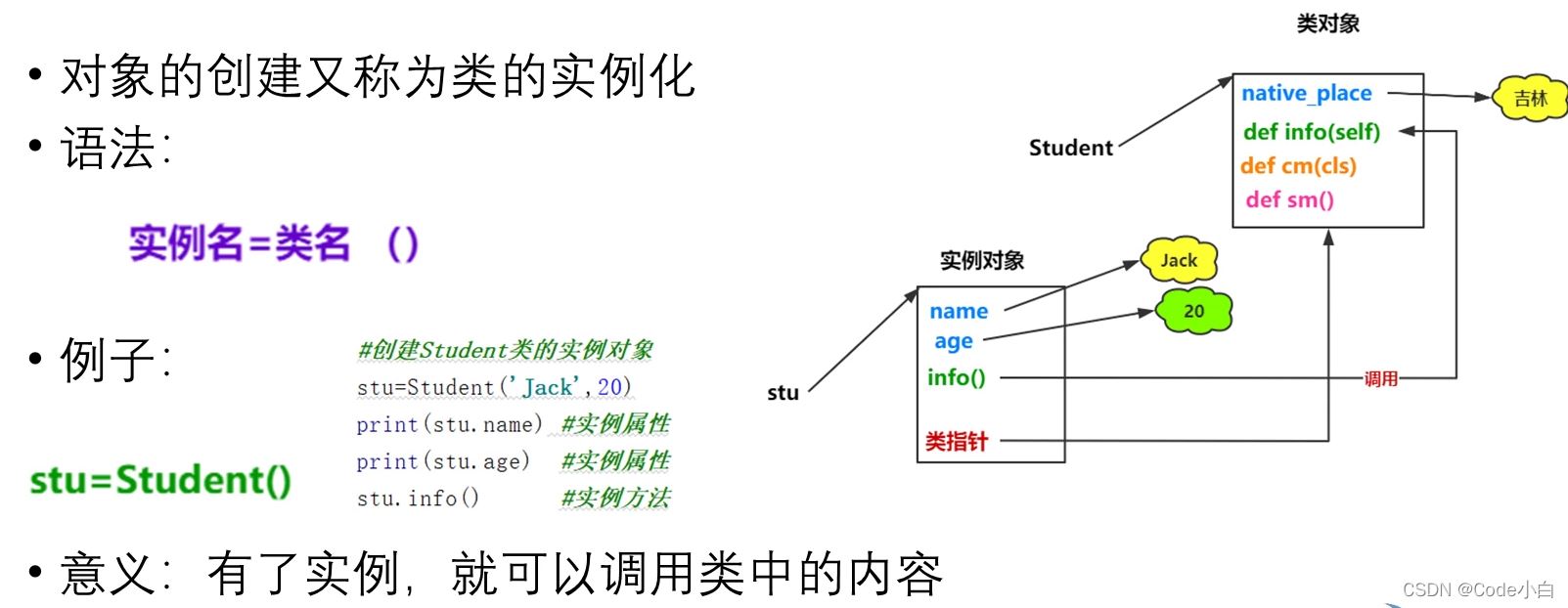
二、类与对象

简单举例:

python中一切皆对象,开局一张图:
三、定义Python中的类

举例1:
class Student: passprint(id(Student)) #1149225945800print(type(Student)) #<class 'type'>print(Student) #<class '__main__.Student'>举例2:
class Student: native_place='吉林' #类属性 def __init__(self,name,age): self.name=name self.age=age #实例方法 def eat(self): print("学生在吃饭") #静态方法 @staticmethod def method(): print("我是静态方法") #类方法 @classmethod def cm(cls): print("我是类方法")四、对象创建
举例1:
#实例对象student1=Student("张三",18)print(student1)print(id(student1))print(type(student1))print("-------------------------------------------")#类对象,代表所在的类print(Student)print(id(Student))print(type(Student))举例2:
#实例对象student1=Student("张三",18)print(student1.name)print(student1.age)#实例方法调用有以下两种使用:print(student1.eat())print(Student.eat(student1))五、类属性、类方法、静态方法

