这篇文章主要介绍如何使用Spring Expression Language,文中介绍的非常详细,具有一定的参考价值,感兴趣的小伙伴们一定要看完!
Spring Expression Language (SpEL)
是强大的表达式语言,支持查询、操作运行时对象图,以及解析逻辑、算术表达式。SpEL可以独立使用,无论你是否使用Spring框架。
1.环境准备
引入依赖:
compile group: 'org.springframework', name: 'spring-expression', version: '5.2.4.RELEASE'
读者可以选择最新版本或合适的版本。当然也可以下载相应jar文件。在调用下面的函数之前,按如下方式初始化一个类级属性SpelExpression解析器:
import org.springframework.expression.Expression;import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;public class ElMain { private ExpressionParser parser; ElMain(){ parser = new SpelExpressionParser(); } public static void main(String[] args) { ElMain elHelper = new ElMain(); elHelper.evaluateLiteralExpresssions(); } private static void print(Object message){ System.out.println(message); }2.SpEL示例应用
2.1. 解析直接文本
private void evaluateLiteralExpresssions() { Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("'Hello World'"); String message = (String) exp.getValue(); print(message); exp = parser.parseExpression("6"); Integer value = exp.getValue(Integer.class); print(value*2); }这里直接解决字符串及数字文本。
2.2. 直接文本上调用方法
private void methodInvocationOnLiterals() { Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("'Hello World'.concat('!')"); String message = (String) exp.getValue(); println(message); exp = parser.parseExpression("'Hello World'.length()"); Integer size = exp.getValue(Integer.class); println(size); exp = parser.parseExpression("'Hello World'.split(' ')[0]"); message = (String)exp.getValue(); println(message); }示例展示了在字符串上直接调用Java String类的public方法。
2.3.访问对象属性和方法
private void accessingObjectProperties() { User user = new User("John", "Doe", true, "john.doe@acme.com",30); Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("firstName"); println((String)exp.getValue(user)); exp = parser.parseExpression("isAdmin()==false"); boolean isAdmin = exp.getValue(user, Boolean.class); println(isAdmin); exp = parser.parseExpression("email.split('@')[0]"); String emailId = exp.getValue(user, String.class); println(emailId); exp = parser.parseExpression("age"); Integer age = exp.getValue(user, Integer.class); println(age); }表达式可以直接使用对象的属性与方法。我们看到方法与属性使用一样,只是多了调用括号。
2.4.执行各种操作(比较、逻辑、算术)
SpEl支持下面几种操作:
关系比较操作:==, !=, <, <=, >, >=
逻辑操作: and, or, not
算术操作: +, -, /, *, %, ^
private void operators() { User user = new User("John", "Doe", true,"john.doe@acme.com", 30); Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("age > 18"); println(exp.getValue(user,Boolean.class)); exp = parser.parseExpression("age < 18 and isAdmin()"); println(exp.getValue(user,Boolean.class)); }2.5.使用多个对象和变量
表达式不仅需要引用对象,而且可能需要引用多个不同类型的对象。我们可以把所有使用的对象都加入至上下文中。使用键值对的方式加入并引用。
private void variables() { User user = new User("John", "Doe", true, "john.doe@acme.com",30); Application app = new Application("Facebook", false); StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(); context.setVariable("user", user); context.setVariable("app", app); Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("#user.isAdmin() and #app.isActive()"); Boolean result = exp.getValue(context,Boolean.class); println(result); }2.6.调用自定义函数
SpEl也可以调用自定义的函数,用户可以扩展业务逻辑。下面首先定义一个函数:
public class StringHelper { public static boolean isValid(String url){ return true; }}下面在SpEl中调用isValid方法:
private void customFunctions() { try { StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(); context.registerFunction("isURLValid", StringHelper.class.getDeclaredMethod("isValid", new Class[] { String.class })); String expression = "#isURLValid('http://google.com')"; Boolean isValid = parser.parseExpression(expression).getValue(context, Boolean.class); println(isValid); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }3.小结
通过示例介绍了SpEl中多种应用场景。读者可以利用这些功能实现更加灵活的功能应用。
Spring表达式语言SpEL
Spring 表达式语言(简称SpEL):是一个支持运行时查询和操作对象图的强大的表达式语言。
语法类似于 EL:SpEL 使用 #{…} 作为定界符,所有在大框号中的字符都将被认为是 SpEL
SpEL 为 bean 的属性进行动态赋值提供了便利.
通过 SpEL 可以实现:
通过 bean 的 id 对 bean 进行引用
调用方法以及引用对象中的属性
计算表达式的值
正则表达式的匹配
SpEL:字面量
字面量的表示:
整数:<property name="count" value="#{5}"/>小数:<property name="frequency" value="#{89.7}"/>科学计数法:<property name="capacity" value="#{1e4}"/>String可以使用单引号或者双引号作为字符串的定界符号:<property name=“name” value="#{'Chuck'}"/> 或<property name='name' value='#{"Chuck"}'/>Boolean:<property name="enabled" value="#{false}"/>如果仅仅是表示字面量,其实是没有必要使用Spring EL表达式的,这里仅仅演示一下而已,日常的开发中很少使用。
SpEL:引用 Bean、属性和方法
引用其他对象
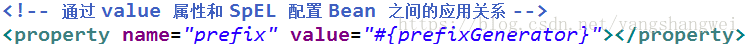
但是我们更常用ref 来实现其他对象的引用
引用其他对象的属性

