面向切面编程AOP
1、场景模拟
搭建子模块:spring6-aop
1.1、声明接口
声明计算器接口Calculator,包含加减乘除的抽象方法
public interface Calculator { int add(int i, int j); int sub(int i, int j); int mul(int i, int j); int div(int i, int j); }1.2、创建实现类
public class CalculatorImpl implements Calculator { @Override public int add(int i, int j) { int result = i + j; System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result); return result; } @Override public int sub(int i, int j) { int result = i - j; System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result); return result; } @Override public int mul(int i, int j) { int result = i * j; System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result); return result; } @Override public int div(int i, int j) { int result = i / j; System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result); return result; }}1.3、创建带日志功能的实现类
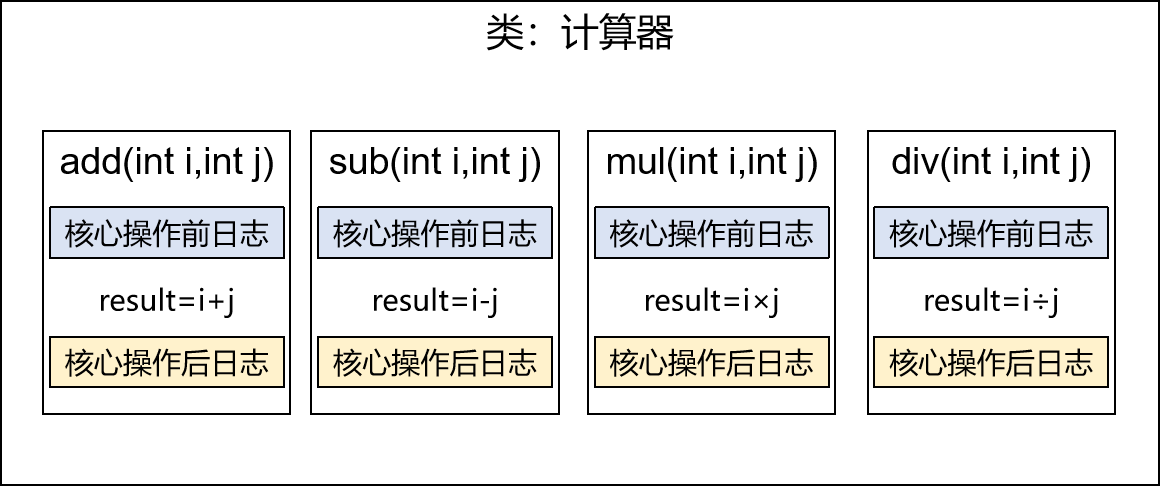
public class CalculatorLogImpl implements Calculator { @Override public int add(int i, int j) { System.out.println("[日志] add 方法开始了,参数是:" + i + "," + j); int result = i + j; System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result); System.out.println("[日志] add 方法结束了,结果是:" + result); return result; } @Override public int sub(int i, int j) { System.out.println("[日志] sub 方法开始了,参数是:" + i + "," + j); int result = i - j; System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result); System.out.println("[日志] sub 方法结束了,结果是:" + result); return result; } @Override public int mul(int i, int j) { System.out.println("[日志] mul 方法开始了,参数是:" + i + "," + j); int result = i * j; System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result); System.out.println("[日志] mul 方法结束了,结果是:" + result); return result; } @Override public int div(int i, int j) { System.out.println("[日志] div 方法开始了,参数是:" + i + "," + j); int result = i / j; System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result); System.out.println("[日志] div 方法结束了,结果是:" + result); return result; }}1.4、提出问题
