本篇内容介绍了“Python函数和模块怎么使用”的有关知识,在实际案例的操作过程中,不少人都会遇到这样的困境,接下来就让小编带领大家学习一下如何处理这些情况吧!希望大家仔细阅读,能够学有所成!
一、函数和模块概述
(一)函数概述
函数可以看成是语句的集合,通过函数调用来执行其包含的语句。函数可以返回一个计算结果,根据每次函数调用的参数,可以返回不同的计算结果。Python利用函数提高代码的重用率,减少了代码冗余。
执行dir(__builtin__)可以查看Python所有内置对象
['ArithmeticError', 'AssertionError', 'AttributeError', 'BaseException', 'BlockingIOError', 'BrokenPipeError', 'BufferError', 'BytesWarning', 'ChildProcessError', 'ConnectionAbortedError', 'ConnectionError', 'ConnectionRefusedError', 'ConnectionResetError', 'DeprecationWarning', 'EOFError', 'Ellipsis', 'EnvironmentError', 'Exception', 'False', 'FileExistsError', 'FileNotFoundError', 'FloatingPointError', 'FutureWarning', 'GeneratorExit', 'IOError', 'ImportError', 'ImportWarning', 'IndentationError', 'IndexError', 'InterruptedError', 'IsADirectoryError', 'KeyError', 'KeyboardInterrupt', 