这篇文章给大家分享的是有关Java多线程的示例分析的内容。小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,一起跟随小编过来看看吧。
线程的创建
继承Thread
实现Runnable
实现Callable
使用继承Thread类来开发多线程的应用程序在设计上是有局限性的,因为Java是单继承。
继承Thread类
public class ThreadDemo1 { // 继承Thread类 写法1 static class MyThread extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { //要实现的业务代码 } } // 写法2 Thread thread = new Thread(){ @Override public void run() { //要实现的业务代码 } };}实现Runnable接口
//实现Runnable接口 写法1class MyRunnable implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { //要实现的业务代码 }}//实现Runnable接口 写法2 匿名内部类class MyRunnable2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { //要实现的业务代码 } }); }}实现Callable接口(Callable + FutureTask 创建带有返回值的线程)
package ThreadDeom;import java.util.concurrent.Callable;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;//创建有返回值的线程 Callable + Futurepublic class ThreadDemo2 { static class MyCallable implements Callable<Integer>{ @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { return 0; } } public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { //创建Callable子对象 MyCallable myCallable = new MyCallable(); //使用FutureTask 接受 Callable FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(myCallable); //创建线程并设置任务 Thread thread = new Thread(futureTask); //启动线程 thread.start(); //得到线程的执行结果 int num = futureTask.get(); }}也可以使用lambda表达式
class ThreadDemo21{ //lambda表达式 Thread thread = new Thread(()-> { //要实现的业务代码 });}Thread的构造方法
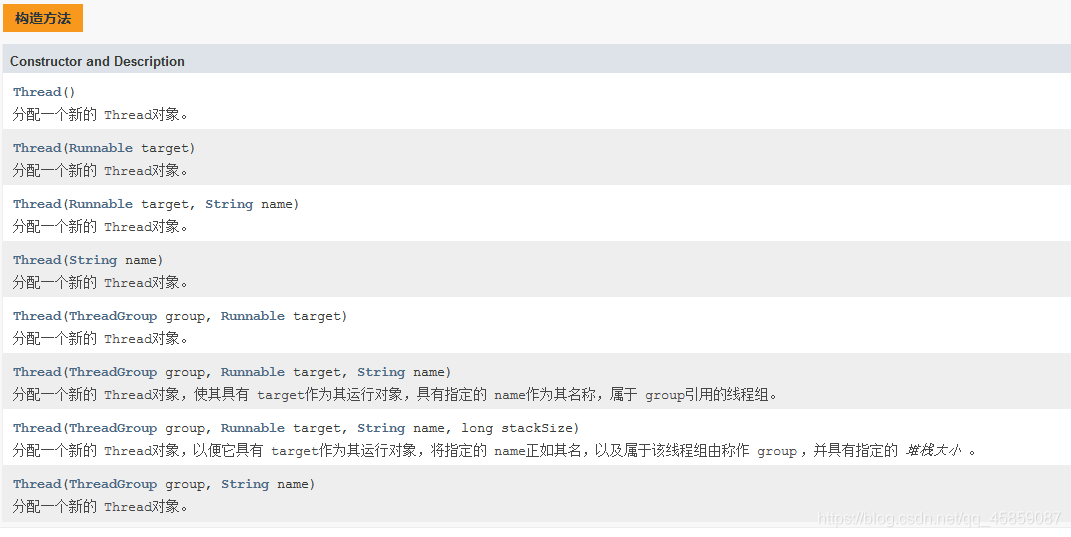
线程常用方法
获取当前线程的引用、线程的休眠
class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread.sleep(1000); //休眠1000毫秒之后打印 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); }}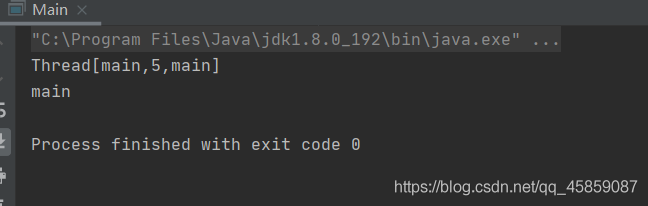
package ThreadDeom;public class ThreadDemo6 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("线程的ID:" + Thread.currentThread().getId()); System.out.println("线程的名称:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); System.out.println("线程的状态:" + Thread.currentThread().getState()); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } },"线程一"); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(100); //打印线程的状态 System.out.println("线程的状态:"+thread.getState()); System.out.println("线程的优先级:"+thread.getPriority()); System.out.println("线程是否存活:"+thread.isAlive()); System.out.println("线程是否是守护线程:"+thread.isDaemon()); System.out.println("线程是否被打断:"+thread.isInterrupted()); }}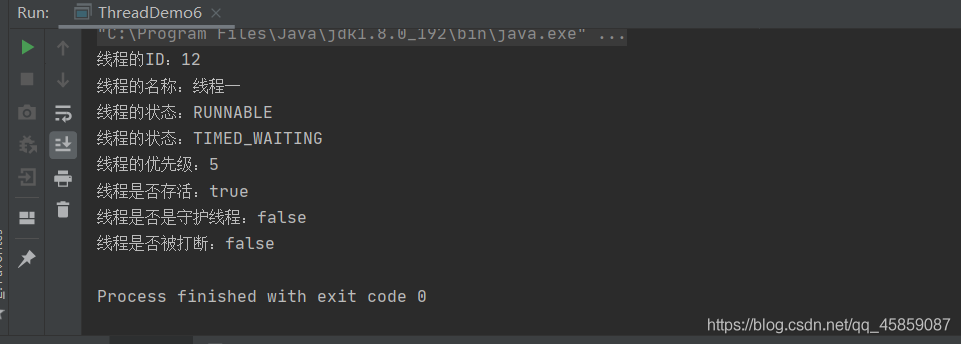
线程的等待
假设有一个坑位,thread1 和 thread2 都要上厕所。一次只能一个人上,thread2只能等待thread1使用完才能使用厕所。就可以使用join()方法,等待线程1执行完,thread2在去执行。?
