这篇文章主要为大家展示了“Java字符串拼接的方法有哪些”,内容简而易懂,条理清晰,希望能够帮助大家解决疑惑,下面让小编带领大家一起研究并学习一下“Java字符串拼接的方法有哪些”这篇文章吧。
> 字符串拼接一般使用“+”,但是“+”不能满足大批量数据的处理,Java中有以下五种方法处理字符串拼接,各有优缺点,程序开发应选择合适的方法实现。
加号 “+”
String contact() 方法
StringUtils.join() 方法
StringBuffer append() 方法
StringBuilder append() 方法
> 经过简单的程序测试,从执行100次到90万次的时间开销如下表:
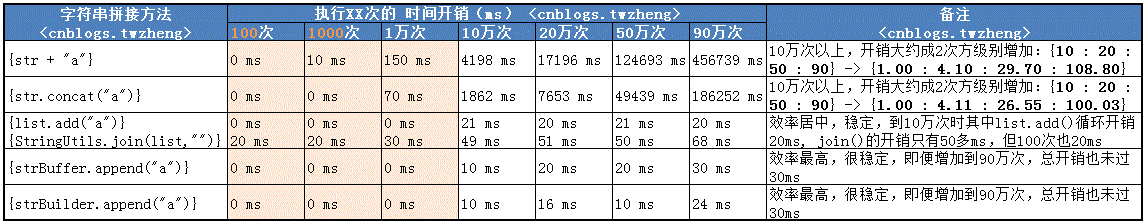
由此可以看出:
方法1 加号 “+” 拼接 和 方法2 String contact() 方法 适用于小数据量的操作,代码简洁方便,加号“+” 更符合我们的编码和阅读习惯;
方法3 StringUtils.join() 方法 适用于将ArrayList转换成字符串,就算90万条数据也只需68ms,可以省掉循环读取ArrayList的代码;
方法4 StringBuffer append() 方法 和 方法5 StringBuilder append() 方法 其实他们的本质是一样的,都是继承自AbstractStringBuilder,效率最高,大批量的数据处理最好选择这两种方法。
方法1 加号 “+” 拼接 和 方法2 String contact() 方法 的时间和空间成本都很高(分析在本文末尾),不能用来做批量数据的处理。
> 源代码,供参考
package cnblogs.twzheng.lab2;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;public class TestString { private static final int max = 100; public void testPlus() { System.out.println(">>> testPlus() <<<"); String str = ""; long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) { str = str + "a"; } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); long cost = end - start; System.out.println(" {str + \"a\"} cost=" + cost + " ms"); } public void testConcat() { System.out.println(">>> testConcat() <<<"); String str = ""; long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) { str = str.concat("a"); } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); long cost = end - start; System.out.println(" {str.concat(\"a\")} cost=" + cost + " ms"); } public void testJoin() { System.out.println(">>> testJoin() <<<"); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) { list.add("a"); } long end1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); long cost1 = end1 - start; StringUtils.join(list, ""); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); long cost = end - end1; System.out.println(" {list.add(\"a\")} cost1=" + cost1 + " ms"); System.out.println(" {StringUtils.join(list, \"\")} cost=" + cost + " ms"); } public void testStringBuffer() { System.out.println(">>> testStringBuffer() <<<"); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); StringBuffer strBuffer = new StringBuffer(); for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) { strBuffer.append("a"); } strBuffer.toString(); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); long cost = end - start; System.out.println(" {strBuffer.append(\"a\")} cost=" + cost + " ms"); } public void testStringBuilder() { System.out.println(">>> testStringBuilder() <<<"); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); StringBuilder strBuilder = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) { strBuilder.append("a"); } strBuilder.toString(); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); long cost = end - start; System.out .println(" {strBuilder.append(\"a\")} cost=" + cost + " ms"); }}> 测试结果:
执行100次, private static final int max = 100;
>>> testPlus() <<< {str + "a"} cost=0 ms>>> testConcat() <<< {str.concat("a")} cost=0 ms>>> testJoin() <<< {list.add("a")} cost1=0 ms {StringUtils.join(list, "")} cost=20 ms>>> testStringBuffer() <<< {strBuffer.append("a")} cost=0 ms>>> testStringBuilder() <<< {strBuilder.append("a")} cost=0 ms执行1000次, private static final int max = 1000;
>>> testPlus() <<< {str + "a"} cost=10 ms>>> testConcat() <<< {str.concat("a")} cost=0 ms>>> testJoin() <<< {list.add("a")} cost1=0 ms {StringUtils.join(list, "")} cost=20 ms>>> testStringBuffer() <<< {strBuffer.append("a")} cost=0 ms>>> testStringBuilder() <<< {strBuilder.append("a")} cost=0 ms执行1万次, private static final int max = 10000;