'LookupError', 'MemoryError', 'ModuleNotFoundError', 'NameError', 'None', 'NotADirectoryError', 'NotImplemented', 'NotImplementedError', 'OSError', 'OverflowError', 'PendingDeprecationWarning', 'PermissionError', 'ProcessLookupError', 'RecursionError', 'ReferenceError', 'ResourceWarning', 'RuntimeError', 'RuntimeWarning', 'StopAsyncIteration', 'StopIteration', 'SyntaxError', 'SyntaxWarning', 'SystemError', 'SystemExit', 'TabError', 'TimeoutError', 'True', 'TypeError', 'UnboundLocalError', 'UnicodeDecodeError', 'UnicodeEncodeError', 'UnicodeError', 'UnicodeTranslateError', 'UnicodeWarning', 'UserWarning', 'ValueError', 'Warning', 'WindowsError', 'ZeroDivisionError', '__IPYTHON__', '__build_class__', '__debug__', '__doc__', '__import__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'abs', 'all', 'any', 'ascii', 'bin', 'bool', 'breakpoint', 'bytearray', 'bytes', 'callable', 'cell_count', 'chr', 'classmethod', 'compile', 'complex', 'copyright', 'credits', 'debugcell', 'debugfile', 'delattr', 'dict', 'dir', 'display', 'divmod', 'enumerate', 'eval', 'exec', 'filter', 'float', 'format', 'frozenset', 'get_ipython', 'getattr', 'globals', 'hasattr', 'hash', 'help', 'hex', 'id', 'input', 'int', 'isinstance', 'issubclass', 'iter', 'len', 'license', 'list', 'locals', 'map', 'max', 'memoryview', 'min', 'next', 'object', 'oct', 'open', 'ord', 'pow', 'print', 'property', 'range', 'repr', 'reversed', 'round', 'runcell', 'runfile', 'set', 'setattr', 'slice', 'sorted', 'staticmethod', 'str', 'sum', 'super', 'tuple', 'type', 'vars', 'zip']演示Python内置函数

(二)模块概述
模块是程序代码和数据的封装。模块中定义的变量、函数或类等可导入到其他文件中使用。Python正是通过模块提供各种功能,例如,在前面用到的sys、os、math、random等都是模块。
