这篇文章主要介绍“怎么用Node创建一个简单的HTTP服务器”的相关知识,小编通过实际案例向大家展示操作过程,操作方法简单快捷,实用性强,希望这篇“怎么用Node创建一个简单的HTTP服务器”文章能帮助大家解决问题。
1. 使用Node.js直接运行JavaScript脚本
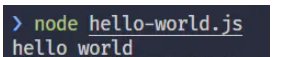
node.js基于Chrome的v8引擎运行js代码,因此我们可以摆脱浏览器环境,直接在控制台中运行js代码,比如下面这个hello world代码
console.log('hello world');
控制台中直接使用node即可运行
2. 创建一个简单的HTTP服务器
node.js的内置模块http提供了基本的http服务的能力,基于CommonJS规范,我们可以使用require导入http模块进行使用http模块中有一个createServer函数能够让我们创建一个http服务器其接收一个回调函数作为参数,这个回调函数接收两个参数 -- request和response。
request包括所有客户端请求的信息,比如url、请求头header、请求方式和请求体等response主要用于返回信息给客户端,封装了一些操作响应体相关的操作,比如response.writeHead方法就可以让我们自定义返回体的头部信息和状态码
当我们将响应体处理好了之后,调用response.end()方法就可以将响应体发送给客户端使用createServer函数只是帮我们创建了一个Server对象,并没有让其开启监听,我们还需要调用server对象的listen方法才可以进行监听,真正作为一个服务器开始运行
listen方法的第一个参数是监听的端口号,第二个参数则是绑定的主机ip,第三个参数是一个回调函数,会被http模块异步调用,当遇到错误的时候,就能够在这个回调函数的第一个参数中获取到抛出的异常 ,我们可以选择对异常进行处理,让我们的服务器更加健壮
下面是使用http模块创建一个简单服务器的例子
const { createServer } = require('http');const HOST = 'localhost';const PORT = '8080';const server = createServer((req, resp) => { // the first param is status code it returns // and the second param is response header info resp.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/plain' }); console.log('server is working...'); // call end method to tell server that the request has been fulfilled resp.end('hello nodejs http server');});server.listen(PORT, HOST, (error) => { if (error) { console.log('Something wrong: ', error); return; } console.log(`server is listening on http://${HOST}:${PORT} ...`);});
可以直接尝试用node运行它,创造一个属于你的服务器!服务器运行后,浏览器访问http://localhost:8080即可访问到这个服务器

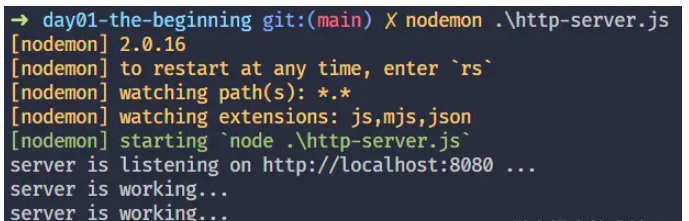
也可以使用nodemon运行它,这样当我们的代码发生变化的时候就不需要手动终止程序再重新运行了
npm i -g nodemon
建议全局安装它,这样就可以直接使用,不需要通过npx nodemon去使用使用也很简单,直接将node命令改成nodemon命令即可
nodemon http-server.js
3. 加上类型提示
前面我们在使用createServer以及resp对象的时候,看不到任何的语法提示,必须随时跟着node官方文档去边用边查,有点不方便但是没关系,我们可以使用ts的.d.ts文件帮助我们提供语法提示功能,注意,我们不是使用ts进行开发,只是使用它的语法提示功能而已
初始化项目 --
npm init -y安装
@types/node--pnpm i @types/node -D在项目目录下创建
jsconfig.json文件,将node_modules排除在外,没必要对其进行检查
{ "compilerOptions": { "checkJs": true }, "exclude": ["node_modules", "**/node_modulesconst createPdf = () => { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { if (!fs.existsSync("example.pdf")) { // create a PDFDocument object const doc = new PDFDocument(); // create write stream by piping the pdf content. doc.pipe(fs.createWriteStream("example.pdf")); // add some contents to pdf document doc.fontSize(16).text("Hello PDF", 100, 100); // complete the operation of generating PDF file. doc.end(); } resolve("success"); });};
这里使用到了管道操作,将PDFDocument对象的内容通过管道传到新创建的写入流中,当完成操作后我们就通过resovle告知外界已经创建好pdf文件了然后在服务端代码中调用
const server = createServer(async (req, resp) => { // change the MIME type to application/pdf resp.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "application/pdf" }); // create pdf file await createPdf(); // read created pdf file fs.readFile("example.pdf", (err, data) => { if (err) { console.error( "an error occurred while reading the pdf file content: ", err ); throw err; } console.log("operation success!"); resp.end(data); });});server.listen(PORT, HOST, (error) => { if (error) { console.log("Something wrong: ", error); return; } console.log(`server is listening on http://${HOST}:${PORT} ...`);});
现在浏览器就可以读取到创建的pdf文件了
8. 返回音频文件
思路依然是一样的,读取一个音频文件,然后通过管道将它送到resp对象中再返回即可
const { createServer } = require("http");const { stat, createReadStream } = require("fs");const HOST = "localhost";const PORT = 8080;const server = createServer((req, resp) => { // change the MIME type to audio/mpe resp.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "audio/mp3" }); const mp3FileName = "audio.mp3"; stat(mp3FileName, (err, stats) => { if (stats.isFile()) { const rs = createReadStream(mp3FileName); // pipe the read stream to resp rs.pipe(resp); } else { resp.end("mp3 file not exists"); } });});server.listen(PORT, HOST, (error) => { if (error) { console.log("Something wrong: ", error); return; } console.log(`server is listening on http://${HOST}:${PORT} ...`);});
打开后就是一个播放音频的界面,这是chrome提供的对音频文件的展示,并且打开控制台会发现有返回音频文件
注意:将音频文件流通过管道传到**resp**后,不需要调用**resp.end()**方法,因为这会关闭整个响应,导致音频文件无法获取
9. 返回视频文件
视频文件和音频文件的处理是一样的,只是MIME的类型要改成video/mp4,其他都一样
const { createServer } = require("http");const { stat, createReadStream } = require("fs");const HOST = "localhost";const PORT = 8080;const server = createServer((req, resp) => { // change the MIME type to audio/mpe resp.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "audio/mp4" }); const mp4FileName = "video.mp4"; stat(mp4FileName, (err, stats) => { if (stats.isFile()) { const rs = createReadStream(mp4FileName); // pipe the read stream to resp rs.pipe(resp); } else { resp.end("mp4 file not exists"); } });});server.listen(PORT, HOST, (error) => { if (error) { console.log("Something wrong: ", error); return; } console.log(`server is listening on http://${HOST}:${PORT} ...`);});
关于“怎么用Node创建一个简单的HTTP服务器”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识,可以关注编程网行业资讯频道,小编每天都会为大家更新不同的知识点。