package ThreadDeom;public class ThreadDemo13 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"?"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"出来了"); } }; Thread t1 = new Thread(runnable,"thread1"); t1.start(); //t1.join(); Thread t2 = new Thread(runnable,"thread2"); t2.start(); }}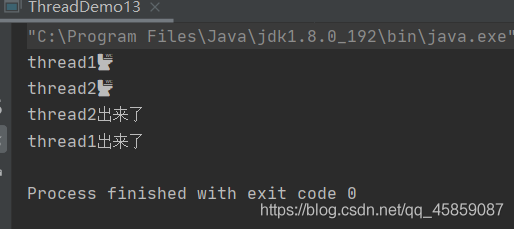
没有join()显然是不行的。加上join()之后:

线程的终止
1.自定义实现线程的终止
package ThreadDeom;public class ThreadDemo11 { private static boolean flag = false; public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (!flag){ System.out.println("我是 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",我还没有被interrupted呢"); try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("我是 "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+",我被interrupted了"); } },"thread"); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(300); flag = true; }}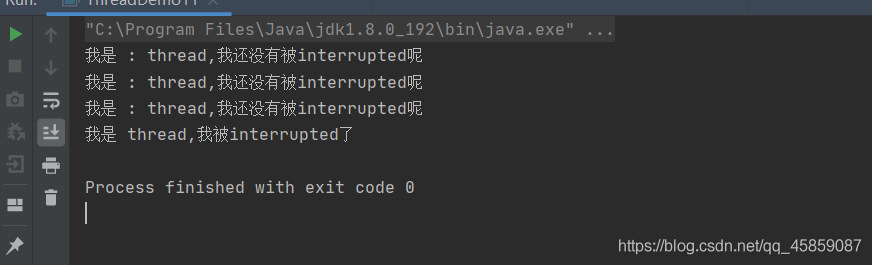
2.使用Thread的interrupted来中断
package ThreadDeom;public class ThreadDemo11 {// private static boolean flag = false; public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (!Thread.interrupted()){ System.out.println("我是 : " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",我还没有被interrupted呢"); try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) {// e.printStackTrace(); break; } } System.out.println("我是 "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+",我被interrupted了"); } },"thread"); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(300); thread.interrupt();// flag = true; }}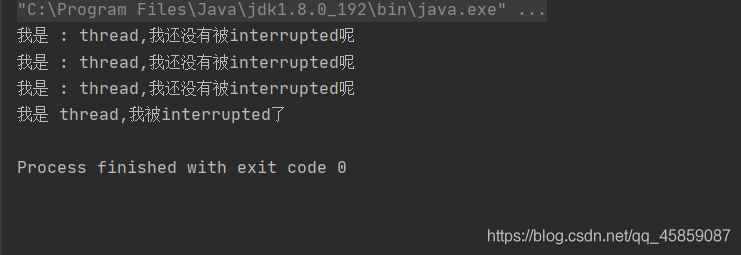