举例1:类属性
#类属性student1=Student("张三",18)student2=Student("李四",19)print(Student.native_place) #吉林print(student1.native_place)#吉林print(student2.native_place)#吉林Student.native_place='四川'print(student1.native_place)#四川print(student2.native_place)#四川#---------------------------------------------------------student1.native_place='广东'print(student1.native_place)#广东print(student2.native_place)#四川举例2:类方法、静态方法
#类方法、静态方法使用student1=Student("张三",18)Student.method()#我是静态方法Student.cm()#我是类方法六、动态绑定属性和方法
Python是动态语言,在创建对象之后,可以动态的绑定属性和方法

举例:属性绑定
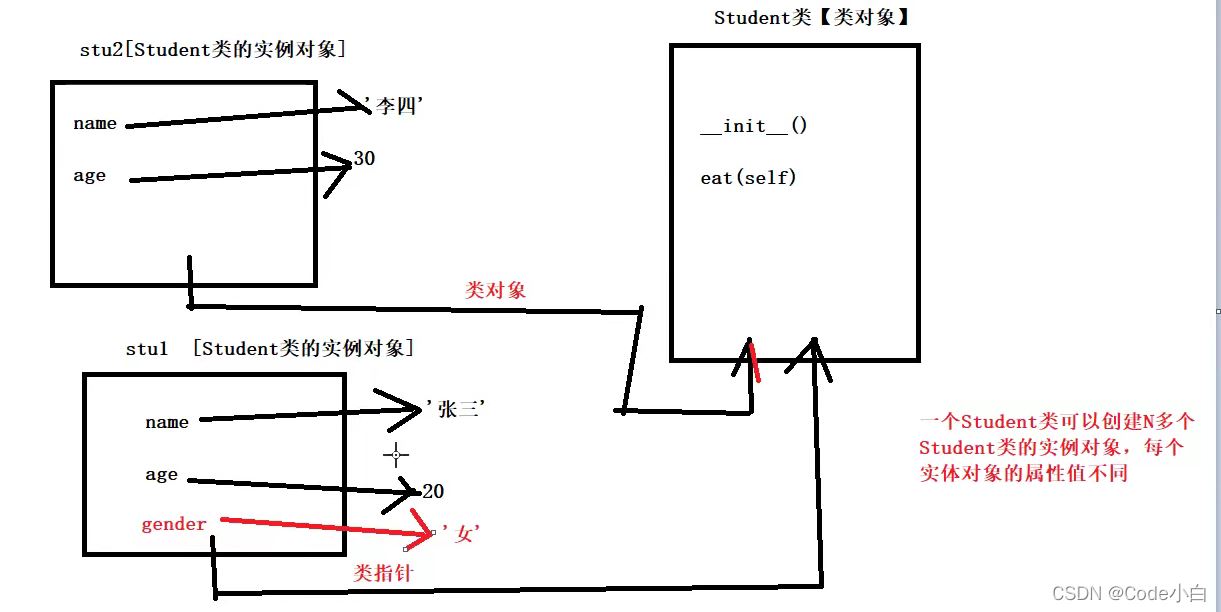
class Student: def __init__(self,name,age): self.name=name self.age=age #实例方法 def eat(self): print("学生在吃饭")student1=Student('张三',19)student2=Student('李四',20)print(id(student1)) #2363920157896print(id(student2)) #2363920157960print("--------绑定属性-------")print("绑定属性-----为student2动态的绑定gender属性-------")student2.gender='男'print(student1.name,student1.age) #张三 19#print(student1.gender) 当student1访问其没有的属性时,会报错AttributeError: 'Student' object has no attribute 'gender'print(student2.name,student2.age,student2.gender) #李四 20 男print("--------绑定方法-------")def show(): print('我是show方法')student1.show=showstudent1.show() #我是show方法student2.show() #报错AttributeError: 'Student' object has no attribute 'show'内存分析:
七、面向对象的三大特征

