本篇内容主要讲解“Vue3的组件通信方式有哪些”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“Vue3的组件通信方式有哪些”吧!
Props
父组件传值给子组件(简称:父传子)
Props 文档
父组件
// Parent.vue<template> <!-- 使用子组件 --> <Child :msg="message" /></template><script setup>import Child from './components/Child.vue' // 引入子组件let message = '雷猴'</script>子组件
// Child.vue<template> <div> {{ msg }} </div></template><script setup>const props = defineProps({ msg: { type: String, default: '' }})console.log(props.msg) // 在 js 里需要使用 props.xxx 的方式使用。在 html 中使用不需要 props</script>在 <script setup> 中必须使用 defineProps API 来声明 props,它具备完整的推断并且在 <script setup> 中是直接可用的。
更多细节请看 文档。
在 <script setup> 中,defineProps 不需要另外引入。
props 其实还能做很多事情,比如:设置默认值 default ,类型验证 type ,要求必传 required ,自定义验证函数 validator 等等。
大家可以去官网看看,这是必须掌握的知识点!
props 文档
emits
子组件通知父组件触发一个事件,并且可以传值给父组件。(简称:子传父)
emits 文档
父组件
// Parent.vue<template> <div>父组件:{{ message }}</div> <!-- 自定义 changeMsg 事件 --> <Child @changeMsg="changeMessage" /></template><script setup>import { ref } from 'vue'import Child from './components/Child.vue'let message = ref('雷猴')// 更改 message 的值,data是从子组件传过来的function changeMessage(data) { message.value = data}</script>子组件
// Child.vue<template> <div> 子组件:<button @click="handleClick">子组件的按钮</button> </div></template><script setup>// 注册一个自定义事件名,向上传递时告诉父组件要触发的事件。const emit = defineEmits(['changeMsg'])function handleClick() { // 参数1:事件名 // 参数2:传给父组件的值 emit('changeMsg', '鲨鱼辣椒')}</script>和 props 一样,在 <script setup> 中必须使用 defineEmits API 来声明 emits,它具备完整的推断并且在 <script setup> 中是直接可用的。更多细节请看 文档。
在 <script setup> 中,defineEmits 不需要另外引入。
expose / ref
子组件可以通过 expose 暴露自身的方法和数据。
父组件通过 ref 获取到子组件并调用其方法或访问数据。
expose 文档
用例子说话
父组件
// Parent.vue<template> <div>父组件:拿到子组件的message数据:{{ msg }}</div> <button @click="callChildFn">调用子组件的方法</button> <hr> <Child ref="com" /></template><script setup>import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue'import Child from './components/Child.vue'const com = ref(null) // 通过 模板ref 绑定子组件const msg = ref('')onMounted(() => { // 在加载完成后,将子组件的 message 赋值给 msg msg.value = com.value.message})function callChildFn() { // 调用子组件的 changeMessage 方法 com.value.changeMessage('蒜头王八') // 重新将 子组件的message 赋值给 msg msg.value = com.value.message}</script>子组件
// Child.vue<template> <div>子组件:{{ message }}</div></template><script setup>import { ref } from 'vue'const message = ref('蟑螂恶霸')function changeMessage(data) { message.value = data}使用 defineExpose 向外暴露指定的数据和方法defineExpose({ message, changeMessage})</script>在 <script setup> 中,defineExpose 不需要另外引入。
expose 文档
defineExpose 文档
Non-Props
所谓的 Non-Props 就是 非 Prop 的 Attribute。
意思是在子组件中,没使用 prop 或 emits 定义的 attribute,可以通过 $attrs 来访问。
常见的有 class 、style 和 id。
非 Prop 的 Attribute 文档
还是举个例子会直观点
单个根元素的情况
父组件
// Parent.vue<template> <Child msg="雷猴 世界!" name="鲨鱼辣椒" /></template><script setup>import { ref } from 'vue'import Child from './components/Child.vue'</script>子组件