3.Thraed.interrupted()方法和Threaed.currentThread().interrupt()的区别
Thread.interrupted()方法第一次接收到终止的状态后,之后会将状态复位,Thread.interrupted()是静态的,是全局的。
Threaed.currentThread().interrupt()只是普通的方法。
Thraed.interrupted()方法
package ThreadDeom;public class ThreadDemo12 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(() ->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.interrupted()); } }); thread.start(); thread.interrupt(); }}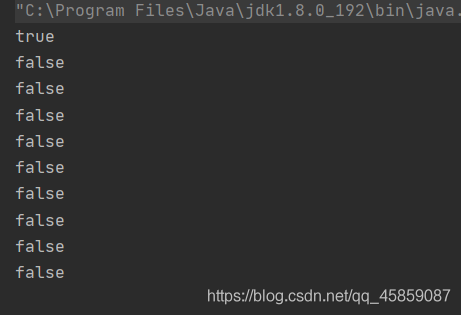
Threaed.currentThread().interrupt()
package ThreadDeom;public class ThreadDemo12 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(() ->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {// System.out.println(Thread.interrupted()); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()); } }); thread.start(); thread.interrupt(); }}
yield()方法
让出CPU的执行权
package ThreadDeom;public class ThreadDemo15 { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { Thread.yield(); System.out.println("thread1"); } }); thread1.start(); Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { System.out.println("thread2"); } }); thread2.start(); }}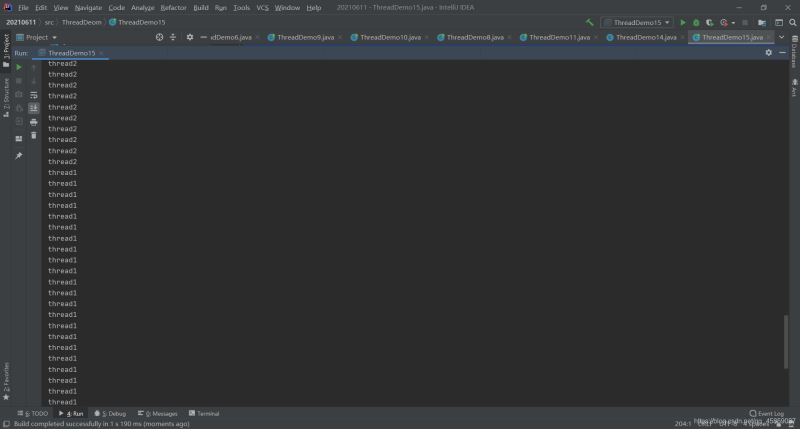
线程的状态
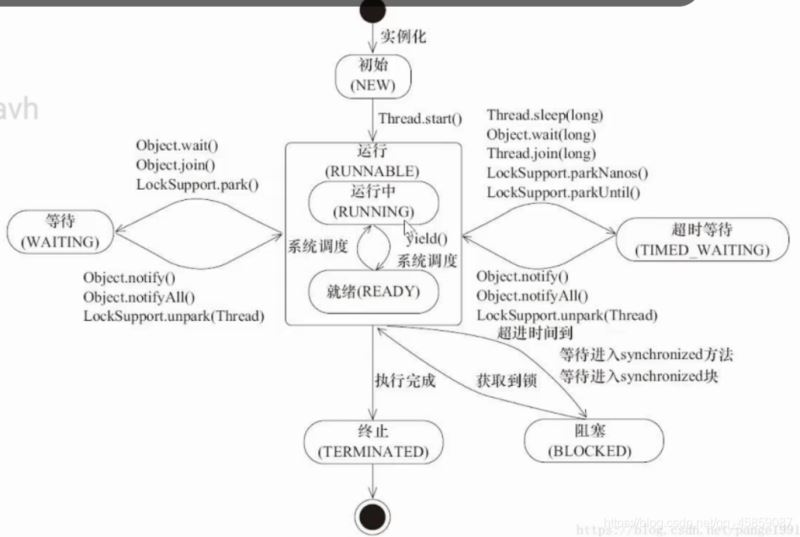
打印出线程的所有的状态,所有的线程的状态都在枚举中。?