>>> testPlus() <<< {str + "a"} cost=150 ms>>> testConcat() <<< {str.concat("a")} cost=70 ms>>> testJoin() <<< {list.add("a")} cost1=0 ms {StringUtils.join(list, "")} cost=30 ms>>> testStringBuffer() <<< {strBuffer.append("a")} cost=0 ms>>> testStringBuilder() <<< {strBuilder.append("a")} cost=0 ms执行10万次, private static final int max = 100000;
>>> testPlus() <<< {str + "a"} cost=4198 ms>>> testConcat() <<< {str.concat("a")} cost=1862 ms>>> testJoin() <<< {list.add("a")} cost1=21 ms {StringUtils.join(list, "")} cost=49 ms>>> testStringBuffer() <<< {strBuffer.append("a")} cost=10 ms>>> testStringBuilder() <<< {strBuilder.append("a")} cost=10 ms执行20万次, private static final int max = 200000;
>>> testPlus() <<< {str + "a"} cost=17196 ms>>> testConcat() <<< {str.concat("a")} cost=7653 ms>>> testJoin() <<< {list.add("a")} cost1=20 ms {StringUtils.join(list, "")} cost=51 ms>>> testStringBuffer() <<< {strBuffer.append("a")} cost=20 ms>>> testStringBuilder() <<< {strBuilder.append("a")} cost=16 ms执行50万次, private static final int max = 500000;
>>> testPlus() <<< {str + "a"} cost=124693 ms>>> testConcat() <<< {str.concat("a")} cost=49439 ms>>> testJoin() <<< {list.add("a")} cost1=21 ms {StringUtils.join(list, "")} cost=50 ms>>> testStringBuffer() <<< {strBuffer.append("a")} cost=20 ms>>> testStringBuilder() <<< {strBuilder.append("a")} cost=10 ms执行90万次, private static final int max = 900000;
>>> testPlus() <<< {str + "a"} cost=456739 ms>>> testConcat() <<< {str.concat("a")} cost=186252 ms>>> testJoin() <<< {list.add("a")} cost1=20 ms {StringUtils.join(list, "")} cost=68 ms>>> testStringBuffer() <<< {strBuffer.append("a")} cost=30 ms>>> testStringBuilder() <<< {strBuilder.append("a")} cost=24 ms> 查看源代码,以及简单分析
String contact 和 StringBuffer,StringBuilder 的源代码都可以在Java库里找到,有空可以研究研究。
其实每次调用contact()方法就是一次数组的拷贝,虽然在内存中是处理都是原子性操作,速度非常快,但是,最后的return语句会创建一个新String对象,限制了concat方法的速度。
public String concat(String str) { int otherLen = str.length(); if (otherLen == 0) { return this; } int len = value.length; char buf[] = Arrays.copyOf(value, len + otherLen); str.getChars(buf, len); return new String(buf, true); }StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 的append方法都继承自AbstractStringBuilder,整个逻辑都只做字符数组的加长,拷贝,到最后也不会创建新的String对象,所以速度很快,完成拼接处理后在程序中用strBuffer.toString()来得到最终的字符串。
public AbstractStringBuilder append(String str) { if (str == null) str = "null"; int len = str.length(); ensureCapacityInternal(count + len); str.getChars(0, len, value, count); count += len; return this; } private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minimumCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code if (minimumCapacity - value.length > 0) expandCapacity(minimumCapacity); } void expandCapacity(int minimumCapacity) { int newCapacity = value.length * 2 + 2; if (newCapacity - minimumCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minimumCapacity; if (newCapacity < 0) { if (minimumCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); newCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE; } value = Arrays.copyOf(value, newCapacity); }字符串的加号“+” 方法, 虽然编译器对其做了优化,使用StringBuilder的append方法进行追加,但是每循环一次都会创建一个StringBuilder对象,且都会调用toString方法转换成字符串,所以开销很大。
注:执行一次字符串“+”,相当于 str = new StringBuilder(str).append("a").toString();
本文开头的地方统计了时间开销,根据上述分析再想想空间的开销。常说拿空间换时间,反过来是不是拿时间换到了空间呢,但是在这里,其实时间是消耗在了重复的不必要的工作上(生成新的对象,toString方法),所以对大批量数据做处理时,加号“+” 和 contact 方法绝对不能用,时间和空间成本都很高。
以上是“Java字符串拼接的方法有哪些”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的内容对大家有所帮助,如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注编程网行业资讯频道!







