时序预测 | MATLAB实现基于PSO-BiLSTM、BiLSTM时间序列预测对比
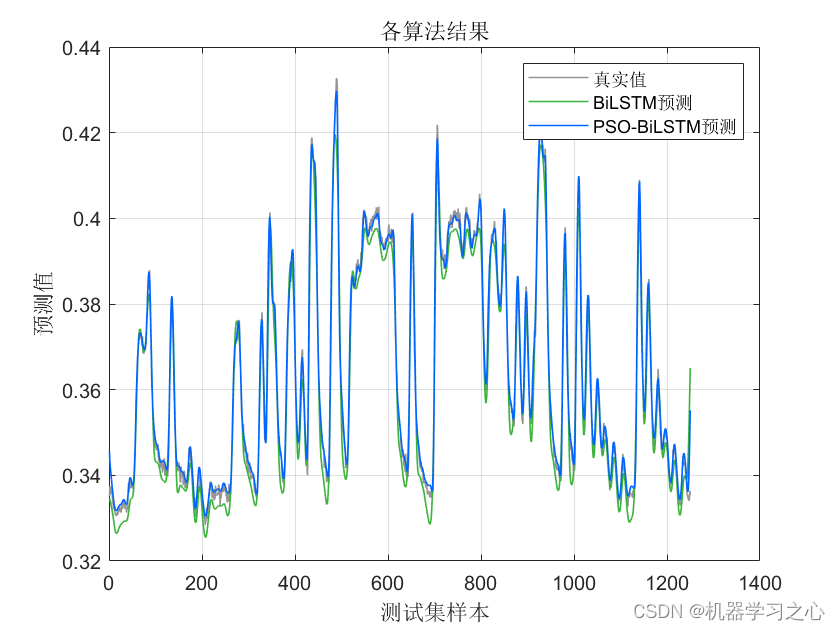
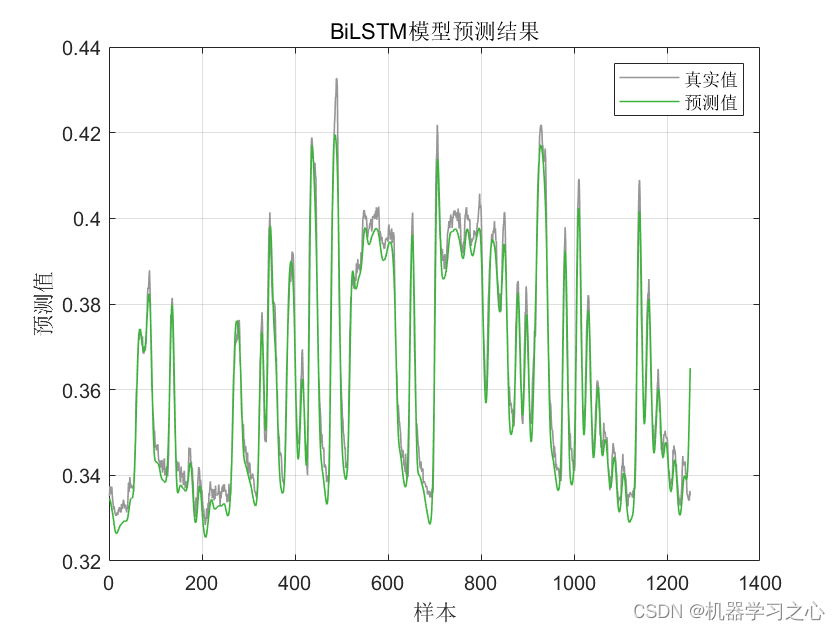
效果一览

基本描述
MATLAB实现基于PSO-BiLSTM、BiLSTM时间序列预测对比。
1.Matlab实现PSO-BiLSTM和BiLSTM神经网络时间序列预测;
2.输入数据为单变量时间序列数据,即一维数据;
3.运行环境Matlab2020及以上,依次运行Main1BiLSTMTS、Main2PSOBiLSTMTS、Main3CDM即可,其余为函数文件无需运行,所有程序放在一个文件夹,data为数据集;
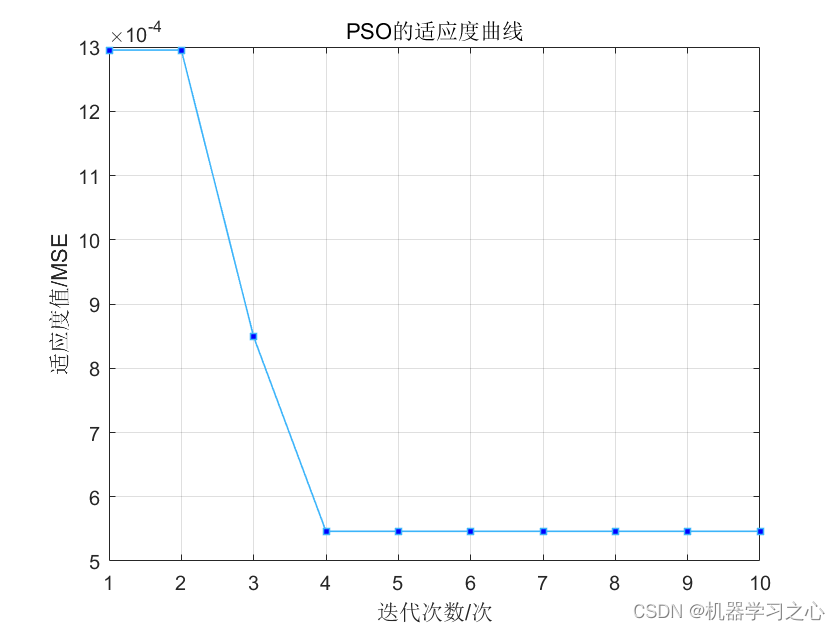
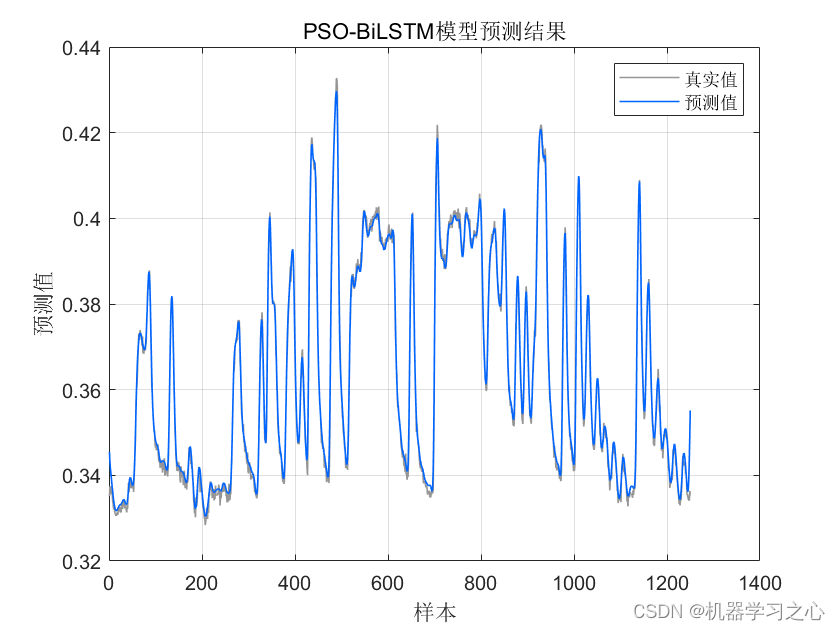
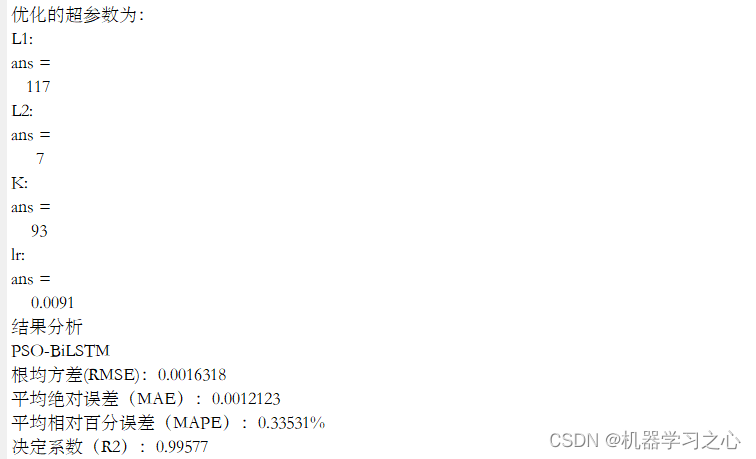
BiLSTM(双向长短时记忆模型)与粒子群算法优化后的BiLSTM(PSOBiLSTM)对比实验,可用于风电、光伏等负荷预测,时序预测,数据为单输入单输出,PSO优化超参数为隐含层1节点数、隐含层2节点数、最大迭代次数和学习率。
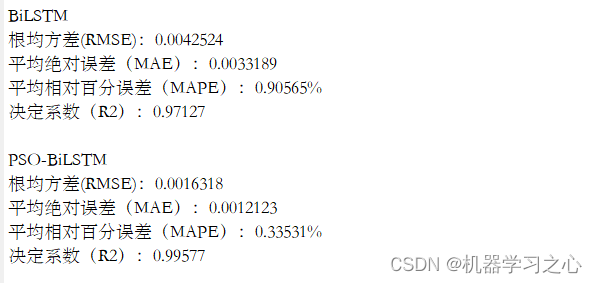
命令窗口输出MAE、MAPE、RMSE和R2;
程序设计
- 完整程序和数据下载:私信博主回复MATLAB实现基于PSO-BiLSTM、BiLSTM时间序列预测对比。
for i=1:PopNum%随机初始化速度,随机初始化位置 for j=1:dim if j==dim% % 隐含层节点与训练次数是整数 学习率是浮点型 pop(i,j)=(xmax(j)-xmin(j))*rand+xmin(j); else pop(i,j)=round((xmax(j)-xmin(j))*rand+xmin(j)); % end endend% calculate the fitness_value of Poppbest = pop;gbest = zeros(1,dim);data1 = zeros(Maxstep,PopNum,dim);data2 = zeros(Maxstep,PopNum);for i = 1:PopNum fit(i) = fitness(pop(i,:),p_train,t_train,p_test,t_test); f_pbest(i) = fit(i);endg = min(find(f_pbest == min(f_pbest(1:PopNum))));gbest = pbest(g,:);f_gbest = f_pbest(g);%-------- in the loop -------------for step = 1:Maxstep mbest =sum(pbest(:))/PopNum; % linear weigh factor b = 1-step/Maxstep*0.5; data1(step,:,:) = pop; data2(step,:) = fit; for i = 1:PopNum a = rand(1,dim); u = rand(1,dim); p = a.*pbest(i,:)+(1-a).*gbest; pop(i,:) = p + b*abs(mbest-pop(i,:)).*... log(1./u).*(1-2*(u >= 0.5)); % boundary detection for j=1:dim if j ==dim if pop(i,j)>xmax(j) | pop(i,j)<xmin(j) pop(i,j)=(xmax(j)-xmin(j))*rand+xmin(j); % end else pop(i,j)=round(pop(i,j)); if pop(i,j)>xmax(j) | pop(i,j)<xmin(j) pop(i,j)=round((xmax(j)-xmin(j))*rand+xmin(j)); % end end end fit(i) = fitness(pop(i,:),p_train,t_train,p_test,t_test); if fit(i) < f_pbest(i) pbest(i,:) = pop(i,:); f_pbest(i) = fit(i); end if f_pbest(i) < f_gbest gbest = pbest(i,:); f_gbest = f_pbest(i); end end trace(step)=f_gbest; step,f_gbest,gbest result(step,:)=gbest;endor i=1:N%随机初始化速度,随机初始化位置 for j=1:D if j==D% % 隐含层节点与训练次数是整数 学习率是浮点型 x(i,j)=(xmax(j)-xmin(j))*rand+xmin(j); else