1、sys模块
查看sys模块包含的对象(属性和方法)
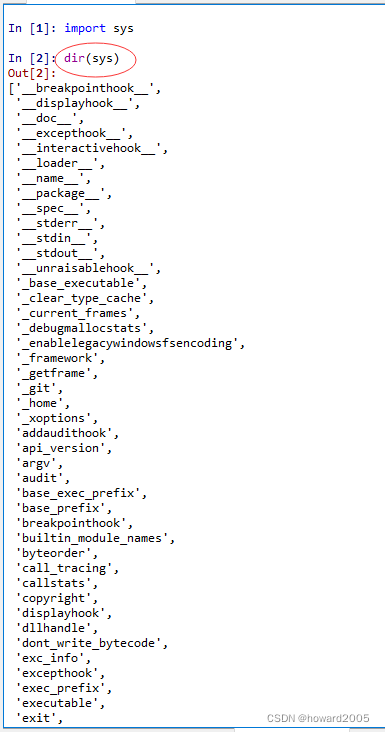
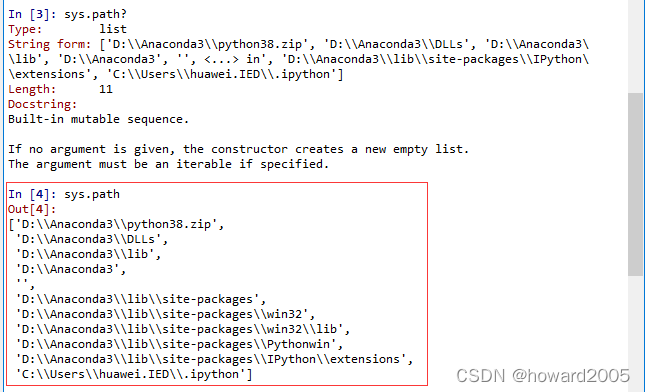
使用sys模块的path
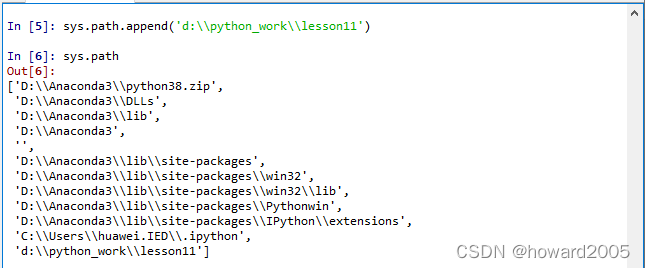
2、os模块
导入os模块

获取当前工作目录

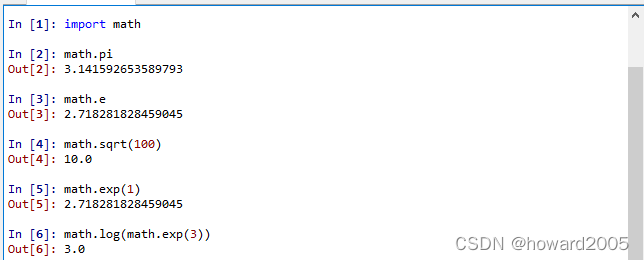
3、math模块
4、random模块

二、函数
在编写程序时,往往会遇到在多处使用的类似代码。这时,可将重复代码提取出来,定义为函数。从而简化编程工作量,也使代码结构简化。
函数有三要素:函数名(
function name)、参数列表(parameter list)、返回值(return value)参数有两种类型:位置参数(
positional parameter)、键参数(key parameter)
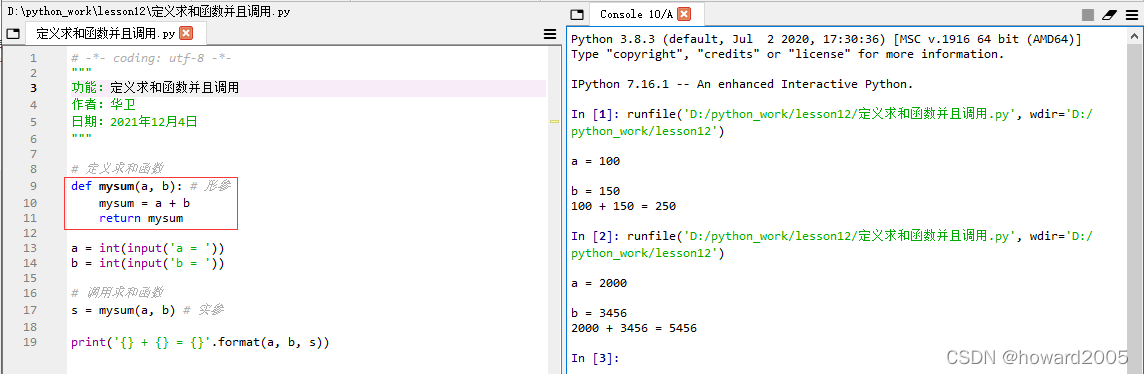
(一)定义函数
1、语法格式
def: define
def 函数名(参数表): 函数体(语句组) return 返回值如果我们定义一个函数,没有写return语句,系统会自动给它添加一个return None
2、函数类型
无参函数
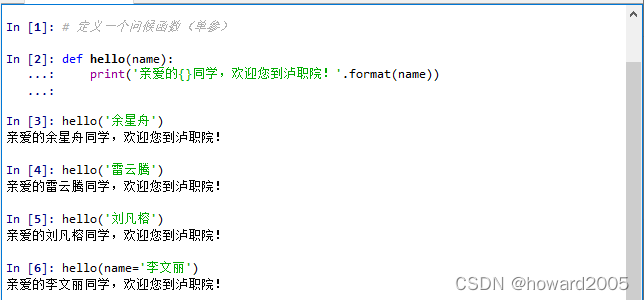
单参函数
多参函数
3、案例演示
定义无参函数

定义单参函数(调用时可以用位置参数,也可以用键参数)
定义多参函数

说明:定义函数时的参数叫做形式参数(formal paramter),简称形参(虚参);调用函数时的参数叫做实际参数(actual parameter),简称实参。调用函数,就是将实参传递给形参,进行处理之后,得到返回值。
定义有返回值的函数
(二)调用函数
1、简要说明
