小编给大家分享一下FastApi+Vue+LayUI如何实现前后端分离,相信大部分人都还不怎么了解,因此分享这篇文章给大家参考一下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后大有收获,下面让我们一起去了解一下吧!
前言
在前面的Api开发中,我们使用FastApi已经可以很好的实现。但是实际使用中,我们通常建议前后端项目分离。今天我们就使用FastApi+Vue+LayUI做一个前后端分离的Demo。
项目设计
后端
后端我们采用FastApi在新的test视图中,定义一个路由,并将其注册到app中,并且在test视图中定义一个接口,实现模拟从数据库读取数据供前端调用渲染。
代码
test.py
from fastapi import FastAPI,Depends,Header,HTTPException,APIRouterfrom fastapi.param_functions import Bodyfrom starlette.requests import Requestfrom starlette.templating import Jinja2Templatesfrom starlette import statusimport uvicornfrom deta import Detafrom fastapi.responses import StreamingResponsefrom fastapi.responses import JSONResponse# 实例化路由器router = APIRouter()templates = Jinja2Templates('templates')# 注意,视图这里使用router来声明请求方式&URI@router.get('/info')def user_list(): # vue的响应数据 items = [ {'id':'1','name':'phyger'}, {'id':'2','name':'fly'}, {'id':'3','name':'enheng'}, ] return JSONResponse(content=items)@router.get('/')def welcome(): return "这里是测试路由"'''实际上,这里的home.html也是需要前端服务去向用户渲染的,但是我们为了方便演示,未启动前端服务器,直接将前端代码写在了home.html中,实际上,当用户请求/check的时候,前端代码会去请求/info接口获取数据,从而实现前端页面的数据渲染。'''@router.get('/check')def home(request:Request): return templates.TemplateResponse(name='home.html',context={'request':request,})前端
前端我们直接导入Vue、LayUI、Axios的JS和CSS的CDN资源,在Vue实例的mount阶段,使用axios调用后端接口拿到数据,使用LayUI的样式对table元素进行美化。
代码
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script> <script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script> <!-- 引入 layui.css --> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://www.layuicdn.com/layui/css/layui.css" rel="external nofollow" /> <!-- 引入 layui.js --> <script src="https://www.layuicdn.com/layui/layui.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script> <title>Home</title></head><body> <div id="app"> <table class="layui-table"> <tr v-for="p in infos"> <td>[[ p.id ]]</td> <td>[[ p.name ]]</td> </tr> </table> </div> <table id="test" class="layui-table"></table><script type="text/javascript"> const Vapp = Vue.createApp({ data() { return { infos: [{id:1,name:'phyger'}], info: "hello vue..." } }, mounted() { this.showinfo(); }, methods: { showinfo(){ axios.get('/test/info') .then(response=>{ this.infos=response.data; console.log(response); console.log(this.infos); }) ,err=>{ console.log(err); }; }, }, }) Vapp.config.compilerOptions.delimiters = ['[[', ']]'] Vapp.mount('#app')</script></body></html>运行项目
启动 FastApi 后端服务器,访问 /test/check 接口。
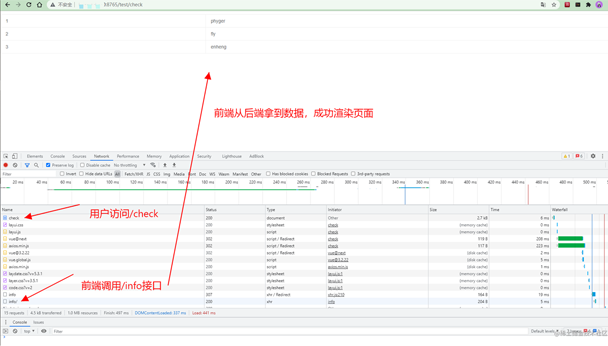
Q&A
Q:为什么在请求/info 接口总会出现一个 Temporary Redirect 重定向呢?

A:原因是因为我们在 FastApi 接口定义的时候,uri 的格式不规范导致,uri 的结尾不需要/,如果你接口增加了/,我们使用浏览器访问 uri,浏览器会忽略结尾的/,FastApi 会在内部进行查重定向,将浏览器不带/的请求重定向到我们定义的带/的视图函数上。
以上是“FastApi+Vue+LayUI如何实现前后端分离”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的内容对大家有所帮助,如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注编程网行业资讯频道!