package ThreadDeom;public class ThreadDemo14 { public static void main(String[] args) { for (Thread.State state: Thread.State.values()) { System.out.println(state); } }}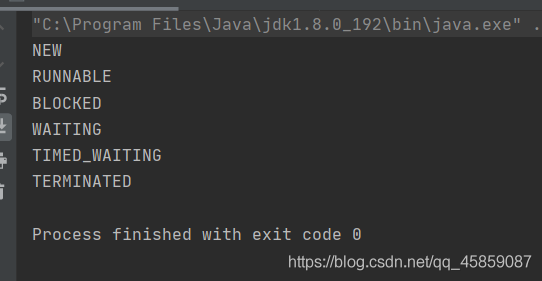
NEW创建了线程但是还没有开始工作RUNNABLE正在Java虚拟机中执行的线程BLOCKED受到阻塞并且正在等待某个监视器的锁的时候所处的状态WAITTING无限期的等待另一个线程执行某个特定操作的线程处于这个状态TIME_WAITTING有具体等待时间的等待TERMINATED已经退出的线程处于这种状态
package ThreadDeom;class TestThreadDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); System.out.println(thread.getState()); thread.start(); System.out.println(thread.getState()); Thread.sleep(100); System.out.println(thread.getState()); thread.join(); System.out.println(thread.getState()); }}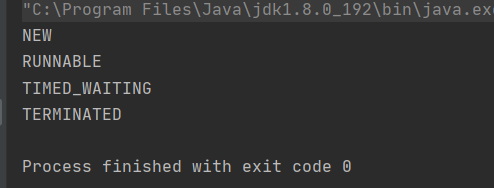
线程的优先级
在Java中线程 的优先级分为1 ~ 10 一共十个等级
package ThreadDeom;public class ThreadDemo9 { public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("t1"); } }); //最大优先级 t1.setPriority(10); t1.start(); Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("t2"); } }); //最小优先级 t2.setPriority(1); t2.start(); Thread t3 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("t3"); } }); t3.setPriority(1); t3.start(); } }}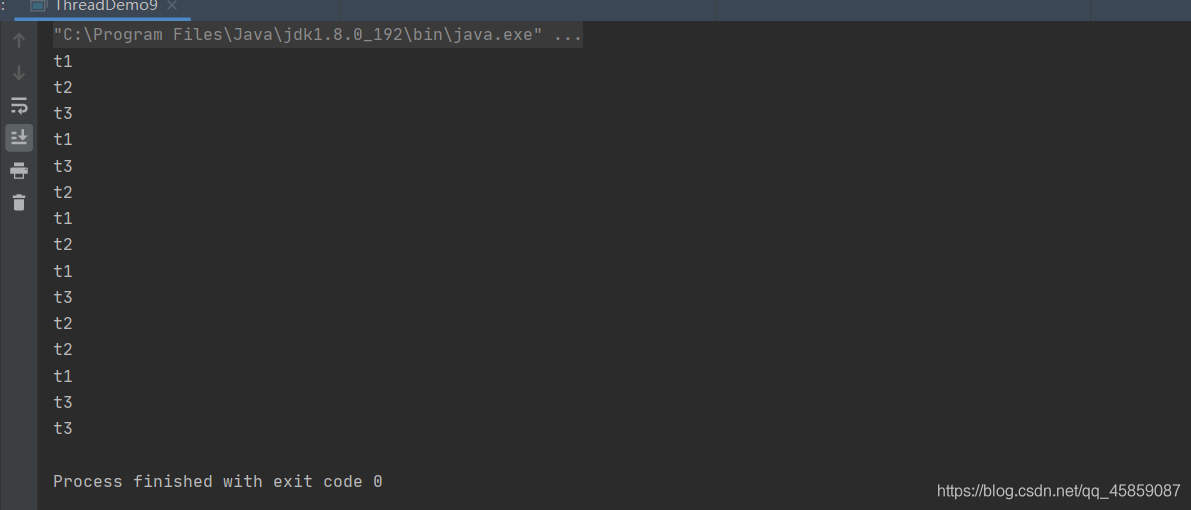
线程的优先级不是绝对的,只是给程序的建议。
线程之间的优先级具有继承的特性,如果A线程启动了B线程,那么B的线程的优先级与A是一样的。?
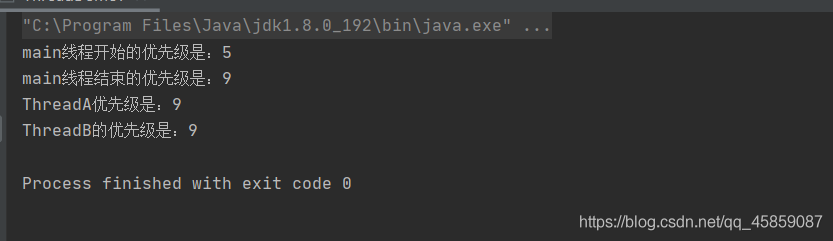
package ThreadDeom;class ThreadA extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("ThreadA优先级是:" + this.getPriority()); ThreadB threadB = new ThreadB(); threadB.start(); }}class ThreadB extends ThreadA{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("ThreadB的优先级是:" + this.getPriority()); }}public class ThreadDemo7 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("main线程开始的优先级是:" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); System.out.println("main线程结束的优先级是:" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA(); threadA.start(); }}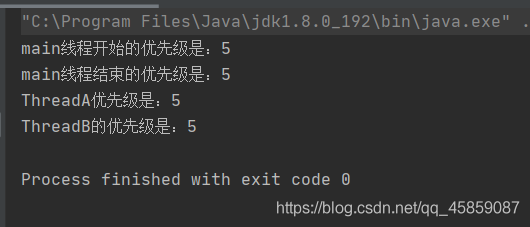
再看?
package ThreadDeom;class ThreadA extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("ThreadA优先级是:" + this.getPriority()); ThreadB threadB = new ThreadB(); threadB.start(); }}class ThreadB extends ThreadA{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("ThreadB的优先级是:" + this.getPriority()); }}public class ThreadDemo7 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("main线程开始的优先级是:" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); Thread.currentThread().setPriority(9); System.out.println("main线程结束的优先级是:" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA(); threadA.start(); }}结果为?