// Child.vue<template> <div>子组件:打开控制台看看</div></template>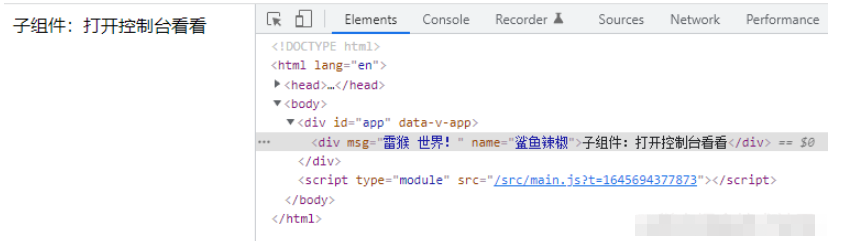
打开控制台可以看到,属性被挂到 HTML 元素上了。
多个元素的情况
但在 Vue3 中,组件已经没规定只能有一个根元素了。如果子组件是多个元素时,上面的例子就不生效了。
// Child.vue<template> <div>子组件:打开控制台看看</div> <div>子组件:打开控制台看看</div></template>
此时可以使用 $attrs 的方式进行绑定。
// Child.vue<template> <div :message="$attrs.msg">只绑定指定值</div> <div v-bind="$attrs">全绑定</div></template>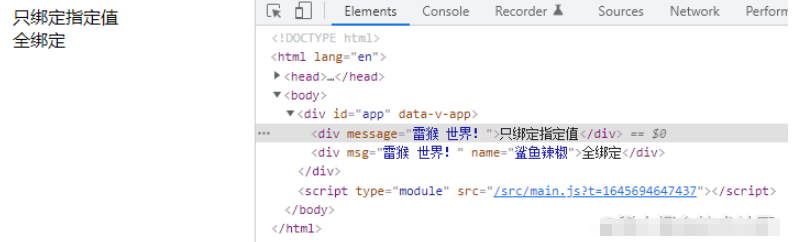
v-model
v-model 是 Vue 的一个语法糖。在 Vue3 中的玩法就更多(晕)了。
单值的情况
组件上的 v-model 使用 modelValue 作为 prop 和 update:modelValue 作为事件。
v-model 参数文档
父组件
// Parent.vue<template> <Child v-model="message" /></template><script setup>import { ref } from 'vue'import Child from './components/Child.vue'const message = ref('雷猴')</script>子组件
// Child.vue<template> <div @click="handleClick">{{modelValue}}</div></template><script setup>import { ref } from 'vue'// 接收const props = defineProps([ 'modelValue' // 接收父组件使用 v-model 传进来的值,必须用 modelValue 这个名字来接收])const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue']) // 必须用 update:modelValue 这个名字来通知父组件修改值function handleClick() { // 参数1:通知父组件修改值的方法名 // 参数2:要修改的值 emit('update:modelValue', '喷射河马')}</script>你也可以这样写,更加简单
子组件
// Child.vue<template> <div @click="$emit('update:modelValue', '喷射河马')">{{modelValue}}</div></template><script setup>import { ref } from 'vue'// 接收const props = defineProps([ 'modelValue' // 接收父组件使用 v-model 传进来的值,必须用 modelValue 这个名字来接收])</script>多个 v-model 绑定
多个 v-model 绑定 文档
父组件
// Parent.vue<template> <Child v-model:msg1="message1" v-model:msg2="message2" /></template><script setup>import { ref } from 'vue'import Child from './components/Child.vue'const message1 = ref('雷猴')const message2 = ref('蟑螂恶霸')</script>子组件
// Child.vue<template> <div><button @click="changeMsg1">修改msg1</button> {{msg1}}</div> <div><button @click="changeMsg2">修改msg2</button> {{msg2}}</div></template><script setup>import { ref } from 'vue'// 接收const props = defineProps({ msg1: String, msg2: String})const emit = defineEmits(['update:msg1', 'update:msg2'])function changeMsg1() { emit('update:msg1', '鲨鱼辣椒')}function changeMsg2() { emit('update:msg2', '蝎子莱莱')}</script>v-model 修饰符
v-model 还能通过 . 的方式传入修饰。
v-model 修饰符 文档
父组件
// Parent.vue<template> <Child v-model.uppercase="message" /></template><script setup>import { ref } from 'vue'import Child from './components/Child.vue'const message = ref('hello')</script>子组件
// Child.vue<template> <div>{{modelValue}}</div></template><script setup>import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue'const props = defineProps([ 'modelValue', 'modelModifiers'])const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue'])onMounted(() => { // 判断有没有 uppercase 修饰符,有的话就执行 toUpperCase() 方法 if (props.modelModifiers.uppercase) { emit('update:modelValue', props.modelValue.toUpperCase()) }})</script>插槽 slot
插槽可以理解为传一段 HTML 片段给子组件。子组件将 <slot> 元素作为承载分发内容的出口。
插槽 文档
本文打算讲讲日常用得比较多的3种插槽:默认插槽、具名插槽、作用域插槽。
默认插槽
插槽的基础用法非常简单,只需在 子组件 中使用 <slot> 标签,就会将父组件传进来的 HTML 内容渲染出来。
