本篇内容主要讲解“Android怎么使用socket进行二进制流数据传输”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“Android怎么使用socket进行二进制流数据传输”吧!
简单的自定义协议
我们自定义一个简单的通信协议,协议一共传输两种信息,第一种是文字,第二种是二进制流(其实文字也可以用二进制流表示),传输过程如下图所示。
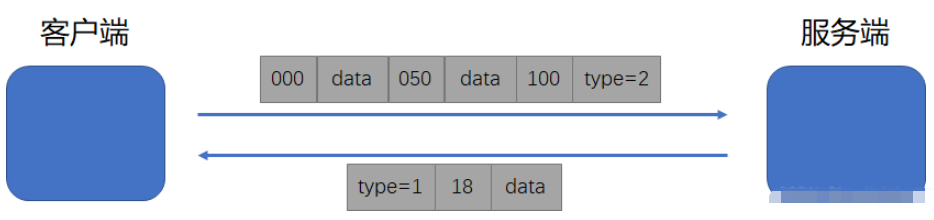
我们定义的简单通信协议规则如下
首先发送一个字节的信息(就是图中的type),表示一段消息的开始,同时也表明了后面二进制数据的类型(文字信息还是二进制流数据)
每一个chunk都由三个字节的长度信息和相应的二进制流信息组成,接收方在接收到三个字节的长度信息后,继续使用相应大小的缓冲区接收后面的流数据
当接收到三个字节的000的时候表示数据接收完成,接收方将二进制流数据拼接起来即可
我们规定一个最大的分段长度,一旦发送的数据超过这个分段长度就需要进行分段发送。
发送的代码示例如下
// 发送文件 public void sendFile(int size) { new Thread(()->{ try { // 表示发送文件 outputStream.write("2".getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } for(int i=0; i<size/SocketUtil.MAX_CHUNK+1; i++) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); if (i!=size / SocketUtil.MAX_CHUNK) { for (int j = 0; j < SocketUtil.MAX_CHUNK; j++) { sb.append('a'); } } else if(i==size/SocketUtil.MAX_CHUNK && size%SocketUtil.MAX_CHUNK==0) { break; } else { for (int j = 0; j < size % SocketUtil.MAX_CHUNK; j++) { sb.append('a'); } } try { SocketUtil.sendInfo("[客户端]发送一个数据包,大小" + sb.toString().getBytes().length + "B"); // 发送chunk的长度 outputStream.write(SocketUtil.intToStr(sb.toString().getBytes().length).getBytes()); // 发送chunk块 outputStream.write(sb.toString().getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // 最后发送000表示结束 try { outputStream.write("000".getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); }接收二进制流的代码示例如下
// 读取二进制信息 public static byte[] readBytes(InputStream inputStream, String log) { byte[] len = new byte[3]; byte[] allbytes = new byte[10000]; int idx = 0; try { inputStream.read(len); // 然后再根据读取的长度信息读取二进制流 // 只要不是最后一个二进制流就继续读取 while (SocketUtil.parseLen(len) != 0) { byte[] temp = new byte[SocketUtil.parseLen(len)]; inputStream.read(temp); idx = SocketUtil.appendBytes(allbytes, temp, idx); String info = "[" + log + "]接收一个数据包,大小" + SocketUtil.parseLen(len) + "B"; SocketUtil.sendInfo(info); inputStream.read(len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return SocketUtil.getNewArr(allbytes, idx); }其实我理解的所谓的通信协议,就是发送方和接收方都遵守的某种规则,按照这种规则发送和接收数据就可以保证数据的完整性。
完整的代码
这段代码只有四个java文件,非常简单,只是一个极简的通信协议模型。
首先来看一下界面定义
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <EditText android:id="@+id/text_file_size" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="请输入待发送文件大小"/> <Button android:id="@+id/button_send" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="发送文件"/> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="消息栏:"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/text_info" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"/></LinearLayout>然后是MainActivity
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private EditText text_file_size; private Button button_send; private TextView text_info; private BroadcastReceiver broadcastReceiver; private SocketClient socketClient; private SocketServer socketServer; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); SocketUtil.context = MainActivity.this; // 初始化控件 initView(); // 注册广播接收器 register(); socketServer = new SocketServer(); socketClient = new SocketClient(); } private void initView() { text_file_size = findViewById(R.id.text_file_size); button_send = findViewById(R.id.button_send); button_send.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Integer size = Integer.parseInt(text_file_size.getText().toString()); socketClient.sendFile(size); } }); text_info = findViewById(R.id.text_info); text_info.setMovementMethod(new ScrollingMovementMethod()); } private void register() { broadcastReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() { @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { String info = intent.getStringExtra("info"); text_info.append(info + "\n"); } }; IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter("main.info"); registerReceiver(broadcastReceiver, filter); }}我们将需要重复用到的一些代码都放到工具类中
