本篇内容主要讲解“Go语言中Get/Post请求测试实例分析”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“Go语言中Get/Post请求测试实例分析”吧!
gin安装
先将gin安装一下,安装依赖go语言还是比较方便的。
在安装之前先配置一下goproxy。
命令如下:
go env -w GO111MODULE=ongo env -w GOPROXY=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/goproxy/ //阿里代理go env -w GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn //七牛云代理安装一下gin,命令如下:
go get github.com/gin-gonic/ginGet请求测试
实现一个web服务还是比较简单的,创建一个router,绑定路由规则即可。先测试几个Get请求。
样例代码如下:
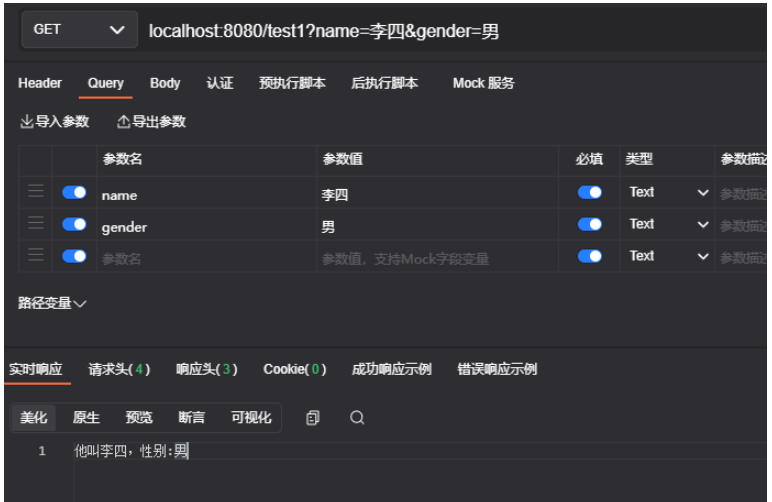
package main import ("github.com/gin-gonic/gin""net/http") func main() {router := gin.Default()router.GET("/", func(context *gin.Context) {context.String(http.StatusOK, "hello world")}) router.GET("/test/:name", func(context *gin.Context) {name := context.Param("name")context.String(http.StatusOK, "check param %s", name)}) router.GET("/test1", func(context *gin.Context) {name := context.DefaultQuery("name", "张三")gender := context.Query("gender")context.String(http.StatusOK, "他叫%s,性别:%s", name, gender)}) router.Run(":8080")}执行结果
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Running in "debug" mode. Switch to "release" mode in production.
- using env: export GIN_MODE=release
- using code: gin.SetMode(gin.ReleaseMode)
[GIN-debug] GET / --> main.main.func1 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] GET /test/:name --> main.main.func2 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] GET /test1 --> main.main.func3 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] You trusted all proxies, this is NOT safe. We recommend you to set a value.
Please check https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/gin-gonic/gin#readme-don-t-trust-all-proxies for details.
[GIN-debug] Listening and serving HTTP on :8080
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] You trusted all proxies, this is NOT safe. We recommend yo
u to set a value.
Please check https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/gin-gonic/gin#readme-don-t-trust-all-
proxies for details.
[GIN-debug] Listening and serving HTTP on :8080
测试一下,这里我是用的接口测试工具为ApiPost


注意
在使用context.DefaultQuery方法的时候,可以提供一个默认值。
除了可以使用":"来获取路径参数外,可以使用"*",可以匹配更多规则。我个人感觉我不会这么用get请求参数。
Post请求测试
Post请求是在项目中使用的比较多的,而且不管是使用form获取参数还是body,都十分常见。
同时返回的数据也不可能使用一行字符串,实际项目中还是使用json格式居多。
所以下面我使用form参数和body参数实现了一下post测试接口。
完成代码如下
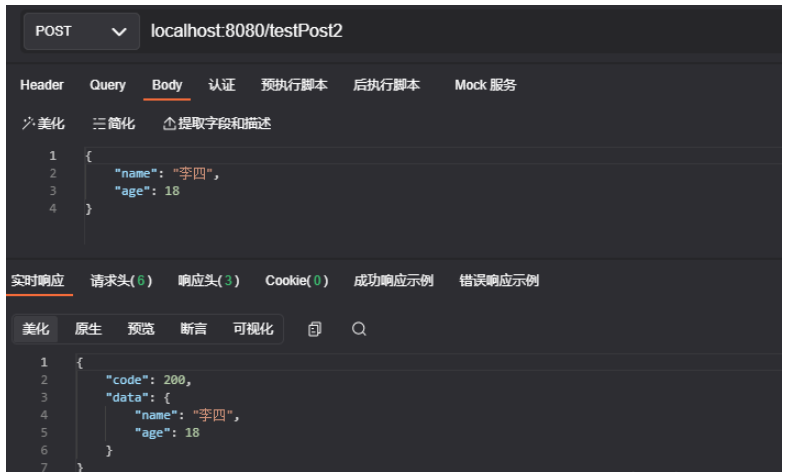
package main import ("encoding/json""fmt""github.com/gin-gonic/gin""io/ioutil""net/http") type Result struct {Name string `json:"name"`Age int `json:"age"`} //反序列化为结构体对象func parseJson(a string) Result {fmt.Printf("原始字符串: %s\n", a)var c Resultif err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(a), &c); err != nil {fmt.Println("Error =", err)return c}return c} func main() {router := gin.Default()router.GET("/", func(context *gin.Context) {context.String(http.StatusOK, "hello world")}) router.GET("/test/:name", func(context *gin.Context) {name := context.Param("name")context.String(http.StatusOK, "check param %s", name)}) router.GET("/test1", func(context *gin.Context) {name := context.DefaultQuery("name", "张三")gender := context.Query("gender")context.String(http.StatusOK, "他叫%s,性别:%s", name, gender)}) router.POST("/testPost", func(context *gin.Context) {name := context.PostForm("name")nick := context.DefaultPostForm("nick", "leo")context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"status": gin.H{"code": http.StatusOK,"success": true,},"name": name,"nick": nick,})}) router.POST("/testPost2", func(context *gin.Context) {data, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(context.Request.Body)fmt.Println(string(data))context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"code": http.StatusOK,"data": parseJson(string(data)),})}) router.Run(":8080")}测试一下testPost和testPost2接口

注意
使用context.DefaultPostForm方法可以提供一个默认值。
可以使用gin.H方法构造json结构返回。
将获得打参数反序列化为结构体,这部分的代码使用到之前讲json解析的笔记。
到此,相信大家对“Go语言中Get/Post请求测试实例分析”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是编程网网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!