默认插槽 文档
父组件
// Parent.vue<template> <Child> <div>雷猴啊</div> </Child></template>子组件
// Child.vue<template> <div> <slot></slot> </div></template>具名插槽
具名插槽 就是在 默认插槽 的基础上进行分类,可以理解为对号入座。
具名插槽 文档
父组件
// Parent.vue<template> <Child> <template v-slot:monkey> <div>雷猴啊</div> </template> <button>鲨鱼辣椒</button> </Child></template>子组件
// Child.vue<template> <div> <!-- 默认插槽 --> <slot></slot> <!-- 具名插槽 --> <slot name="monkey"></slot> </div></template>父组件需要使用 <template> 标签,并在标签上使用 v-solt: + 名称 。
子组件需要在 <slot> 标签里用 name= 名称 对应接收。
这就是 对号入座。
最后需要注意的是,插槽内容的排版顺序,是 以子组件里的排版为准。
上面这个例子就是这样,你可以仔细观察子组件传入顺序和子组件的排版顺序。
作用域插槽
如果你用过 Element-Plus 这类 UI框架 的 Table ,应该就能很好的理解什么叫作用域插槽。
作用域插槽 文档
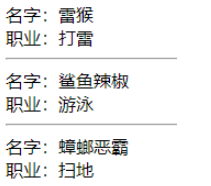
父组件
// Parent.vue<template> <!-- v-slot="{scope}" 获取子组件传上来的数据 --> <!-- :list="list" 把list传给子组件 --> <Child v-slot="{scope}" :list="list"> <div> <div>名字:{{ scope.name }}</div> <div>职业:{{ scope.occupation }}</div> <hr> </div> </Child></template><script setup>import { ref } from 'vue'import Child from './components/Child.vue'const list = ref([ { name: '雷猴', occupation: '打雷'}, { name: '鲨鱼辣椒', occupation: '游泳'}, { name: '蟑螂恶霸', occupation: '扫地'},])</script>子组件
// Child.vue<template> <div> <!-- 用 :scope="item" 返回每一项 --> <slot v-for="item in list" :scope="item" /> </div></template><script setup>const props = defineProps({ list: { type: Array, default: () => [] }})</script>我没写样式,所以用 hr 元素让视觉上看上去比较清晰 我就是懒。
provide / inject
遇到多层传值时,使用 props 和 emit 的方式会显得比较笨拙。这时就可以用 provide 和 inject 了。
provide 是在父组件里使用的,可以往下传值。
inject 是在子(后代)组件里使用的,可以网上取值。
无论组件层次结构有多深,父组件都可以作为其所有子组件的依赖提供者。
provide / inject 文档
父组件
// Parent.vue<template> <Child></Child></template><script setup>import { ref, provide, readonly } from 'vue'import Child from './components/Child.vue'const name = ref('猛虎下山')const msg = ref('雷猴')// 使用readonly可以让子组件无法直接修改,需要调用provide往下传的方法来修改provide('name', readonly(name))provide('msg', msg)provide('changeName', (value) => { name.value = value})</script>子组件
// Child.vue<template> <div> <div>msg: {{ msg }}</div> <div>name: {{name}}</div> <button @click="handleClick">修改</button> </div></template><script setup>import { inject } from 'vue'const name = inject('name', 'hello') // 看看有没有值,没值的话就适用默认值(这里默认值是hello)const msg = inject('msg')const changeName = inject('changeName')function handleClick() { // 这样写不合适,因为vue里推荐使用单向数据流,当父级使用readonly后,这行代码是不会生效的。没使用之前才会生效。 // name.value = '雷猴' // 正确的方式 changeName('虎躯一震') // 因为 msg 没被 readonly 过,所以可以直接修改值 msg.value = '世界'}</script>provide 可以配合 readonly 一起使用,详情可以看上面例子和注释。
provide 和 inject 其实主要是用在深层关系中传值,上面的例子只有父子2层,只是为了举例说明 我懒。
总线 bus
在 Vue2 有总线传值的方法,我们在 Vue3 中也可以自己模拟。
这个方式其实有点像 Vuex 或者 Pinia 那样,弄一个独立的工具出来专门控制数据。
但和 Vuex 或 Pinia 相比,我们自己写的这个方法并没有很好的数据跟踪之类的特性。
原理
我们创建一个 Bus.js 文件,用来控制数据和注册事件的。
Bus.js 里有一个 Bus 类
eventList 是必须项,用来存放事件列表的。
constructor 里除了 eventList 外,其他都是自定义数据,公共数据就是存在这里的。
$on 方法用来注册事件。
$emit 方法可以调用 $on 里的事件。