调用其他方法,还可以链式操作


调用静态方法或静态属性
通过 T() 调用一个类的静态方法,它将返回一个 Class Object,然后再调用相应的方法或属性:
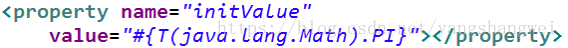
SpEL支持的运算符号
算数运算符:+, -, *, /, %, ^
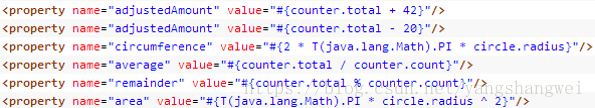
加号还可以用作字符串连接
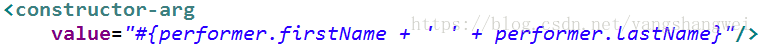
比较运算符: <, >, ==, <=, >=, lt, gt, eq, le, ge
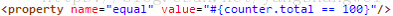

逻辑运算符号: and, or, not, |

if-else 运算符:?: (ternary), ?: (Elvis)
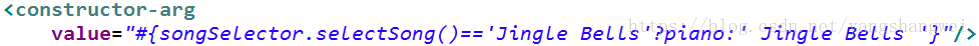
if-else 的变体

正则表达式:matches

示例-基于xml的方式
package com.xgj.spel;public class Address { private String city; private String street; public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public String getStreet() { return street; } public void setStreet(String street) { this.street = street; } @Override public String toString() { return "Address [city=" + city + ", street=" + street + ", getClass()=" + getClass() + ", hashCode()=" + hashCode() + ", toString()=" + super.toString() + "]"; }}package com.xgj.spel;public class Car { private String brand; private double price; // 调用静态方法或静态属性:通过 T() 调用一个类的静态方法,它将返回一个 Class Object,然后再调用相应的方法或属性 private long weight; public long getWeight() { return weight; } public void setWeight(long weight) { this.weight = weight; } public String getBrand() { return brand; } public void setBrand(String brand) { this.brand = brand; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return "Car [brand=" + brand + ", price=" + price + ", weight=" + weight + "]"; }}package com.xgj.spel;public class Boss { private String name; private Car car; // 通过 Spring El 引用 Address的city private String city; // 通过 Car的price属性,确定info ,如果car.price>=500000 ,info 为CEO,否则为 Staff private String info; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Car getCar() { return car; } public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public String getInfo() { return info; } public void setInfo(String info) { this.info = info; } @Override public String toString() { return "Boss [name=" + name + ", car=" + car + ", city=" + city + ", info=" + info + "]"; }}配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="car" class="com.xgj.spel.Car" p:brand="Bench" p:price="700000" p:weight="#{T(java.lang.Math).PI * 4567}" /> <!-- 通过Spring El表达式为属性赋值一个字面值 , 当然了,如果是字面值就没有必要使用Spring El表达式了,这里仅仅是演示该用法 --> <bean id="address" class="com.xgj.spel.Address" p:city="#{'NanJing'}" p:street="RuanJianDaDao" /> <bean id="boss" class="com.xgj.spel.Boss" p:name="Artisan" p:city="#{address.city}" p:car-ref="car" p:info="#{car.price > 500000 ? 'CEO' : 'staff'}" /></beans>测试类:
package com.xgj.spel;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class SpelTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String configLocation = "com/xgj/spel/beans_spel.xml"; ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(configLocation); Car car = (Car) ctx.getBean("car"); System.out.println(car); Boss boss = (Boss) ctx.getBean("boss"); System.out.println(boss); }}结果:
2018-04-07 21:21:30,804 INFO [main] (AbstractApplicationContext.java:583) - Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@4af6178d: startup date [Sat Apr 07 21:21:30 BOT 2018]; root of context hierarchy
2018-04-07 21:21:30,907 INFO [main] (XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:317) - Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource [com/xgj/spel/beans_spel.xml]