①现有代码缺陷
针对带日志功能的实现类,我们发现有如下缺陷:
- 对核心业务功能有干扰,导致程序员在开发核心业务功能时分散了精力
- 附加功能分散在各个业务功能方法中,不利于统一维护
②解决思路
解决这两个问题,核心就是:解耦。我们需要把附加功能从业务功能代码中抽取出来。
③困难
解决问题的困难:要抽取的代码在方法内部,靠以前把子类中的重复代码抽取到父类的方式没法解决。所以需要引入新的技术。
2、代理模式
2.1、概念
①介绍
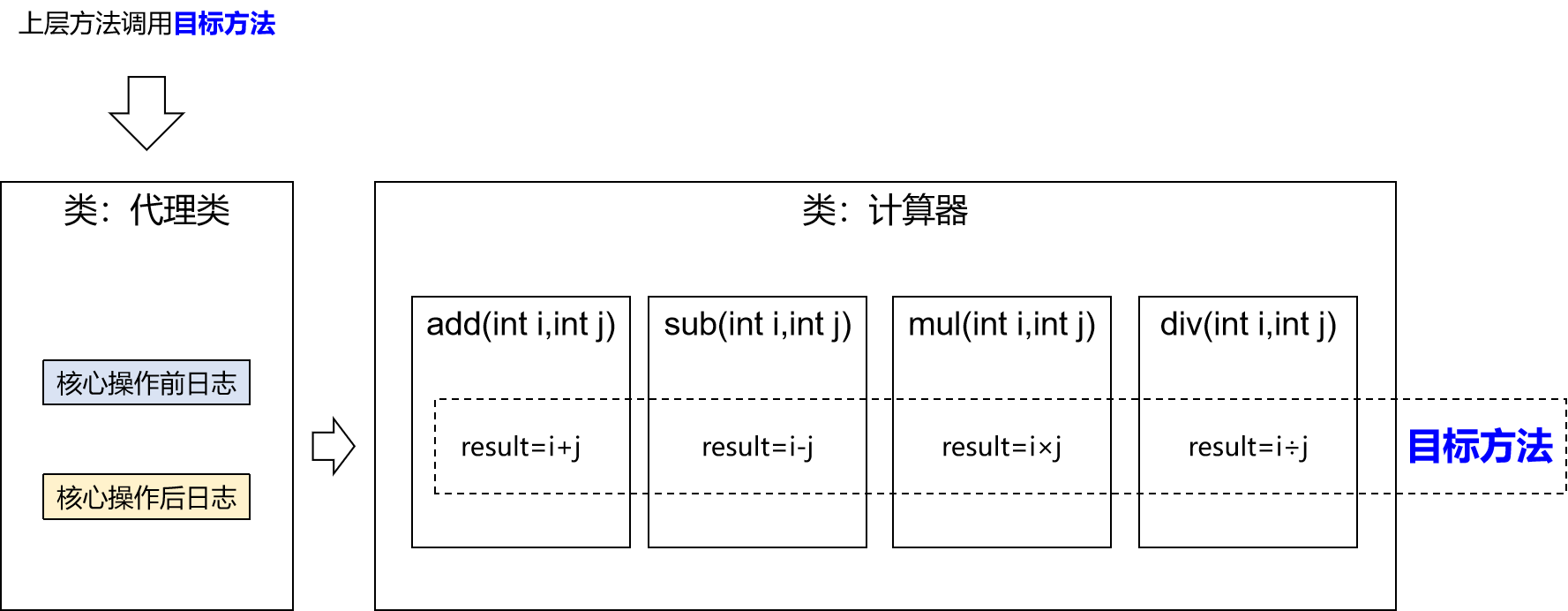
二十三种设计模式中的一种,属于结构型模式。它的作用就是通过提供一个代理类,让我们在调用目标方法的时候,不再是直接对目标方法进行调用,而是通过代理类间接调用。让不属于目标方法核心逻辑的代码从目标方法中剥离出来——解耦。调用目标方法时先调用代理对象的方法,减少对目标方法的调用和打扰,同时让附加功能能够集中在一起也有利于统一维护。
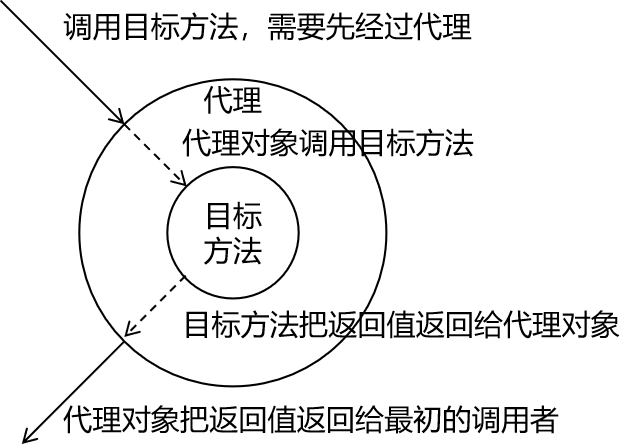
②生活中的代理
- 广告商找大明星拍广告需要经过经纪人
- 合作伙伴找大老板谈合作要约见面时间需要经过秘书
- 房产中介是买卖双方的代理
③相关术语
- 代理:将非核心逻辑剥离出来以后,封装这些非核心逻辑的类、对象、方法。
- 目标:被代理“套用”了非核心逻辑代码的类、对象、方法。
2.2、静态代理
创建静态代理类:
public class CalculatorStaticProxy implements Calculator { // 将被代理的目标对象声明为成员变量 private Calculator target; public CalculatorStaticProxy(Calculator target) { this.target = target; } @Override public int add(int i, int j) { // 附加功能由代理类中的代理方法来实现 System.out.println("[日志] add 方法开始了,参数是:" + i + "," + j); // 通过目标对象来实现核心业务逻辑 int addResult = target.add(i, j); System.out.println("[日志] add 方法结束了,结果是:" + addResult); return addResult; }}静态代理确实实现了解耦,但是由于代码都写死了,完全不具备任何的灵活性。就拿日志功能来说,将来其他地方也需要附加日志,那还得再声明更多个静态代理类,那就产生了大量重复的代码,日志功能还是分散的,没有统一管理。
提出进一步的需求:将日志功能集中到一个代理类中,将来有任何日志需求,都通过这一个代理类来实现。这就需要使用动态代理技术了。
2.3、动态代理
生产代理对象的工厂类:
public class ProxyFactory { private Object target; public ProxyFactory(Object target) { this.target = target; } public Object getProxy(){ ClassLoader classLoader = target.getClass().getClassLoader(); Class<?