守护线程
Java中有两种线程:一种是用户线程,一种就是守护线程。
什么是守护线程?守护线程是一种特殊的线程,当进程中不存在用户线程的时候,守护线程就会自动销毁。典型的守护线程就是垃圾回收线程,当进程中没有了非守护线程,则垃圾回收线程也就没有存在的必要了。
Daemon线程的作用就是为其他线程的运行提供便利的。?
package ThreadDeom;public class ThreadDemo8 { static private int i = 0; public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true){ i++; System.out.println(i); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }); //设置守护线程 thread.setDaemon(true); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(5000); System.out.println("我是守护线程thread 当用户线程执行完成后 我也就销毁了?哭了"); }}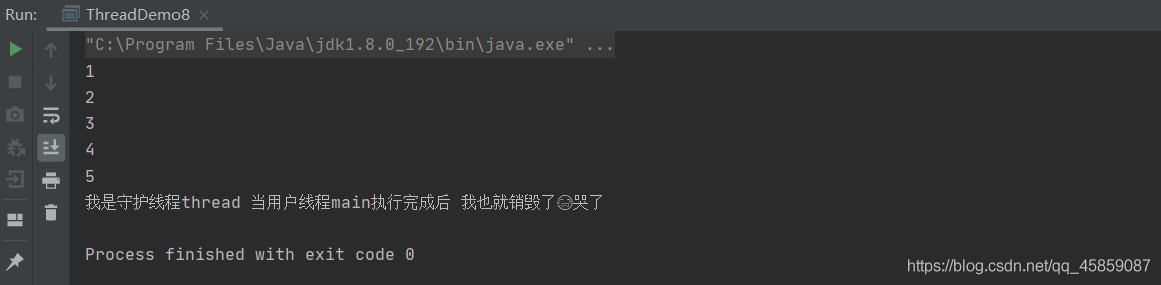
注意:守护线程的设置必须放在start()之前,否则就会报错。
在守护线程中创建的线程默认也是守护线程。
package ThreadDeom;public class ThreadDemo10 { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread thread1 = new Thread(()->{ Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> { },"thread2"); System.out.println("thread2是守护线程吗?:" + thread2.isDaemon()); },"thread1"); System.out.println("thread1是守护线程吗?:" + thread1.isDaemon()); //thread1.setDaemon(true); thread1.start(); // System.out.println("thread1是守护线程吗?:" + thread1.isDaemon()); }}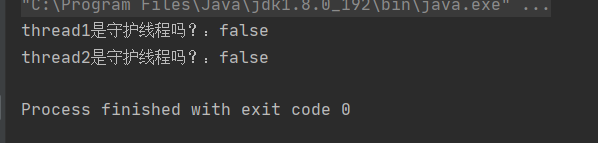
再看?
package ThreadDeom;public class ThreadDemo10 { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread thread1 = new Thread(()->{ Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> { },"thread2"); System.out.println("thread2是守护线程吗?:" + thread2.isDaemon()); },"thread1"); System.out.println("thread1是守护线程吗?:" + thread1.isDaemon()); thread1.setDaemon(true); thread1.start(); System.out.println("thread1是守护线程吗?:" + thread1.isDaemon()); }}