$off 方法可以注销 eventList 里的事件。
然后需要用到总线的组件,都导入 Bus.js ,就可以共同操作一份数据了。
Bus.js
import { ref } from 'vue'class Bus { constructor() { // 收集订阅信息,调度中心this.eventList = {}, // 事件列表,这项是必须的 // 下面的都是自定义值this.msg = ref('这是一条总线的信息') } // 订阅 $on(name, fn) {this.eventList[name] = this.eventList[name] || []this.eventList[name].push(fn) } // 发布 $emit(name, data) {if (this.eventList[name]) { this.eventList[name].forEach((fn) => { fn(data) });} } // 取消订阅 $off(name) { if (this.eventList[name]) { delete this.eventList[name]} }}export default new Bus()父组件
// Parent.vue<template> <div> 父组件: <span >message: {{ message }}</span> <span>msg: {{ msg }}</span> </div> <Child></Child></template><script setup>import { ref } from 'vue'import Bus from './Bus.js'import Child from './components/Child.vue'const msg = ref(Bus.msg)const message = ref('hello')// 用监听的写法Bus.$on('changeMsg', data => { message.value = data})</script>子组件
// Child.vue<template> <div> 子组件: <button @click="handleBusEmit">触发Bus.$emit</button> <button @click="changeBusMsg">修改总线里的 msg</button> </div></template><script setup>import Bus from '../Bus.js'function handleBusEmit() { Bus.$emit('changeMsg', '雷猴啊')}function changeBusMsg() { // console.log(Bus.msg) Bus.msg.value = '在子组件里修改了总线的值'}</script>这个方法其实还挺好用的,但光看可能有点懵,请大家务必亲手敲一下代码实践一下。
getCurrentInstance
getcurrentinstance 是 vue 提供的一个方法,支持访问内部组件实例。
getCurrentInstance 只暴露给高阶使用场景,典型的比如在库中。强烈反对在应用的代码中使用 getCurrentInstance。请不要把它当作在组合式 API 中获取 this 的替代方案来使用。
说白了,这个方法 适合在开发组件库的情况下使用,不适合日常业务开发中使用。
getCurrentInstance 只能在 setup 或生命周期钩子中调用。
getcurrentinstance 文档
在 <script setup> 中,我模拟了类似 $parent 和 $children 的方式。
父组件
// Parent.vue<template> <div>父组件 message 的值: {{ message }}</div> <button @click="handleClick">获取子组件</button> <Child></Child> <Child></Child></template><script setup>import { ref, getCurrentInstance, onMounted } from 'vue'import Child from './components/Child.vue'const message = ref('雷猴啊')let instance = nullonMounted(() => { instance = getCurrentInstance()})// 子组件列表let childrenList = []// 注册组件function registrationCom(com) { childrenList.push(com)}function handleClick() { if (childrenList.length > 0) { childrenList.forEach(item => { console.log('组件实例:', item) console.log('组件名(name):', item.type.name) console.log('组件输入框的值:', item.devtoolsRawSetupState.inputValue) console.log('---------------------------------------') }) }}</script>子组件
// Child.vue<template> <div> <div>----------------------------</div> 子组件:<button @click="handleClick">获取父组件的值</button> <br> <input type="text" v-model="inputValue"> </div></template><script>export default { name: 'ccccc'}</script><script setup>import { getCurrentInstance, onMounted, nextTick, ref } from 'vue'const inputValue = ref('')let instance = nullonMounted(() => { instance = getCurrentInstance() nextTick(() => { instance.parent.devtoolsRawSetupState.registrationCom(instance) })})function handleClick() { let msg = instance.parent.devtoolsRawSetupState.message msg.value = '哈哈哈哈哈哈'}</script>可以将代码复制到你的项目中运行试试看,最好还是敲一遍咯。