>[] interfaces = target.getClass().getInterfaces(); InvocationHandler invocationHandler = new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { Object result = null; try { System.out.println("[动态代理][日志] "+method.getName()+",参数:"+ Arrays.toString(args)); result = method.invoke(target, args); System.out.println("[动态代理][日志] "+method.getName()+",结果:"+ result); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("[动态代理][日志] "+method.getName()+",异常:"+e.getMessage()); } finally { System.out.println("[动态代理][日志] "+method.getName()+",方法执行完毕"); } return result; } }; return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, invocationHandler); }}2.4、测试
@Testpublic void testDynamicProxy(){ ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory(new CalculatorLogImpl()); Calculator proxy = (Calculator) factory.getProxy(); proxy.div(1,0); //proxy.div(1,1);}3、AOP概念及相关术语
3.1、概述
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)是一种设计思想,是软件设计领域中的面向切面编程,它是面向对象编程的一种补充和完善,它以通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理方式实现,在不修改源代码的情况下,给程序动态统一添加额外功能的一种技术。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
3.2、相关术语
①横切关注点
分散在每个各个模块中解决同一样的问题,如用户验证、日志管理、事务处理、数据缓存都属于横切关注点。
从每个方法中抽取出来的同一类非核心业务。在同一个项目中,我们可以使用多个横切关注点对相关方法进行多个不同方面的增强。
这个概念不是语法层面的,而是根据附加功能的逻辑上的需要:有十个附加功能,就有十个横切关注点。
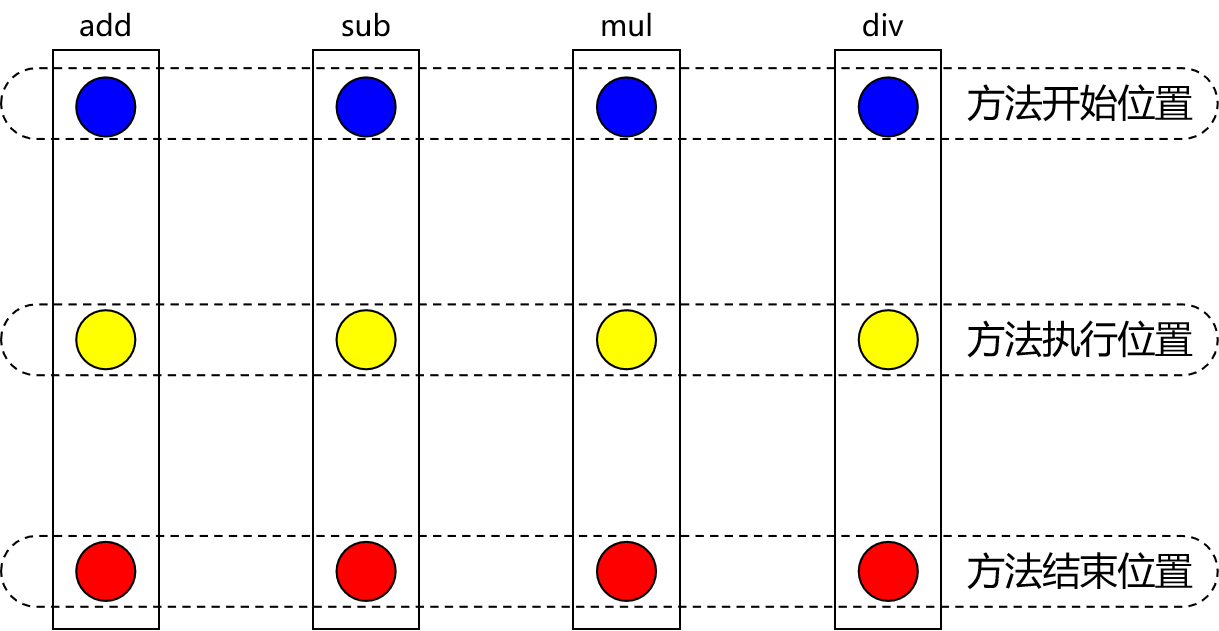
②通知(增强)
增强,通俗说,就是你想要增强的功能,比如 安全,事务,日志等。
每一个横切关注点上要做的事情都需要写一个方法来实现,这样的方法就叫通知方法。
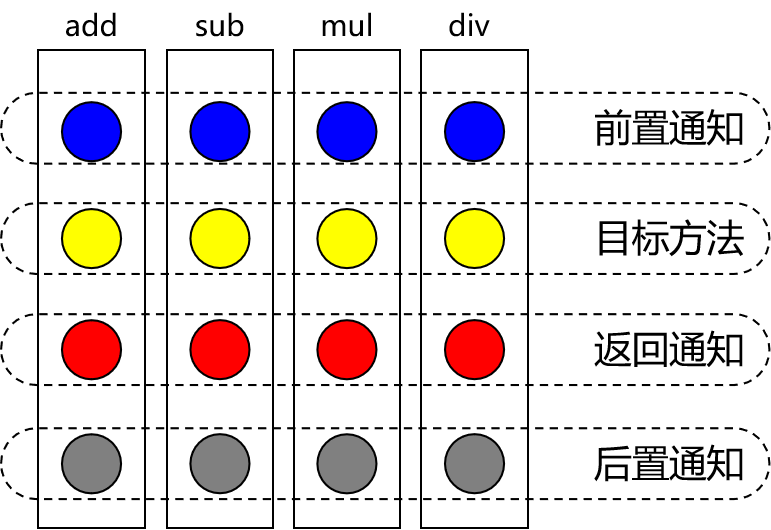
- 前置通知:在被代理的目标方法前执行
- 返回通知:在被代理的目标方法成功结束后执行(寿终正寝)
- 异常通知:在被代理的目标方法异常结束后执行(死于非命)
- 后置通知:在被代理的目标方法最终结束后执行(盖棺定论)
- 环绕通知:使用try…catch…finally结构围绕整个被代理的目标方法,包括上面四种通知对应的所有位置
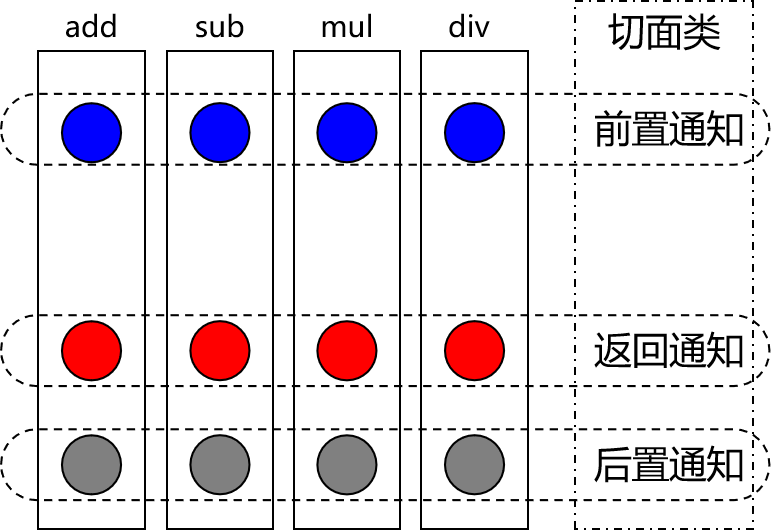
③切面
封装通知方法的类。
④目标
被代理的目标对象。
⑤代理
向目标对象应用通知之后创建的代理对象。
⑥连接点
这也是一个纯逻辑概念,不是语法定义的。
把方法排成一排,每一个横切位置看成x轴方向,把方法从上到下执行的顺序看成y轴,x轴和y轴的交叉点就是连接点。通俗说,就是spring允许你使用通知的地方
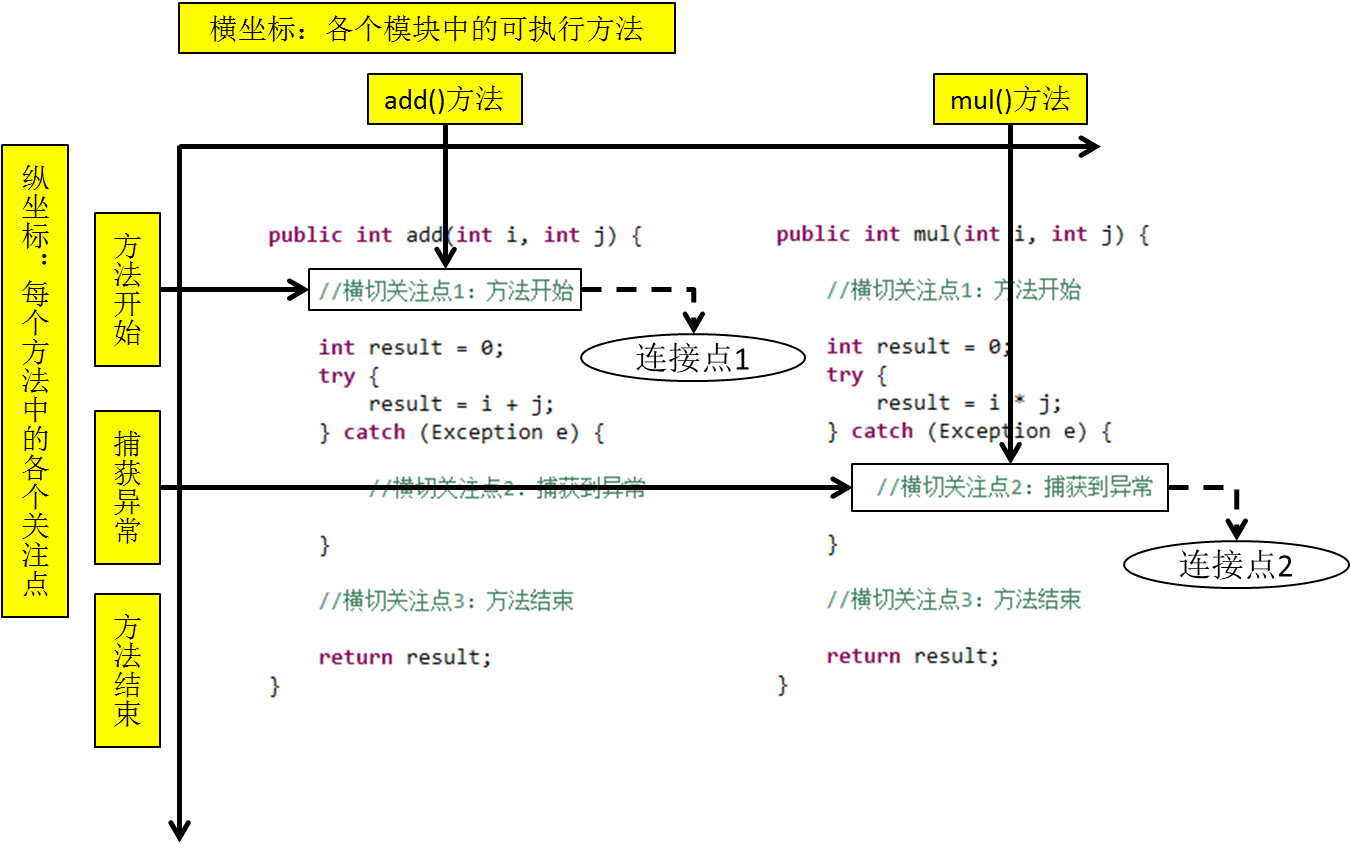
⑦切入点
定位连接点的方式。
每个类的方法中都包含多个连接点,所以连接点是类中客观存在的事物(从逻辑上来说)。