封装
class Car: def __init__(self,brand,age): self.brand=brand self.__age=age def show(self): print(self.brand,self.__age)car1=Car('宝马X5',50)print(car1.brand) #宝马X5# print(car1.__age) __标识的属性限制其在类外使用,在类的内部可以使用,在外面访问是会报错#若要使用__标识的属性,可以先用dir()查出属性,再访问print(dir(car1))#输出['_Car__age', '__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__', 'brand', 'show']print(car1._Car__age)#50继承(与其他语言不同,python支持多继承)
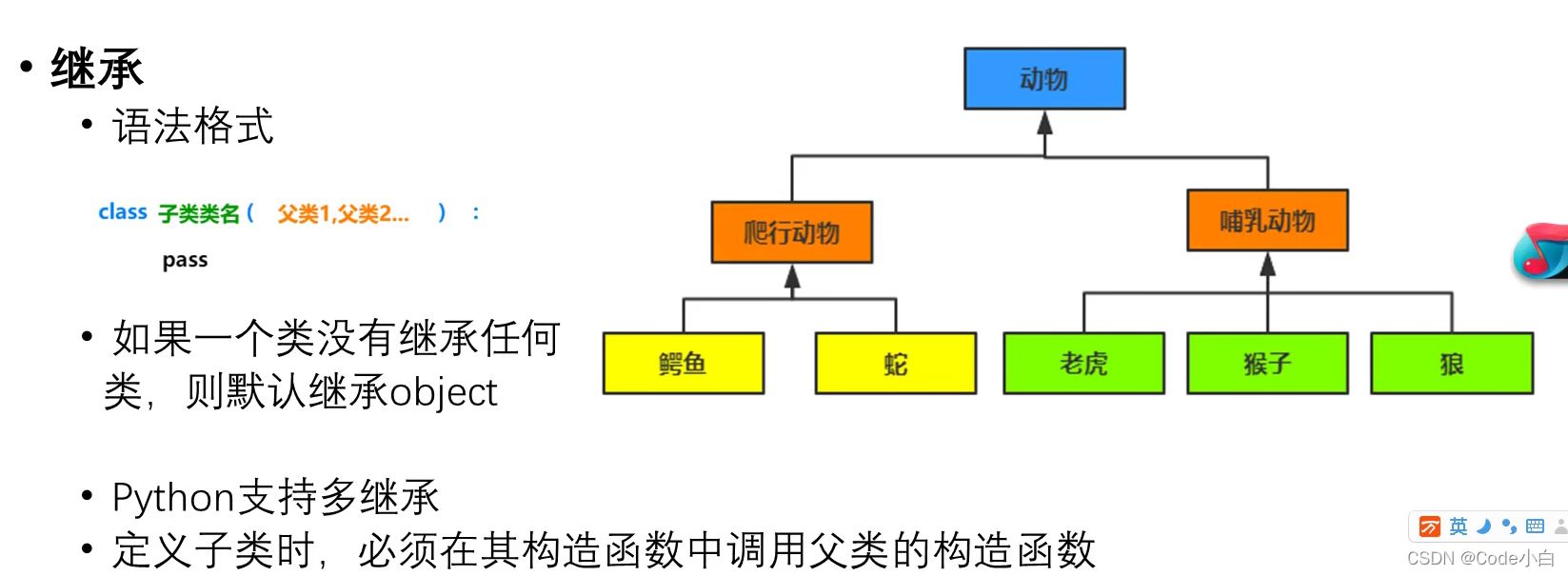

举例:
class People: def __init__(self,name,age): self.name=name self.age=age def info(self): print(self.name,self.age)class Student(People): def __init__(self,name,age,sno): super().__init__(name,age) self.sno=snoclass Teacher(People): def __init__(self,name,age,teachofage): super().__init__(name,age) self.teachofage=teachofagestudent1=Student('张三',18,122)teacher1=Teacher('李四',36,10)student1.info() #张三 18teacher1.info() #李四 36八、方法重写

举例:
class People: def __init__(self,name,age): self.name=name self.age=age def info(self): print(self.name,self.age)class Student(People): def __init__(self,name,age,sno): super().__init__(name,age) self.sno=sno def info(self): super().info() print(self.sno)class Teacher(People): def __init__(self,name,age,teachofage): super().__init__(name,age) self.teachofage=teachofage def info(self): super().info() print(self.teachofage)student1=Student('张三',18,122)teacher1=Teacher('李四',36,10)student1.info() teacher1.info()结果为:

以上是“Python面向对象和类的示例分析”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的内容对大家有所帮助,如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注编程网行业资讯频道!