线程组
为了便于对某些具有相同功能的线程进行管理,可以把这些线程归属到同一个线程组中,线程组中既可以有线程对象,也可以有线程组,组中也可以有线程。使用线程模拟赛跑
public class ThreadDemo5 { //线程模拟赛跑(未使用线程分组) public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "到达了终点"); } }, "选手一"); Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(1200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "到达了终点"); } }, "选手二"); t1.start(); t2.start(); System.out.println("所有选手到达了终点"); }}运行结果:
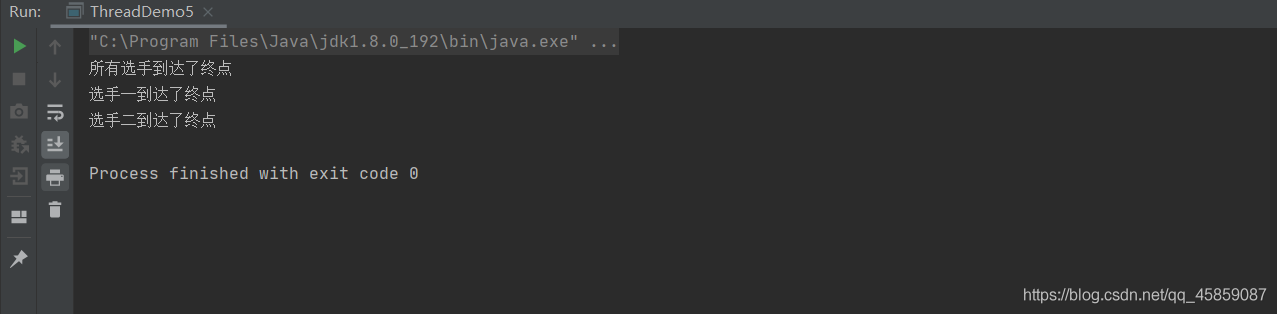
不符合预期效果,就可以使用线程组来实现
package ThreadDeom;class ThreadGroup1 { //线程分组模拟赛跑 public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadGroup threadGroup = new ThreadGroup("Group"); Thread t1 = new Thread(threadGroup, new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("选手一到达了终点"); } }); Thread t2 = new Thread(threadGroup, new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(1200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("选手二到达了终点"); } }); t2.start(); t1.start(); while (threadGroup.activeCount() != 0) { } System.out.println("所有选手到达了终点"); }}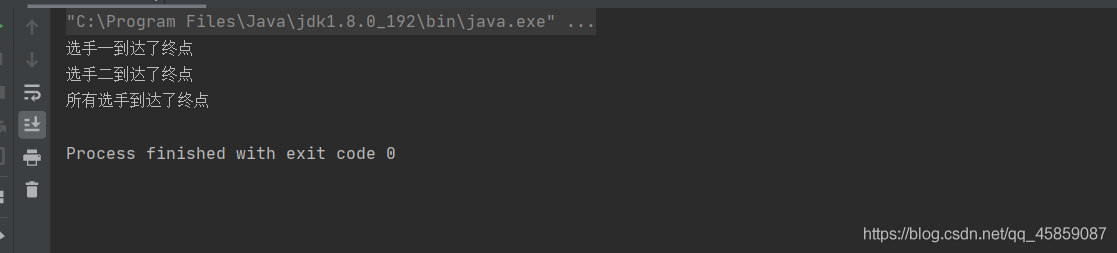
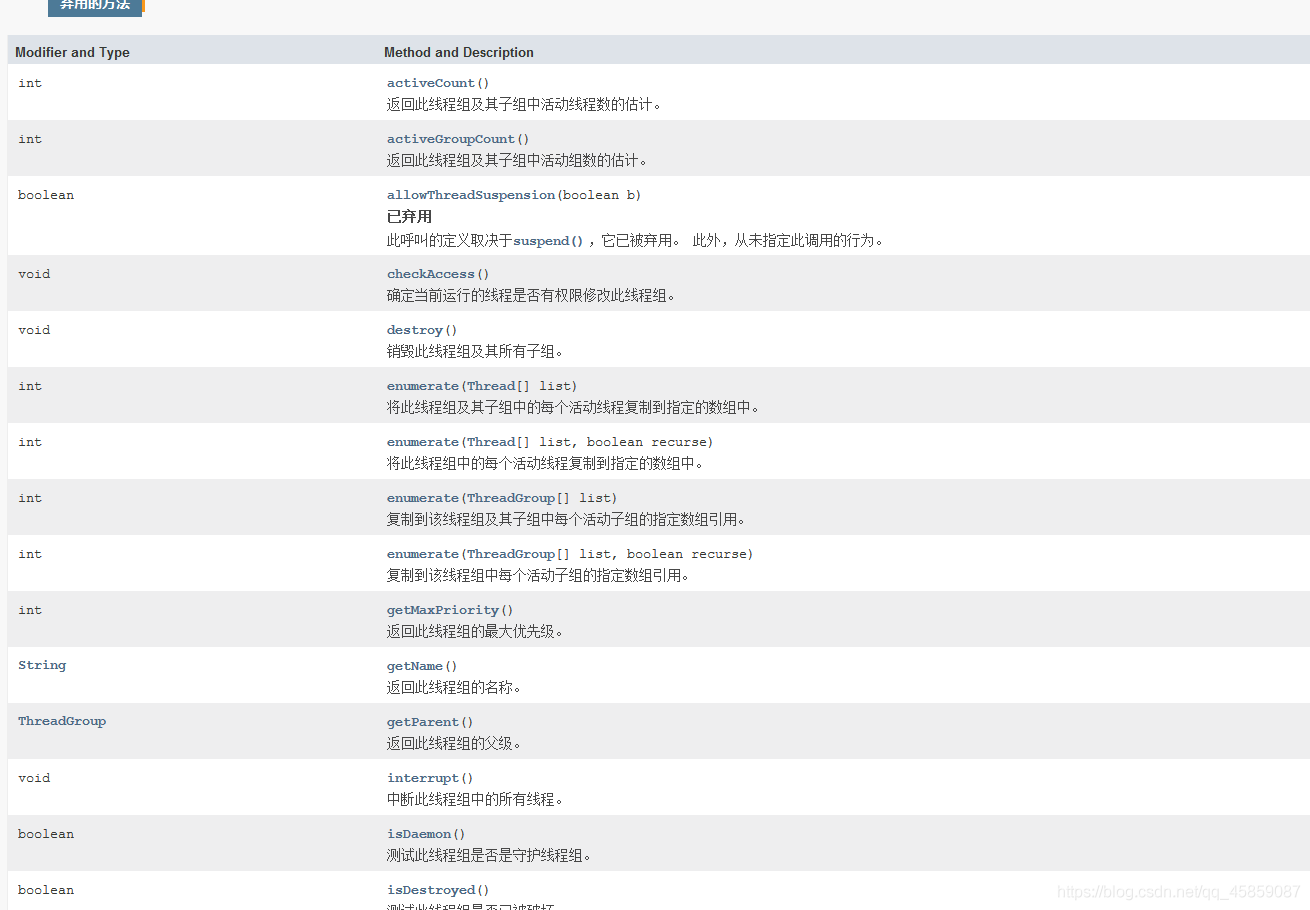
线程组常用的方法
线程安全问题
来看单线程情况下让count分别自增和自减10000次
package ThreadDeom;class Counter { private static int count = 0; public void increase(){ for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { count++; } } public void decrease(){ for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { count--; } } public int getCount(){ return count; }}public class ThreadDemo16 { public static void main(String[] args) { //单线程 Counter counter = new Counter(); counter.increase(); counter.decrease(); System.out.println(counter.getCount()); }}结果符合预期