如果把连接点看作数据库中的记录,那么切入点就是查询记录的 SQL 语句。
Spring 的 AOP 技术可以通过切入点定位到特定的连接点。通俗说,要实际去增强的方法
切点通过 org.springframework.aop.Pointcut 接口进行描述,它使用类和方法作为连接点的查询条件。
3.3、作用
-
简化代码:把方法中固定位置的重复的代码抽取出来,让被抽取的方法更专注于自己的核心功能,提高内聚性。
-
代码增强:把特定的功能封装到切面类中,看哪里有需要,就往上套,被套用了切面逻辑的方法就被切面给增强了。
4、基于注解的AOP
4.1、技术说明
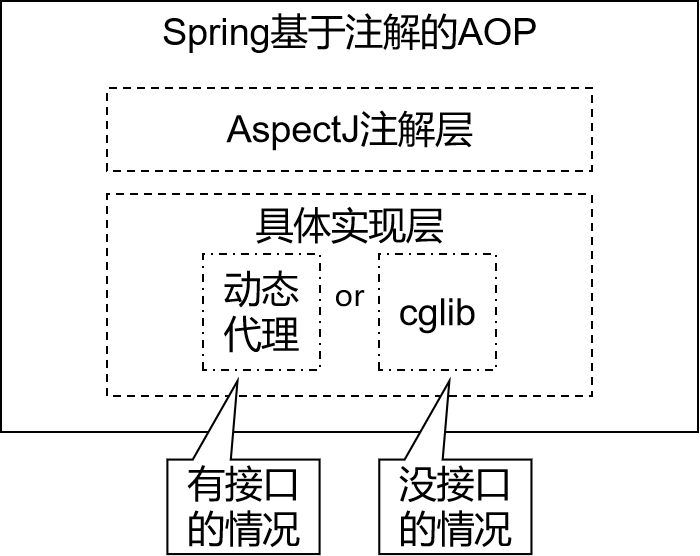
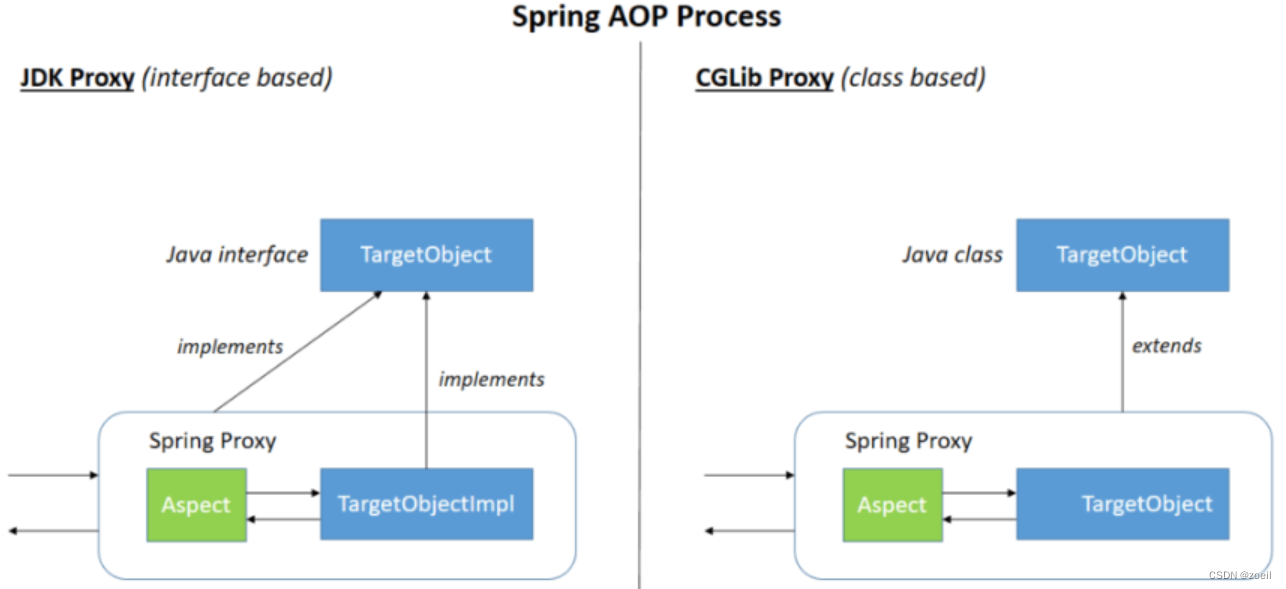
- 动态代理分为JDK动态代理和cglib动态代理
- 当目标类有接口的情况使用JDK动态代理和cglib动态代理,没有接口时只能使用cglib动态代理
- JDK动态代理动态生成的代理类会在com.sun.proxy包下,类名为$proxy1,和目标类实现相同的接口
- cglib动态代理动态生成的代理类会和目标在在相同的包下,会继承目标类
- 动态代理(InvocationHandler):JDK原生的实现方式,需要被代理的目标类必须实现接口。因为这个技术要求代理对象和目标对象实现同样的接口(兄弟两个拜把子模式)。
- cglib:通过继承被代理的目标类(认干爹模式)实现代理,所以不需要目标类实现接口。
- AspectJ:是AOP思想的一种实现。本质上是静态代理,将代理逻辑“织入”被代理的目标类编译得到的字节码文件,所以最终效果是动态的。weaver就是织入器。Spring只是借用了AspectJ中的注解。
4.2、准备工作
①添加依赖
在IOC所需依赖基础上再加入下面依赖即可:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId> <artifactId>spring-contextartifactId> <version>6.0.2version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId> <artifactId>spring-aopartifactId> <version>6.0.2version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId> <artifactId>spring-aspectsartifactId> <version>6.0.2version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.junit.jupitergroupId> <artifactId>junit-jupiter-apiartifactId> <version>5.3.1version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId> <artifactId>log4j-coreartifactId> <version>2.19.0version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId> <artifactId>log4j-slf4j2-implartifactId> <version>2.19.0version> dependency>dependencies>②准备被代理的目标资源
接口:
public interface Calculator { int add(int i, int j); int sub(int i, int j); int mul(int i, int j); int div(int i, int j); }实现类:
@Componentpublic class CalculatorImpl implements Calculator { @Override public int add(int i, int j) { int result = i + j; System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result); return result; } @Override public int sub(int i, int j) { int result = i - j; System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result); return result; } @Override public int mul(int i, int j) { int result = i * j; System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result); return result; } @Override public int div(int i, int j) { int result = i / j; System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result); return result; }}4.3、创建切面类并配置
// @Aspect表示这个类是一个切面类@Aspect// @Component注解保证这个切面类能够放入IOC容器@Componentpublic class LogAspect { @Before("execution(public int com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))") public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); String args = Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()); System.out.println("Logger-->前置通知,方法名:"+methodName+",参数:"+args); } @After("execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))") public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("Logger-->后置通知,方法名:"+methodName); } @AfterReturning(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))", returning = "result") public void afterReturningMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("Logger-->返回通知,方法名:"+methodName+",结果:"+result); } @AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))", throwing = "ex") public void afterThrowingMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable ex){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("Logger-->异常通知,方法名:"+methodName+",异常:"+ex); } @Around("execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))") public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); String args = Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()); Object result = null; try { System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法执行之前"); //目标对象(连接点)方法的执行 result = joinPoint.proceed(); System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法返回值之后"); } catch (Throwable throwable) { throwable.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法出现异常时"); } finally { System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法执行完毕"); } return result; } }在Spring的配置文件中配置:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.aop.annotation">context:component-scan> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy />beans>执行测试:
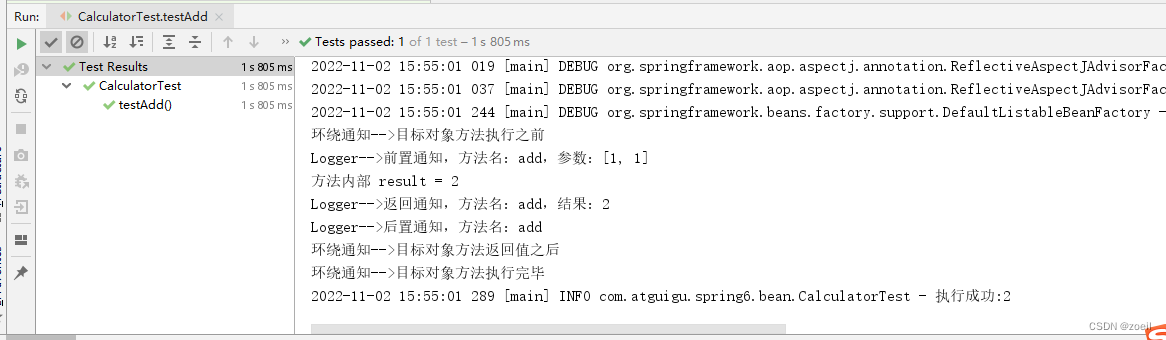
public class CalculatorTest { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CalculatorTest.class); @Test public void testAdd(){ ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); Calculator calculator = ac.getBean( Calculator.class); int add = calculator.add(1, 1); logger.info("执行成功:"+add); }}执行结果:
4.4、各种通知
- 前置通知:使用@Before注解标识,在被代理的目标方法前执行
- 返回通知:使用@AfterReturning注解标识,在被代理的目标方法成功结束后执行(寿终正寝)
- 异常通知:使用@AfterThrowing注解标识,在被代理的目标方法异常结束后执行(死于非命)
- 后置通知:使用@After注解标识,在被代理的目标方法最终结束后执行(盖棺定论)
- 环绕通知:使用@Around注解标识,使用try…catch…finally结构围绕整个被代理的目标方法,包括上面四种通知对应的所有位置
各种通知的执行顺序:
- Spring版本5.3.x以前:
- 前置通知
- 目标操作
- 后置通知
- 返回通知或异常通知
- Spring版本5.3.x以后:
- 前置通知
- 目标操作
- 返回通知或异常通知
- 后置通知
4.5、切入点表达式语法
①作用
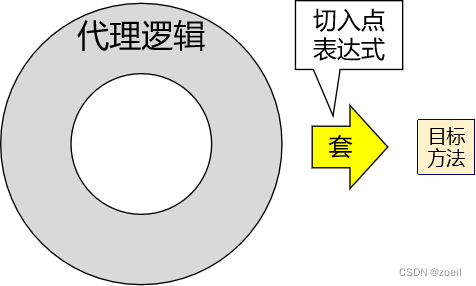
②语法细节
-
用*号代替“权限修饰符”和“返回值”部分表示“权限修饰符”和“返回值”不限
-
在包名的部分,一个“*”号只能代表包的层次结构中的一层,表示这一层是任意的。
- 例如:*.Hello匹配com.Hello,不匹配com.atguigu.Hello
-
在包名的部分,使用“*…”表示包名任意、包的层次深度任意
-
在类名的部分,类名部分整体用*号代替,表示类名任意
-
在类名的部分,可以使用*号代替类名的一部分
- 例如:*Service匹配所有名称以Service结尾的类或接口
-
在方法名部分,可以使用*号表示方法名任意
-
在方法名部分,可以使用*号代替方法名的一部分
- 例如:*Operation匹配所有方法名以Operation结尾的方法
-
在方法参数列表部分,使用(…)表示参数列表任意
-