Vuex
Vuex 主要解决 跨组件通信 的问题。
在 Vue3 中,需要使用 Vuex v4.x 版本。
安装
用 npm 或者 Yarn 安装到项目中。
npm install vuex@next --save# 或yarn add vuex@next --save使用
安装成功后,在 src 目录下创建 store 目录,再在 store 下创建 index.js 文件。
// store/index.jsimport { createStore } from 'vuex'export default createStore({ state: { }, getters: { }, mutations: { }, actions: { }, modules: { }})在 store/index.js 下输入以上内容。
state:数据仓库,用来存数据的。
getters:获取数据的,有点像 computed 的用法(个人觉得)。
mutations: 更改 state 数据的方法都要写在 mutations 里。
actions:异步异步异步,异步的方法都写在这里,但最后还是需要通过 mutations 来修改 state 的数据。
modules:分包。如果项目比较大,可以将业务拆散成独立模块,然后分文件管理和存放。
然后在 src/main.js 中引入
import { createApp } from 'vue'import App from './App.vue'import store from './store'const app = createApp(App)app .use(store) .mount('#app')State
store/index.js
// store/index.jsimport { createStore } from 'vuex'export default createStore({ state: { msg: '雷猴' }})组件
// xxx.vue<script setup>import { useStore } from 'vuex'const store = useStore()console.log(store.state.msg) // 雷猴</script>Getter
我觉得 Getter 方法和 computed 是有点像的。
比如我们需要过滤一下数据,或者返回时组装一下数据,都可以用 Getter 方法。
store/index.js
// store/index.jsimport { createStore } from 'vuex'export default createStore({ state: { msg: '雷猴' }, getters: { getMsg(state) { return state.msg + ' 世界!' } }})组件
// xxx.vue<script setup>import { useStore } from 'vuex'const store = useStore()console.log(store.getters.getMsg) // 雷猴 世界!</script>Mutation
Mutation 是修改 State 数据的唯一方法,这样 Vuex 才可以跟踪数据流向。
在组件中通过 commit 调用即可。
store/index.js
// store/index.jsimport { createStore } from 'vuex'export default createStore({ state: { msg: '雷猴' }, mutations: { changeMsg(state, data) { state.msg = data } }})组件
// xxx.vue<script setup>import { useStore } from 'vuex'const store = useStore()store.commit('changeMsg', '蒜头王八')console.log(store.state.msg) // 蒜头王八</script>Action
我习惯将异步的东西放在 Action 方法里写,然后在组件使用 dispatch 方法调用。
store/index.js
// store/index.jsimport { createStore } from 'vuex'export default createStore({ state: { msg: '雷猴' }, mutations: { changeMsg(state, data) { state.msg = data } }, actions: { fetchMsg(context) { // 模拟ajax请求 setTimeout(() => { context.commit('changeMsg', '鲨鱼辣椒') }, 1000) } }})组件
// xxx.vue<script setup>import { useStore } from 'vuex'const store = useStore()store.dispatch('fetchMsg')</script>Module
Module 就是传说中的分包了。这需要你将不同模块的数据拆分成一个个 js 文件。
我举个例子,目录如下
store|- index.js|- modules/ |- user.js |- goods.jsindex.js对外的出口(主文件)modules/user.js用户相关模块modules/goods.js商品模块
index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex'import user from './modules/user'import goods from './modules/goods'export default createStore({ state: {}, getters: {}, mutations: {}, actions: {}, modules: { user, goods }})user.js
const user = { state: { }, getters: { }, mutations: { }, actions: { }}export default usergoods.js
const goods = { state: { }, getters: { }, mutations: { }, actions: { }}export default goods然后在各个模块里放入相应的数据和方法就行。
