这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关Shell如何获取路径操作,小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后可以有所收获。
pwd 用法
pwd: pwd [-LP]
Print the name of the current working directory.
Options:
-L print the value of $PWD if it names the current working directory
-P print the physical directory, without any symbolic links
pwd:
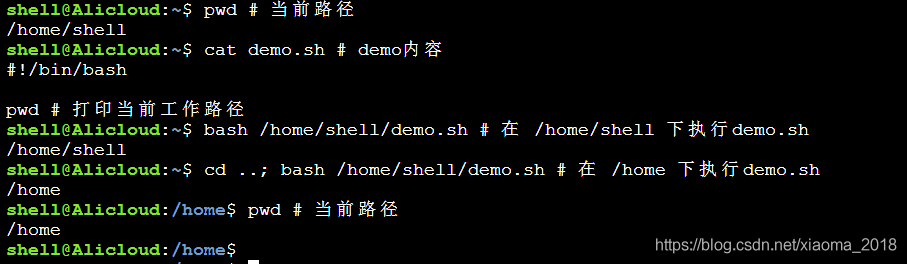
打印出当前工作路径,注意是 ”工作路径“,及脚本在哪个路径执行,该路径就是该脚本的工作路径,如图:
pwd -L:
打印出环境变量 $PWD 的值,如果 PWD 赋值为当前工作路径,pwd 默认同 pwd -L
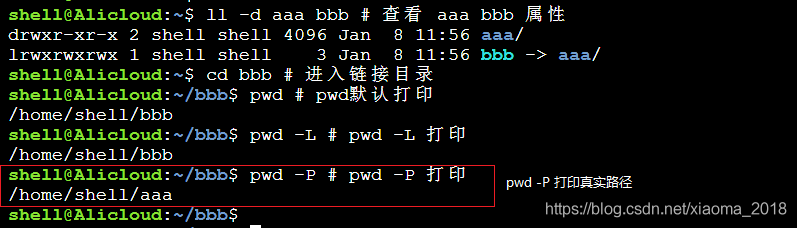
pwd -P:
打印真实路径,不打印链接的路径,区别如图:
basename 用法
Examples:
 basename /usr/bin/sort -> “sort”
 basename include/stdio.h .h -> “stdio”
 basename -s .h include/stdio.h -> “stdio”
 basename -a any/str1 any/str2 -> “str1” followed by “str2”
basename:
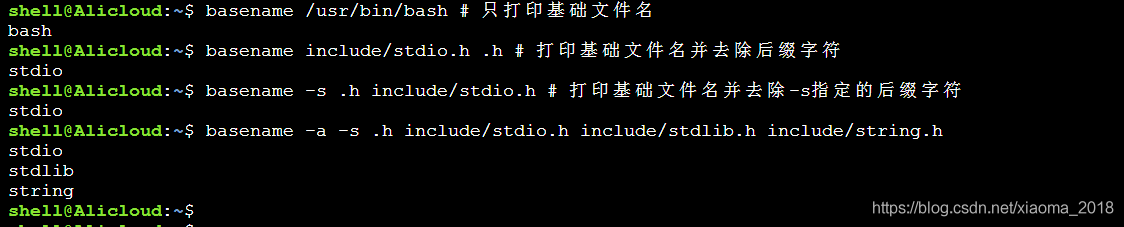
打印除上层路径外的基础文件名;当文件名后存在后缀时,除去后面的后缀,如 # basename include/stdio.h .h 只会打印出 stdio
basename -s:
-s参数后面指定要去除的后缀字符,即:# basename -s .h include/stdio.h 同 # basename include/stdio.h .h 一样只会打印出 stdio
basename -a:
-a参数可追加执行多个文件路径,取每一个路径的基础文件名并打印。用法如下图:
dirname 用法
Examples:
 dirname /usr/bin/ -> “/usr”
 dirname dir1/str dir2/str -> “dir1” followed by “dir2”
 dirname stdio.h -> “.”
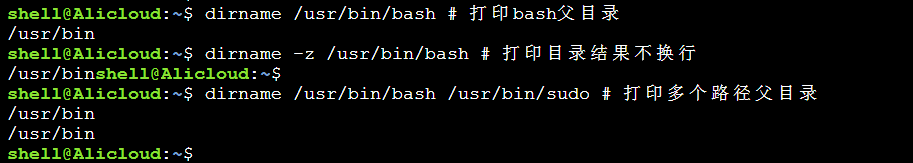
dirname:
去除文件名中的非目录部分,删除最后一个“\”后面的路径,显示父目录
dirname -z:
输出结果不换行
如图所示:
组合使用 参数 $0:
在shell中,$0 指定为命令行参数的第0个参数,即当前脚本的文件名,$1 $2 指传入脚本的第 1 第 2 个参数
dirname 和 $0:
经常看到 $(dirname $0),那么这个变量存放什么,即:当前脚本文件的父目录,注意 $0 为脚本执行时传入的脚本路径名,如下:
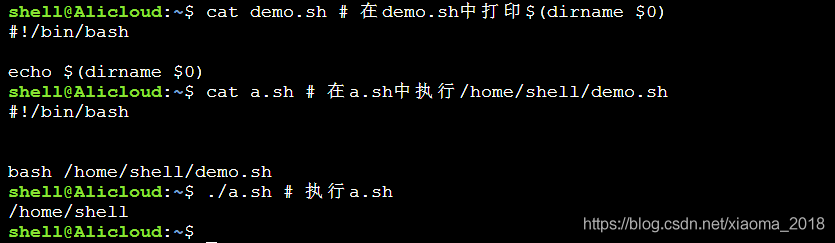
一般在shell中执行文件都用绝对路径,但如果使用相对路径的情况,必须保证相对当前工作路径下的目标路径存在该文件,不然会打印 bash: …/shell/demo.sh: No such file or directory。也就是如果你脚本路径传错了,dirname自然就不能获取到有效的父目录!
通常我们需要把当前脚本的路径作为工作路径来执行某些相对路径文件,这时就需要获取当前被执行脚本的父目录的绝对路径了,而变量 $(cd $(dirname $0); pwd) 就是用来保存当前脚本的父目录的绝对路径的,如下图:
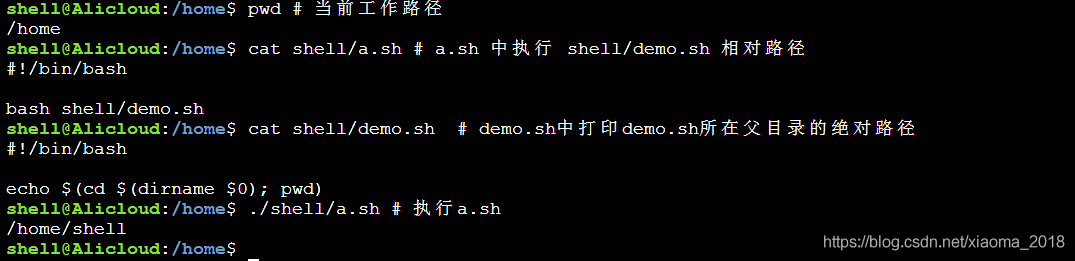
可查看执行 # $(cd $(dirname $0); pwd) 获取当前脚本父目录的绝对路径的过程如下:
+++ dirname shell/demo.sh++ cd shell++ pwd+ echo /home/shell/home/shell关于“Shell如何获取路径操作”这篇文章就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,使各位可以学到更多知识,如果觉得文章不错,请把它分享出去让更多的人看到。