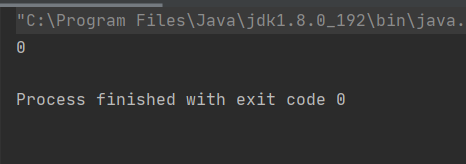
如果想使程序的执行速度快,就可以使用多线程的方式来执行。在来看多线程情况下的问题
public class ThreadDemo16 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { //多线程情况下 Counter counter = new Counter(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(()->{ counter.decrease(); }); Thread thread2 = new Thread(()->{ counter.increase(); }); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread1.join(); thread2.join(); System.out.println(counter.getCount()); }}执行结果:
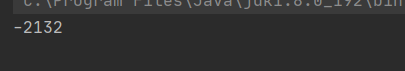
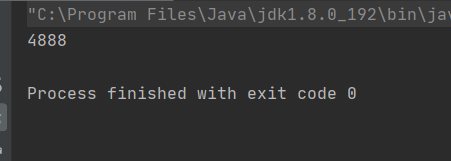
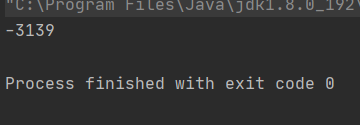
每次的执行结果是不一样的。这就是多线程的不安全问题
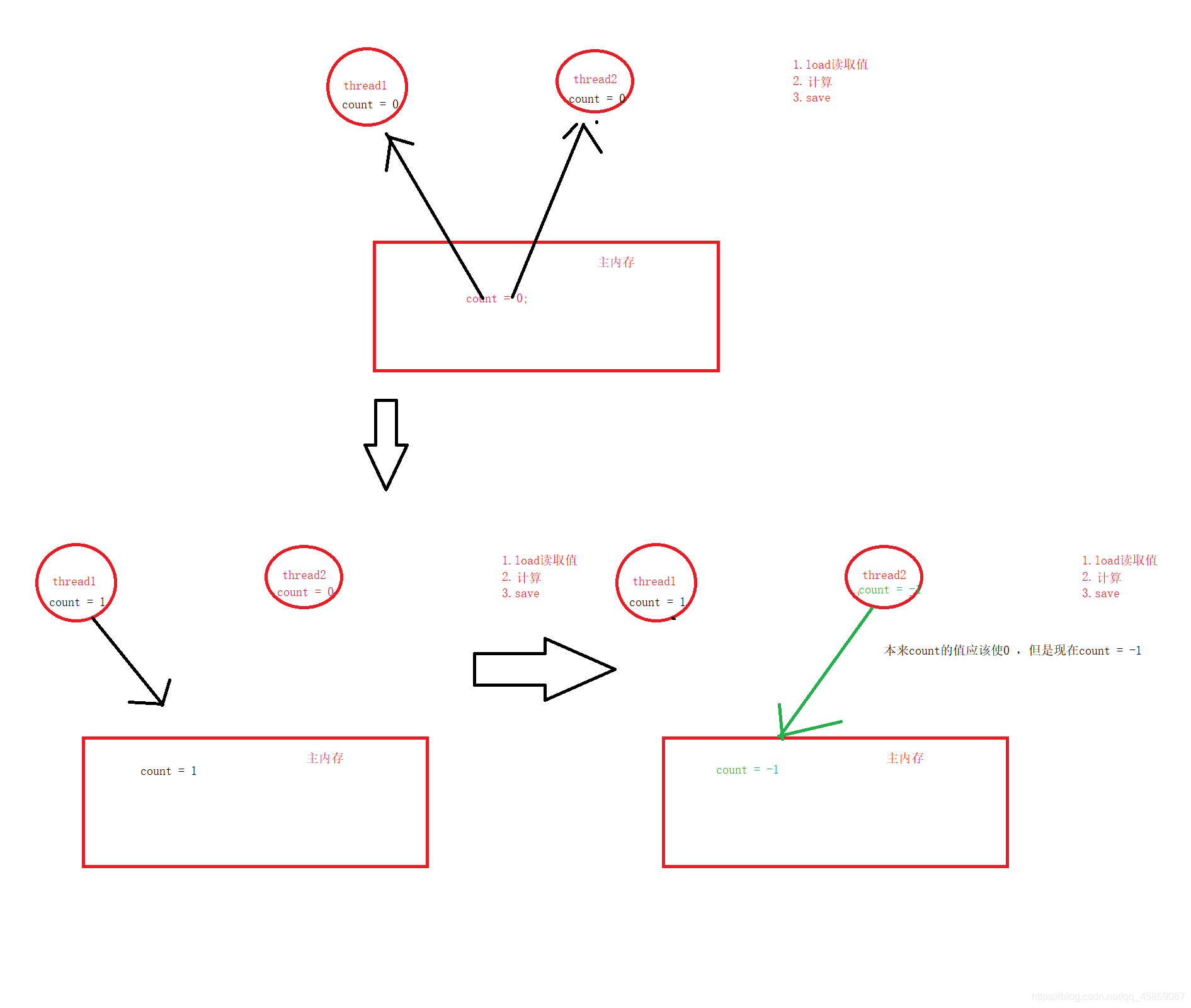
预期的结果是0,但结果却不是。线程不安全问题的原因:
CPU的抢占式执行
多个线程共同操作一个变量
内存可见性
原子性问题
编译器优化(指令重排)
多个线程操作同一个变量
如果多个线程操作的不是一个变量,就不会发生线程的不安全问题,可以将上面的代码修改如下:?
public class ThreadDemo16 { static int res1 = 0; static int res2 = 0; public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Counter counter = new Counter(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { res1 = counter.getCount(); } }); Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { res2 = counter.getCount(); } }); System.out.println(res1 + res2); }}这样就可以了:

内存不可见问题:看下面的代码,是不是到thread2执行的时候,就会改变num的值,从而终止了thread1呢?