在方法参数列表部分,使用(int,…)表示参数列表以一个int类型的参数开头
-
在方法参数列表部分,基本数据类型和对应的包装类型是不一样的
- 切入点表达式中使用 int 和实际方法中 Integer 是不匹配的
-
在方法返回值部分,如果想要明确指定一个返回值类型,那么必须同时写明权限修饰符
- 例如:execution(public int …Service.(…, int)) 正确
例如:execution( int *…Service.(…, int)) 错误
- 例如:execution(public int …Service.(…, int)) 正确

4.6、重用切入点表达式
①声明
@Pointcut("execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.*.*(..))")public void pointCut(){}②在同一个切面中使用
@Before("pointCut()")public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); String args = Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()); System.out.println("Logger-->前置通知,方法名:"+methodName+",参数:"+args);}③在不同切面中使用
@Before("com.atguigu.aop.CommonPointCut.pointCut()")public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); String args = Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()); System.out.println("Logger-->前置通知,方法名:"+methodName+",参数:"+args);}4.7、获取通知的相关信息
①获取连接点信息
获取连接点信息可以在通知方法的参数位置设置JoinPoint类型的形参
@Before("execution(public int com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))")public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){ //获取连接点的签名信息 String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); //获取目标方法到的实参信息 String args = Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()); System.out.println("Logger-->前置通知,方法名:"+methodName+",参数:"+args);}②获取目标方法的返回值
@AfterReturning中的属性returning,用来将通知方法的某个形参,接收目标方法的返回值
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))", returning = "result")public void afterReturningMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("Logger-->返回通知,方法名:"+methodName+",结果:"+result);}③获取目标方法的异常
@AfterThrowing中的属性throwing,用来将通知方法的某个形参,接收目标方法的异常