函数通过函数名加上一组圆括号进行调用,参数放在圆括号内,多个参数之间用逗号分隔。
在Python中,所有的语句都是实时执行的,不像C/C++存在编译过程。def也是一条可执行语句,定义一个函数。所以函数的调用必须在函数定义之后。
在Python中,函数名也是一个变量,它引用return语句返回的值,没有返回值时,函数值为None。
2、案例演示
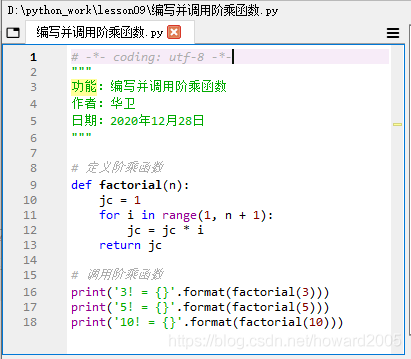
编写并调用阶乘函数 - factorial(n)
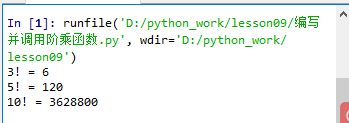
运行程序,查看结果
(三)函数参数
在定义函数时,参数表中的各个参数称为形式参数,简称形参。调用函数时,参数表中提供的参数称为实际参数,简称实参。在Python中,变量保存的是对象的引用,类似C/C++中的指针。实参传递给形参就是将对象的引用赋值给形参。
1、参数的多态性
多态是面向对象的一个特点,指多一个行为针对不同对象可能会得到不同的结果。Python中的变量无类型属性,变量可引用各种不同类型的对象。同一个函数,传递的实际参数类型不同时,可获得不同的结果,体现了多态性。
2、参数赋值传递
通常,函数调用时按参数的先后顺序,将实参传递给形参。例如:调用add(1, 2.5)时,1传递给a,2.5传递给b。Python允许以形参赋值的方式,指定将实参传递给形参。
三、利用函数实现模块化
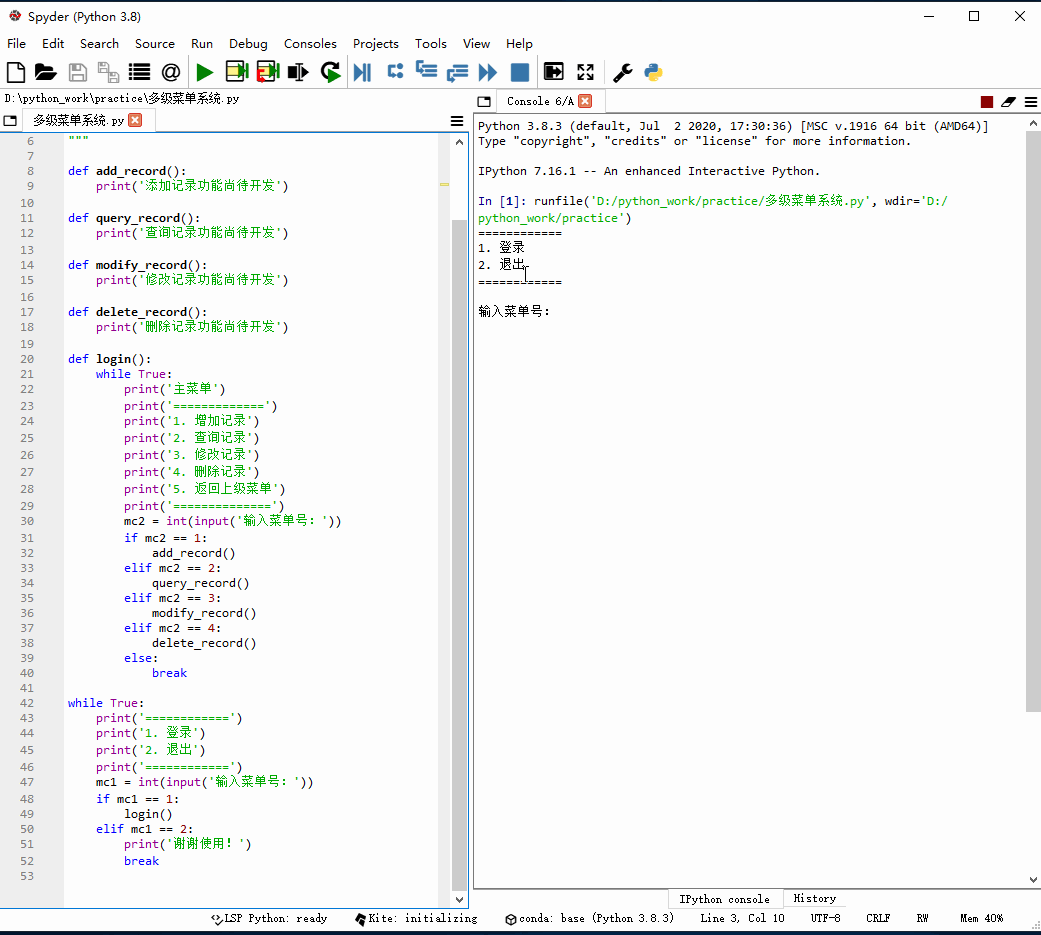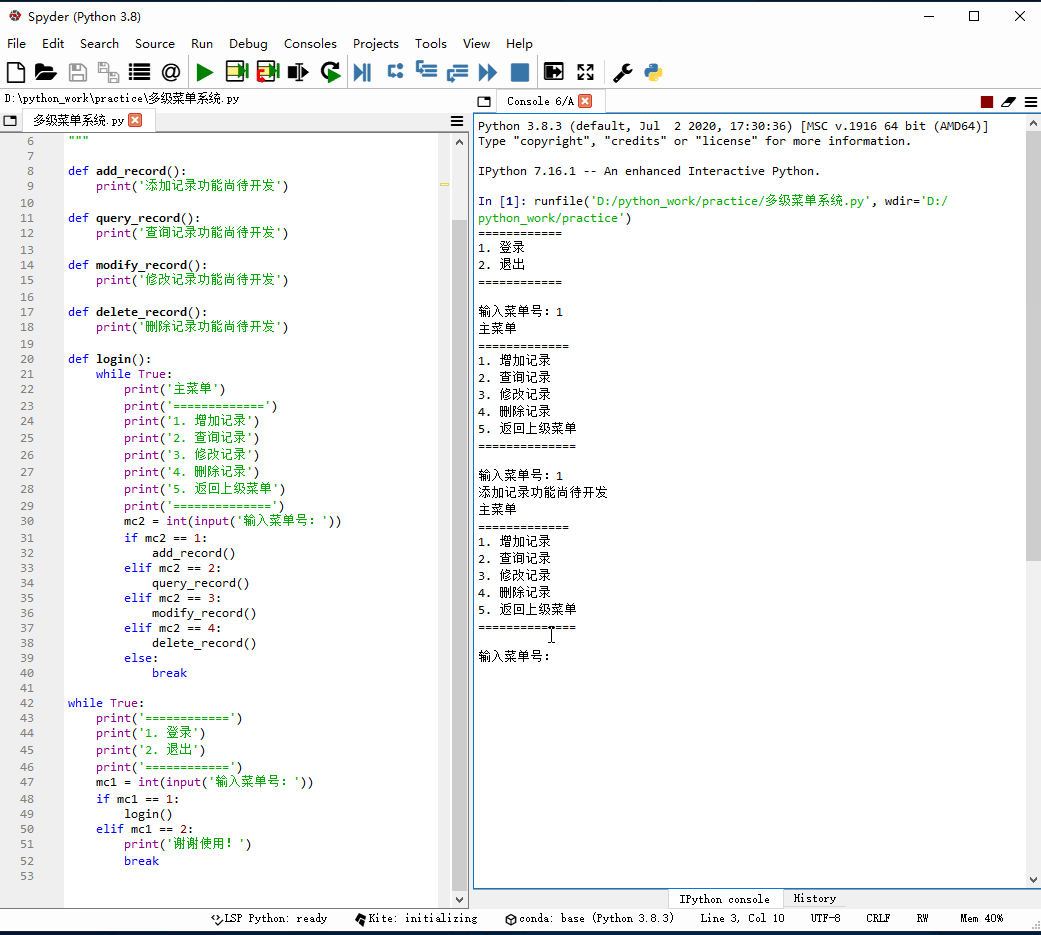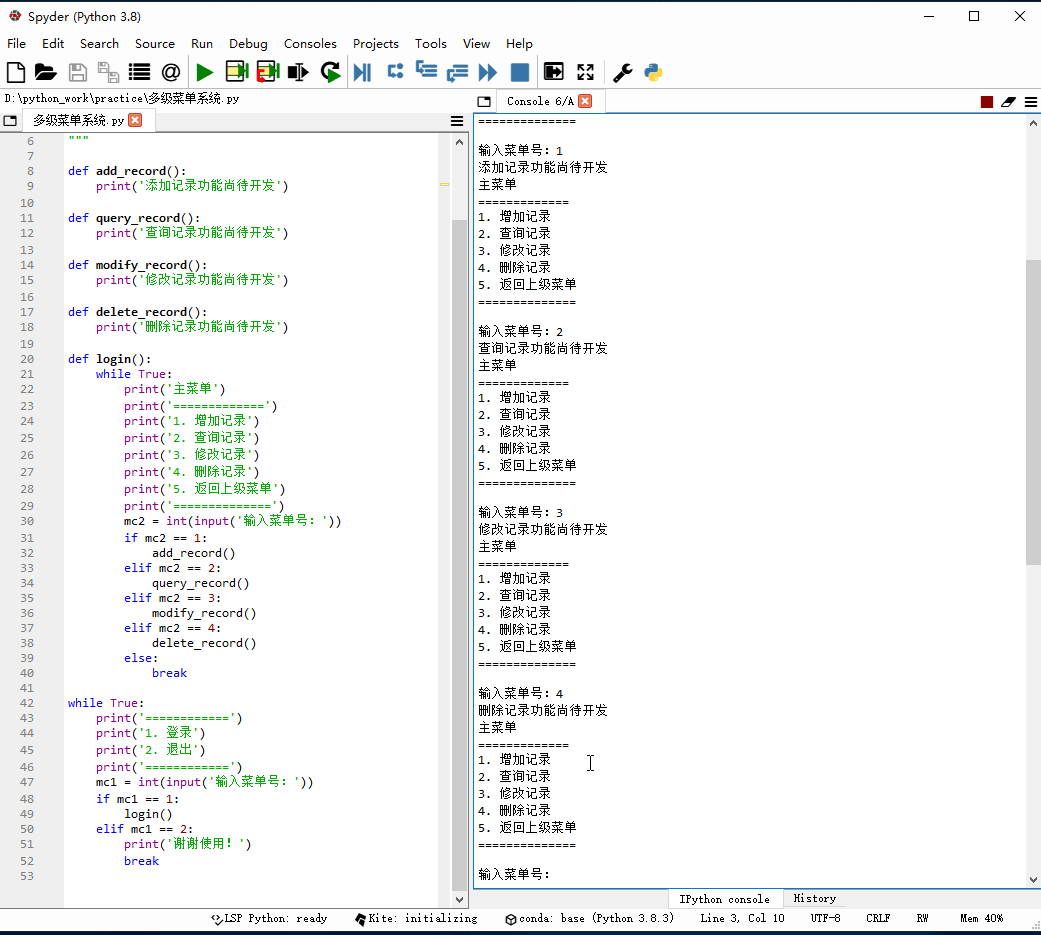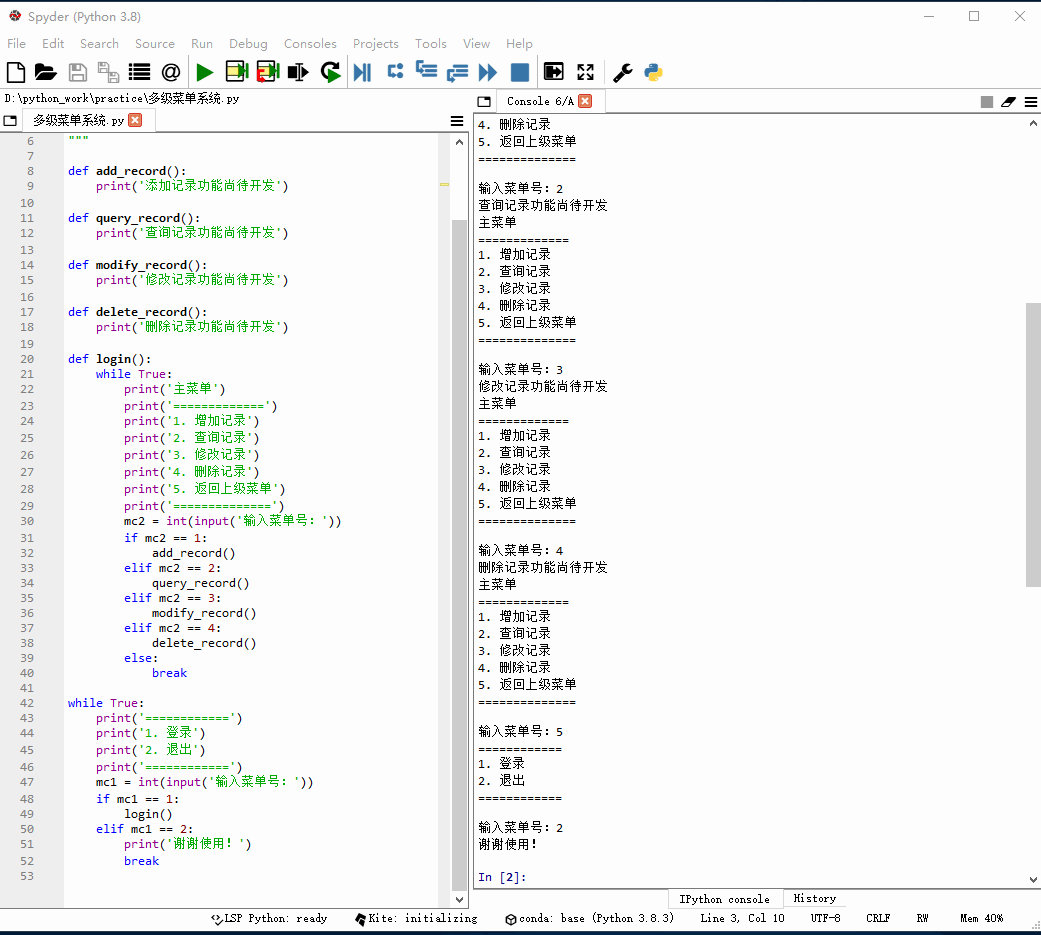
1、创建多级菜单系统
编写程序 - 多级菜单系统.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""功能:多级菜单系统作者:华卫日期:2021年1月4日"""def add_record(): print('添加记录功能尚待开发')def query_record(): print('查询记录功能尚待开发')def modify_record(): print('修改记录功能尚待开发')def delete_record(): print('删除记录功能尚待开发')def login(): while True: print('主菜单') print('=============') print('1. 增加记录') print('2. 查询记录') print('3. 修改记录') print('4. 删除记录') print('5. 返回上级菜单') print('==============') mc2 = int(input('输入菜单号:')) if mc2 == 1: add_record() elif mc2 == 2: query_record() elif mc2 == 3: modify_record() elif mc2 == 4: delete_record() else: breakwhile True: print('============') print('1. 登录') print('2. 退出') print('============') mc1 = int(input('输入菜单号:')) if mc1 == 1: login() elif mc1 == 2: print('谢谢使用!') break2、启动程序,查看效果
“Python函数和模块怎么使用”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识可以关注编程网网站,小编将为大家输出更多高质量的实用文章!






