目录
1、核心配置文件
▶ 官网上可以看配置
注意:配置各个标签需要遵循官网的配置顺序,否则会报错。
▶ 环境配置
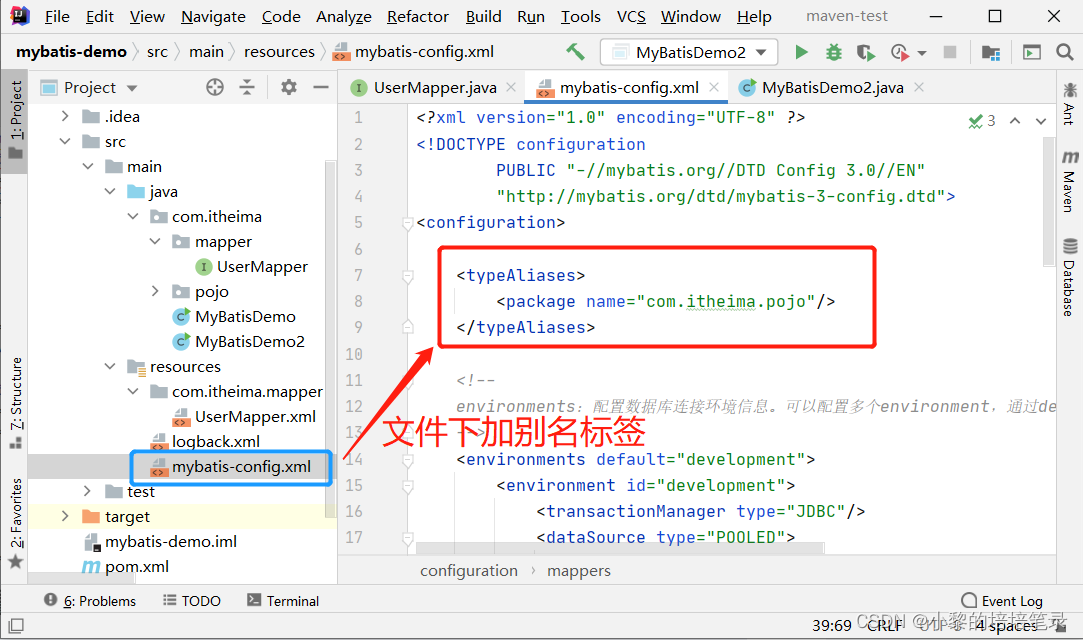
2、配置别名
1、查询操作
▶ 查询所有数据
▷ 书写步骤
编写接口方法:Mapper接口
* 参数:无,(查询所有数据功能是不需要根据任何条件进行查询的,所以此方法不需要参数)。
* 结果:List
,(我们会将查询出来的每一条数据封装成一个 `Brand` 对象,而多条数据封装多个 `Brand` 对象,需要将这些对象封装到List集合中返回)。 * 编写SQL语句:SQL映射文件
* 执行方法、测试
▷ 编写接口
在 `com.itheima.mapper` 包写创建名为 `BrandMapper` 的接口。并在该接口中定义 `List
selectAll()` 方法。自己写的时候注意接口的位置写到什么地方。 public interface BrandMapper { ListselectAll();} ▷ 编写SQL语句
在 `reources` 下创建 `com/itheima/mapper` 目录结构,并在该目录下创建名为 `BrandMapper.xml` 的映射配置文件。自己写的时候找到对应的SQL书写映射文件。
▷ 测试方法
在 `MybatisTest` 类中编写测试查询所有的方法,在测试类中进行测试。
public void testSelectAll() throws IOException { //1. 获取SqlSessionFactory String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2. 获取SqlSession对象 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象 BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class); //4. 执行方法 Listbrands = brandMapper.selectAll(); System.out.println(brands); //5. 释放资源 sqlSession.close();} ▷ 执行结果
存在的问题:从上面结果可以看到 `brandName` 和 `companyName` 这两个属性的数据没有封装成功,查询 实体类 和 表中的字段 发现,在实体类中属性名是 `brandName` 和 `companyName` ,而表中的字段名为 `brand_name` 和 `company_name`,那么我们只需要保持这两部分的名称一致这个问题就迎刃而解。
▷ 解决方式
数据库表的字段名称 和 实体类的属性名称 不一样,则不能自动封装数据: ①起别名:对不一样的列名起别名,让别名和实体类的属性名一样。缺点:每次查询都要定义一次别名sql片段,缺点:不灵活id, brand_name as brandName, company_name as companyName, ordered, description, status ②resultMap: 1. 定义标签 2. 在 id:完成主键字段的映射
column:表的列名
property:实体类的属性名
result:完成一般字段的映射
column:表的列名
property:实体类的属性名▶ 查询详情
▷ 编写步骤
编写接口方法:Mapper接口
* 参数:id
查看详情就是查询某一行数据,所以需要根据id进行查询。而id以后是由页面传递过来。
* 结果:Brand
根据id查询出来的数据只要一条,而将一条数据封装成一个Brand对象即可
* 编写SQL语句:SQL映射文件
* 执行方法、进行测试
▷ 编写接口
Brand selectById(int id);▷ 编写SQL语句
▷ 测试方法
public void testSelectById() throws IOException { //接收参数 int id = 1; //1. 获取SqlSessionFactory String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2. 获取SqlSession对象 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象 BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class); //4. 执行方法 Brand brand = brandMapper.selectById(id); System.out.println(brand); //5. 释放资源 sqlSession.close(); }▷ 参数占位符
1. #{}: 会将其替换为 ?,为了防止SQL注入
2. ${}:拼sql。会存在SQL注入问题
3. 使用时机:
* 参数传递的时候:#{}
* 表名或者列名不固定的情况下:${} 会存在SQL注入问题4.参数类型:parameterType:可以省略
5.特殊字符处理:(比如:< )
* 转义字符:<* CDATA区 :
▶ 多条件查询
▷ 书写步骤
1、编写接口方法
* 参数:所有查询条件
* 结果:List
2、在映射配置文件中编写SQL语句3、编写测试方法并执行
▷ 编写接口
①使用 `@Param("参数名称")` 标记每一个参数,在映射配置文件中就需要使用 `#{参数名称}` 进行占位
ListselectByCondition(@Param("status") int status, @Param("companyName") String companyName, @Param("brandName") String brandName); ②将多个参数封装成一个 实体对象 ,将该实体对象作为接口的方法参数。该方式要求在映射配置文件的SQL中使用 `#{内容}` 时,里面的内容必须和实体类属性名保持一致。
ListselectByCondition(Brand brand); ③将多个参数封装到map集合中,将map集合作为接口的方法参数。该方式要求在映射配置文件的SQL中使用 `#{内容}` 时,里面的内容必须和map集合中键的名称一致。
ListselectByCondition(Map map); ▷ 编写SQL语句
▷ 进行测试
