小编给大家分享一下Java中Scanner和hasNextXXX()怎么用,相信大部分人都还不怎么了解,因此分享这篇文章给大家参考一下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后大有收获,下面让我们一起去了解一下吧!
输入输出
输出
基本语法
System.out.println(msg); //输出一个字符串,自带换行System.out.print(msg); //输出一个字符串,不带换行System.out.printf(msg); //格式化输出,和C语言相同例如:
public class SannerDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("hello world!"); System.out.print("hello world!"); String str = "hello world"; System.out.printf("%s\n",str); }}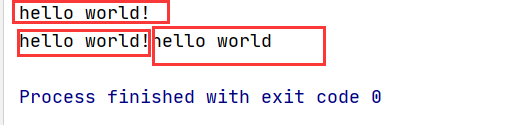
快捷键推荐:在这里,如果使用的是 IDEA的话,可以输入sout然后回车,会自动输出System.out.println();
输入
使用Scanner读取
首先需要导入==import java.util.Scanner;==的包,然后Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);,这段代码的主要作用是,从键盘中输入中读取数据。
然后读取数据:
next()、nextInt()和nextLIne()的区别;
import java.util.Scanner;public class SannerDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int i = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println(i); //读取int型的数据 //读取一行数据 String s1 = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println(s1); //读取字符串 String s2 = sc.next(); System.out.println(s2); }nextInt():
int i = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println(i); //读取int型的数据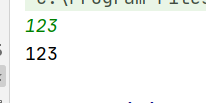

可以读取数字,但是遇到空格,只能读取空格前的数字。
next():
// //读取字符串 String s2 = sc.next(); System.out.println(s2);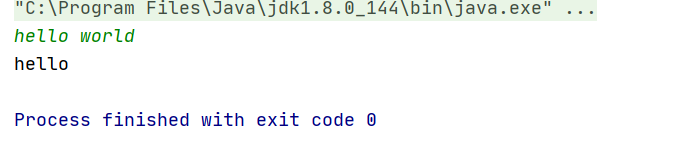
可以读取字符串,但是遇到空格,只能读取空格前的数字。
nextLine():
//读取一行数据 String s1 = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println(s1);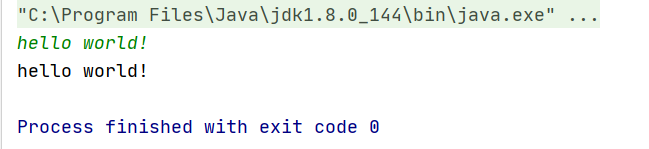
可以读取字符串,并读取这一行 ,但是遇到回车结束。
注意:
next()和nextLine()不可以同时使用:
例如:
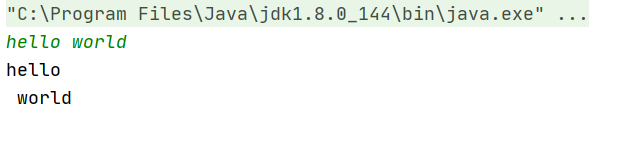
//读取字符串 String s2 = sc.next(); System.out.println(s2); //读取一行数据 String s1 = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println(s1);
这样只会输出一行,这是因为nextLine()读取了回车,然后结束。
next()遇到空客会结束。
使用Scanner循环读取N个数字/字符串
hasNextInt()的使用
import java.util.Scanner;public class SannerDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in); while (sc.hasNextInt()){ int i = sc.nextInt();//输入数字i System.out.println(i);//打印数字i } }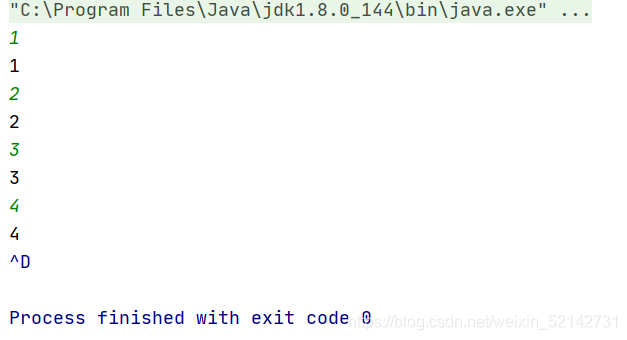
当程序开始之后,会一直循环输入并打印一个数字,知道Ctrl+d结束程序
在这里sc.hasNextInt()的结果是一个boolean的类型,当结果为false是结束。
注意:
Ctrl+d用来结束循环输入多个数据
同理:
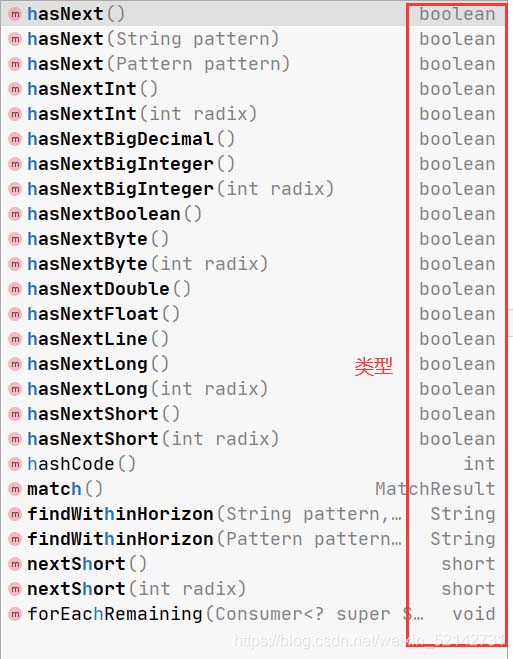
这些方法都可以用于循环数据输入。
关于Scanner中nextxxx()须注意的一点
public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO code application logic here Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); //需要注意的是,如果在通过nextInt()读取了整数后,再接着读取字符串,读出来的是回车换行:"\r\n",因为nextInt仅仅读取数字信息,而不会读走回车换行"\r\n". //所以,如果在业务上需要读取了整数后,接着读取字符串,那么就应该连续执行两次nextLine(),第一次是取走整数,第二次才是读取真正的字符串 int i = s.nextInt(); System.out.println("读取的整数是"+ i); String rn = s.nextLine();//读取到的是空格 String a = s.nextLine();//读取到的是字符串 System.out.println("读取的字符串是:"+a); }以上是“Java中Scanner和hasNextXXX()怎么用”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的内容对大家有所帮助,如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注编程网行业资讯频道!