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))", throwing = "ex")public void afterThrowingMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable ex){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("Logger-->异常通知,方法名:"+methodName+",异常:"+ex);}4.8、环绕通知
@Around("execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))")public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); String args = Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()); Object result = null; try { System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法执行之前"); //目标方法的执行,目标方法的返回值一定要返回给外界调用者 result = joinPoint.proceed(); System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法返回值之后"); } catch (Throwable throwable) { throwable.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法出现异常时"); } finally { System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法执行完毕"); } return result;}4.9、切面的优先级
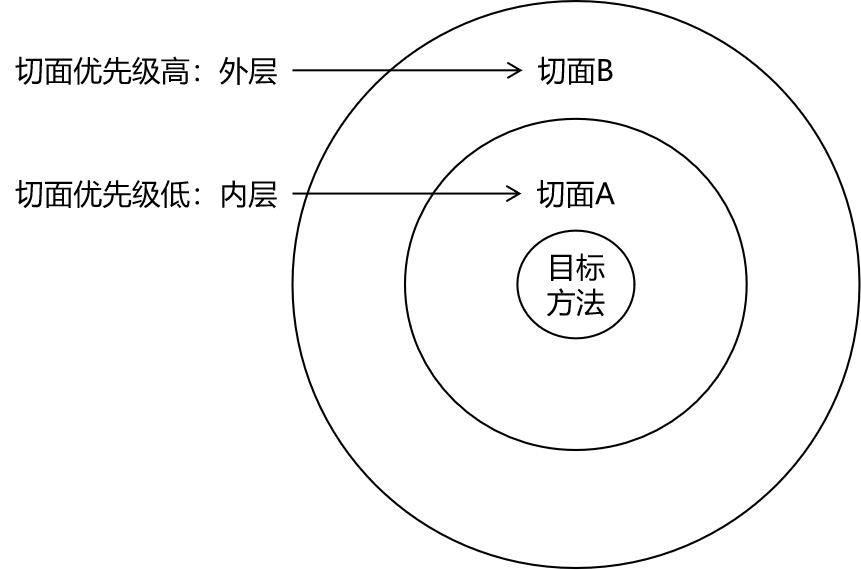
相同目标方法上同时存在多个切面时,切面的优先级控制切面的内外嵌套顺序。
- 优先级高的切面:外面
- 优先级低的切面:里面
使用@Order注解可以控制切面的优先级:
- @Order(较小的数):优先级高
- @Order(较大的数):优先级低
5、基于XML的AOP
5.1、准备工作
参考基于注解的AOP环境
5.2、实现
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.aop.xml">context:component-scan><aop:config> <aop:aspect ref="loggerAspect"> <aop:pointcut id="pointCut" expression="execution(* com.atguigu.aop.xml.CalculatorImpl.*(..))"/> <aop:before method="beforeMethod" pointcut-ref="pointCut">aop:before> <aop:after method="afterMethod" pointcut-ref="pointCut">aop:after> <aop:after-returning method="afterReturningMethod" returning="result" pointcut-ref="pointCut">aop:after-returning> <aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowingMethod" throwing="ex" pointcut-ref="pointCut">aop:after-throwing> <aop:around method="aroundMethod" pointcut-ref="pointCut">aop:around> aop:aspect>aop:config>来源地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_62946761/article/details/133620738