public void testSelectByCondition() throws IOException { //接收参数 int status = 1; String companyName = "华为"; String brandName = "华为"; // 处理参数 companyName = "%" + companyName + "%"; brandName = "%" + brandName + "%"; //1. 获取SqlSessionFactory String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2. 获取SqlSession对象 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象 BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class); //4. 执行方法 Listbrands = brandMapper.selectByCondition(status, companyName, brandName); System.out.println(brands); //5. 释放资源 sqlSession.close(); //封装对象Brand brand = new Brand();brand.setStatus(status);brand.setCompanyName(companyName);brand.setBrandName(brandName);//4.执行方法Listbrands = brandMapper.selectByCondition(brand); Map map = new HashMap();map.put("status" , status);map.put("companyName", companyName);map.put("brandName" , brandName);//4.执行方法Listbrands = brandMapper.selectByCondition(map); ▷ 动态SQL
① if 标签:条件判断,其中test 属性:逻辑表达式。
② where 标签,作用:* 替换where关键字,* 会动态的去掉关键字 ,* 如果所有的参数没有值则不加where关键字
▶ 单个条件的动态SQL
▷ 编写接口
ListselectByConditionSingle(Brand brand); ▷ 编写SQL
▷ 测试方法
public void testSelectByConditionSingle() throws IOException { //接收参数 int status = 1; String companyName = "华为"; String brandName = "华为"; // 处理参数 companyName = "%" + companyName + "%"; brandName = "%" + brandName + "%"; //封装对象 Brand brand = new Brand(); brand.setCompanyName(companyName); //1. 获取SqlSessionFactory String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2. 获取SqlSession对象 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象 BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class); //4. 执行方法 Listbrands = brandMapper.selectByConditionSingle(brand); System.out.println(brands); //5. 释放资源 sqlSession.close();}
2、添加操作
▶ 编写接口
void add(Brand brand);▶ 编写SQL
insert into tb_brand (brand_name, company_name, ordered, description, status) values (#{brandName}, #{companyName}, #{ordered}, #{description}, #{status}); ▶ 测试方法
public void testAdd() throws IOException { //接收参数 int status = 1; String companyName = "波导手机"; String brandName = "波导"; String description = "手机中的战斗机"; int ordered = 100; //封装对象 Brand brand = new Brand(); brand.setStatus(status); brand.setCompanyName(companyName); brand.setBrandName(brandName); brand.setDescription(description); brand.setOrdered(ordered); //1. 获取SqlSessionFactory String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2. 获取SqlSession对象 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象 BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class); //4. 执行方法 brandMapper.add(brand); //提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); //5. 释放资源 sqlSession.close();}▶ 主键返回
在数据添加成功后,有时候需要获取插入数据库数据的主键(主键是自增长)。比如:
* 添加订单数据
* 添加订单项数据,订单项中需要设置所属订单的id
▷ 更改SQL
insert into tb_brand (brand_name, company_name, ordered, description, status) values (#{brandName}, #{companyName}, #{ordered}, #{description}, #{status}); ▷ 在 insert 标签上添加如下属性:
* useGeneratedKeys:是够获取自动增长的主键值。true表示获取
* keyProperty :指定将获取到的主键值封装到哪儿个属性里
3、修改操作
▶ 编写接口
void update(Brand brand);▶ 编写SQL
update tb_brand where id = #{id}; brand_name = #{brandName}, company_name = #{companyName}, ordered = #{ordered}, description = #{description}, status = #{status} ▶ 测试方法
public void testUpdate() throws IOException { //接收参数 int status = 0; int id = 6; //封装对象 Brand brand = new Brand(); brand.setStatus(status); brand.setId(id); //1. 获取SqlSessionFactory String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2. 获取SqlSession对象 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象 BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class); //4. 执行方法 int count = brandMapper.update(brand); System.out.println(count); //提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); //5. 释放资源 sqlSession.close();}