package ThreadDeom;import java.util.Scanner;public class ThreadDemo17 { private static int num = 0; public static void main(String[] args) { Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (num == 0){} } }); thread1.start(); Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("输入一个数字来终止线程thread1"); num = scanner.nextInt(); } }); thread2.start(); }}结果是不能的:
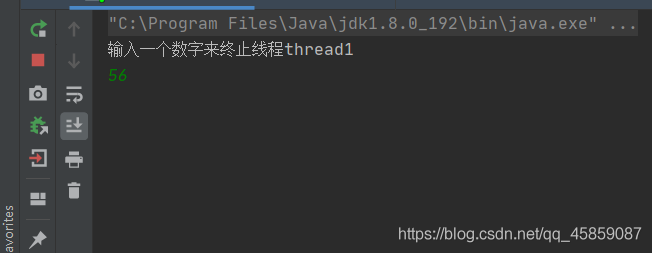
输入一个数字后回车,并没有让thread1的循环结束。这就是内存不可见的问题。
原子性的问题
上面的++和–操作其实是分三步来执行的

假设在第二部的时候,有另外一个线程也来修改值,那么就会出现脏数据的问题了。
所以就会发生线程的不安全问题
编译器优化编译器的优化会打乱原本程序的执行顺序,就有可能导致线程的不安全问题发生。在单线程不会发生线程的不安全问题,在多线程就可能会不安全。
volatile关键字
可以使用volatile关键字,这个关键字可以解决指令重排和内存不可见的问题。

加上volatile关键字之后的运行结果

但是volatile关键字不能解决原子性的问题?:
package ThreadDeom;class Counter1 { private static volatile int count = 0; public void increase() { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { count++; } } public void decrease() { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { count--; } } public int getCount() { return count; }}public class ThreadDemo18 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Counter1 counter1 = new Counter1(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { counter1.decrease(); } }); Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> { counter1.increase(); }); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread1.join(); thread2.join(); System.out.println(counter1.getCount()); }}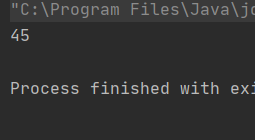
感谢各位的阅读!关于“Java多线程的示例分析”这篇文章就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,让大家可以学到更多知识,如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到吧!