Car [brand=Bench, price=700000.0, weight=14347]
Boss [name=Artisan, car=Car [brand=Bench, price=700000.0, weight=14347], city=NanJing, info=CEO]
示例-基于注解的方式
我们通过一个数据库的例子来演示。虽然可以通过Spring El 表达式从配置文件中加载一个参数值,比如
@Value("#{properties['jdbc.driverClassName']}")是不是容易出错…. Spring提供了更好的方式 context:property-placeholder。
package com.xgj.spel.annotation;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Componentpublic class MyDataSource { private String driverClass; private String url; private String username; private String password; public String getDriverClass() { return driverClass; } @Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}") public void setDriverClass(String driverClass) { this.driverClass = driverClass; } public String getUrl() { return url; } @Value("${jdbc.url}") public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; } public String getUsername() { return username; } // @Value("$(jdbc.username)") @Value("${jdbc.username}") public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } @Value("${jdbc.password}") public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } @Override public String toString() { return "MyDataSource [driverClass=" + driverClass + ", url=" + url + ", username=" + username + ", password=" + password + "]"; }}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd"> <!-- 扫描的基包 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.xgj.spel.annotation"/> <!-- 加载外部properties文件 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:mysql/db_mysql.properties"/> </beans>db_mysql.properties
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driverjdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/artisanjdbc.username=artisanjdbc.password=artisanpackage com.xgj.spel.annotation;import org.junit.Test;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class TestCase { @Test public void test() { String configurationLocation = "com/xgj/spel/annotation/beans_anno.xml"; ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(configurationLocation); MyDataSource myDataSource = (MyDataSource) ctx.getBean("myDataSource"); System.out.println(myDataSource); System.out.println("driverClassName:" + myDataSource.getDriverClass()); System.out.println("url:" + myDataSource.getUrl()); System.out.println("username:" + myDataSource.getUsername()); System.out.println("password:" + myDataSource.getPassword()); }}运行结果
2018-04-07 23:37:11,409 INFO [main] (AbstractApplicationContext.java:583) - Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@761df304: startup date [Sat Apr 07 23:37:11 BOT 2018]; root of context hierarchy
2018-04-07 23:37:11,552 INFO [main] (XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:317) - Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource [com/xgj/spel/annotation/beans_anno.xml]
MyDataSource [driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver, url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/artisan, username=artisan, password=artisan]
driverClassName:com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/artisan
username:artisan
password:artisan
以上是“如何使用Spring Expression Language”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!希望分享的内容对大家有帮助,更多相关知识,欢迎关注编程网行业资讯频道!