4、删除操作
▶ 单行删除
▷ 编写接口
void deleteById(int id);▷ 编写SQL
delete from tb_brand where id = #{id}; ▷ 测试方法
public void testDeleteById() throws IOException { //接收参数 int id = 6; //1. 获取SqlSessionFactory String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2. 获取SqlSession对象 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); //3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象 BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class); //4. 执行方法 brandMapper.deleteById(id); //提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); //5. 释放资源 sqlSession.close();}▶ 批删除除
▷ 编写接口
void deleteByIds(int[] ids);▷ 编写SQL:foreach 标签
用来迭代任何可迭代的对象(如数组,集合):
①collection 属性:
* mybatis会将数组参数,封装为一个Map集合。
* 默认:array = 数组
* 使用@Param注解改变map集合的默认key的名称
②item 属性:本次迭代获取到的元素。
③separator 属性:集合项迭代之间的分隔符。`foreach` 标签不会错误地添加多余的分隔符。也就是最后一次迭代不会加分隔符。
④open 属性:该属性值是在拼接SQL语句之前拼接的语句,只会拼接一次
⑤close 属性:该属性值是在拼接SQL语句拼接后拼接的语句,只会拼接一次delete from tb_brand where id in #{id} ;▷ 测试方法
public void testDeleteByIds() throws IOException { //接收参数 int[] ids = {5,7,8}; //1. 获取SqlSessionFactory String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); //2. 获取SqlSession对象 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); //3. 获取Mapper接口的代理对象 BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class); //4. 执行方法 brandMapper.deleteByIds(ids); //提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); //5. 释放资源 sqlSession.close();}
5、MyBatis参数传递
▶ 多个参数
我们在接口方法中定义多个参数,Mybatis 会将这些参数封装成 Map 集合对象,值就是参数值,而键在没有使用 `@Param` 注解时有以下命名规则:
▷ 以 arg 开头 :第一个参数就叫 arg0,第二个参数就叫 arg1,以此类推。如:
> map.put("arg0",参数值1);
> map.put("arg1",参数值2);▷ 以 param 开头 : 第一个参数就叫 param1,第二个参数就叫 param2,依次类推。如:
> map.put("param1",参数值1);
> map.put("param2",参数值2);① 验证一:
接口:
User select(String username,String password);SQL:
或
结果:
② 验证二:
将接口更改:
User select(@Param("username") String username, String password);则会看到下列运行结果
结论:以后接口参数是多个时,在每个参数上都使用 `@Param` 注解。这样代码的可读性更高。
▶ 单个参数
▷ POJO 类型
直接使用。要求 `属性名` 和 `参数占位符名称` 一致
▷ Map 集合类型
直接使用。要求 `map集合的键名` 和 `参数占位符名称` 一致
▷ Collection 集合类型
Mybatis 会将集合封装到 map 集合中,如下:
* map.put("arg0",collection集合);
* map.put("collection",collection集合;==》可以使用 `@Param` 注解替换map集合中默认的 arg 键名。
▷ List 集合类型
Mybatis 会将集合封装到 map 集合中,如下:
* map.put("arg0",list集合);
* map.put("collection",list集合);
* map.put("list",list集合);==》可以使用 `@Param` 注解替换map集合中默认的 arg 键名。
▷ Array 类型
Mybatis 会将集合封装到 map 集合中,如下:
* map.put("arg0",数组);
* map.put("array",数组);==》可以使用 `@Param` 注解替换map集合中默认的 arg 键名。==
▷ 其他类型
比如int类型,`参数占位符名称` 叫什么都可以。尽量做到见名知意
▷ 注解实现
@Select(value = "select * from tb_user where id = #{id}")public User select(int id);▷ 注意
注解是用来替换映射配置文件方式配置的,所以使用了注解,就不需要再映射配置文件中书写对应的 `statement`。
▷ Mybatis 针对 CURD 操作都提供了对应的注解。如下:
查询 :@Select
添加 :@Insert
修改 :@Update
删除 :@Delete▷ 注解实现方式
在接口中直接这样写:
@Select(value = "select * from tb_user where id = #{id}")public User select(int id);而编写SQL语句的那个配置文件就不需要在写SQL语句了。
▷ 注解完成简单功能,配置文件完成复杂功能。
来源地址:https://blog.csdn.net/yzh2776680982/article/details/126728008