在组建中调用方法和访问数据,都和之前的用法差不多的。
以上就是 Vuex 的基础用法。除此之外,Vuex 还有各种语法糖,大家可以自行查阅 官方文档
Pinia
Pinia 是最近比较火热的一个工具,也是用来处理 跨组件通信 的,极大可能成为 Vuex 5 。
Pinia 文档
从我使用 Pinia 一阵后的角度来看,Pinia 跟 Vuex 相比有以下优点:
调用时代码跟简洁了。
对 TS 更友好。
合并了 Vuex 的 Mutation 和 Action 。天然的支持异步了。
天然分包。
除此之外,Pinia 官网还说它适用于 Vue2 和 Vue3。但我没试过在 Vue2 中使用 我懒得试。
Pinia 简化了状态管理模块,只用这3个东西就能应对日常大多任务。
state:存储数据的仓库
getters:获取和过滤数据(跟 computed 有点像)
actions:存放 “修改 state ”的方法
我举个简单的例子
安装
npm install pinia# 或yarn add pinia注册
在 src 目录下创建 store 目录,再在 store 里创建 index.js 和 user.js
目录结构如下
store|- index.js|- user.jsindex.js
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'const store = createPinia()export default storeuser.js
常见的写法有2种,选其中一种就行。
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'// 写法1export const useUserStore = defineStore({ id: 'user', // id必填,且需要唯一 state: () => { return { name: '雷猴' } }, getters: { fullName: (state) => { return '我叫 ' + state.name } }, actions: { updateName(name) { this.name = name } }})// 写法2export const useUserStore = defineStore('user',{ state: () => { return { name: '雷猴' } }, getters: { fullName: (state) => { return '我叫 ' + state.name } }, actions: { updateName(name) { this.name = name } }})然后在 src/main.js 中引入 store/index.js
src/main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue'import App from './App.vue'import store from './store'const app = createApp(App)app .use(store) .mount('#app')在组件中使用
组件
// xxx.vue<template> <div> <div>name: {{ name }}</div> <div>全名:{{ fullName }}</div> <button @click="handleClick">修改</button> </div></template><script setup>import { computed } from 'vue'import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'const userStore = useUserStore()// const name = computed(() => userStore.name)// 建议const { name, fullName } = storeToRefs(userStore)function handleClick() { // 不建议这样改 // name.value = '蝎子莱莱' // 推荐的写法!!! userStore.updateName('李四')}</script>啰嗦两句
其实 Pinia 的用法和 Vuex 是挺像的,默认就是分包的逻辑,在这方面我支持 菠萝(Pinia)。
Pinia 还提供了多种语法糖,强烈建议阅读一下 官方文档。
mitt.js
我们前面用到的 总线 Bus 方法,其实和 mitt.js 有点像,但 mitt.js 提供了更多的方法。
比如:
on:添加事件
emit:执行事件
off:移除事件
clear:清除所有事件
mitt.js 不是专门给 Vue 服务的,但 Vue 可以利用 mitt.js 做跨组件通信。
github 地址
npm 地址
安装
npm i mitt使用
我模拟一下 总线Bus 的方式。
我在同级目录创建3个文件用作模拟。
Parent.vueChild.vueBus.jsBus.js
// Bus.jsimport mitt from 'mitt'export default mitt()Parent.vue
// Parent.vue<template> <div> Mitt <Child /> </div></template><script setup>import Child from './Child.vue'import Bus from './Bus.js'Bus.on('sayHello', () => console.log('雷猴啊'))</script>Child.vue
// Child.vue<template> <div> Child:<button @click="handleClick">打声招呼</button> </div></template><script setup>import Bus from './Bus.js'function handleClick() { Bus.emit('sayHello')}</script>此时,点击 Child.vue 上的按钮,在控制台就会执行在 Parent.vue 里定义的方法。
到此,相信大家对“Vue3的组件通信方式有哪些”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是编程网网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!