x(i,j)=round((xmax(j)-xmin(j))*rand+xmin(j)); % end end v(i,:)=rand(1,D);end%------先计算各个粒子的适应度,并初始化Pi和Pg----------------------for i=1:N p(i)=fitness(x(i,:),p_train,t_train,p_test,t_test); y(i,:)=x(i,:); end[fg,index]=min(p);pg = x(index,:); %Pg为全局最优%------进入主要循环,按照公式依次迭代------------for t=1:M for i=1:N v(i,:)=w*v(i,:)+c1*rand*(y(i,:)-x(i,:))+c2*rand*(pg-x(i,:)); x(i,:)=x(i,:)+v(i,:); for j=1:D if j ~=D x(i,j)=round(x(i,j)); end if x(i,j)>xmax(j) | x(i,j)<xmin(j) if j==D x(i,j)=(xmax(j)-xmin(j))*rand+xmin(j); % else x(i,j)=round((xmax(j)-xmin(j))*rand+xmin(j)); % end end end temp=fitness(x(i,:),p_train,t_train,p_test,t_test); if temp<p(i) p(i)=temp; y(i,:)=x(i,:); end if p(i)<fg pg=y(i,:); fg=p(i); end end trace(t)=fg; result(t,:)=pg;参考资料
[1] https://blog.csdn.net/kjm13182345320/article/details/127596777?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
[2] https://download.csdn.net/download/kjm13182345320/86830096?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
来源地址:https://blog.csdn.net/kjm13182345320/article/details/132557833