public class SocketUtil { public static Context context; // 一次最多传输多少字节 public static int MAX_CHUNK = 100; public static void sendInfo(String info) { Intent intent = new Intent("main.info"); intent.putExtra("info", info); context.sendBroadcast(intent); } // 读取二进制信息 public static byte[] readBytes(InputStream inputStream, String log) { byte[] len = new byte[3]; byte[] allbytes = new byte[10000]; int idx = 0; try { inputStream.read(len); // 然后再根据读取的长度信息读取二进制流 // 只要不是最后一个二进制流就继续读取 while (SocketUtil.parseLen(len) != 0) { byte[] temp = new byte[SocketUtil.parseLen(len)]; inputStream.read(temp); idx = SocketUtil.appendBytes(allbytes, temp, idx); String info = "[" + log + "]接收一个数据包,大小" + SocketUtil.parseLen(len) + "B"; SocketUtil.sendInfo(info); inputStream.read(len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return SocketUtil.getNewArr(allbytes, idx); } // 将int转成String public static String intToStr(int len) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); if(len < 100) { sb.append("0"); } else if (len < 10) { sb.append("00"); } sb.append(Integer.toString(len)); return sb.toString(); } public static int parseLen(byte[] len) { return Integer.parseInt(new String(len, 0, len.length)); } public static int appendBytes(byte[] arr1, byte[] arr2, int st) { for(int i=st; i<arr2.length; i++) { arr1[i] = arr2[i-st]; } return arr2.length+st; } public static byte[] getNewArr(byte[] arr, int idx) { byte[] newarr = new byte[idx]; for(int i=0; i<idx; i++) { newarr[i] = arr[i]; } return newarr; }}最后是定义我们的客户端和服务端
public class SocketClient { private final String HOST = "localhost"; private final int PORT = 50055; private Socket socket = null; private OutputStream outputStream = null; private InputStream inputStream = null; public SocketClient() { conn(); while(socket == null) {} SocketUtil.sendInfo("服务端连接成功..."); try { outputStream = socket.getOutputStream(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // 连接服务端 private void conn() { new Thread(()->{ try { socket = new Socket(HOST, PORT); inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); while(true) { // 接收服务端消息0 byte[] type = new byte[1]; inputStream.read(type); if (new String(type, 0, 1).equals("1")) { byte[] infobytes = SocketUtil.readBytes(inputStream, "客户端"); String info = "[客户端]接收消息:" + new String(infobytes, 0, infobytes.length); SocketUtil.sendInfo(info); SocketUtil.sendInfo("===================================="); } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); } // 发送文件 public void sendFile(int size) { new Thread(()->{ try { // 表示发送文件 outputStream.write("2".getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } for(int i=0; i<size/SocketUtil.MAX_CHUNK+1; i++) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); if (i!=size / SocketUtil.MAX_CHUNK) { for (int j = 0; j < SocketUtil.MAX_CHUNK; j++) { sb.append('a'); } } else if(i==size/SocketUtil.MAX_CHUNK && size%SocketUtil.MAX_CHUNK==0) { break; } else { for (int j = 0; j < size % SocketUtil.MAX_CHUNK; j++) { sb.append('a'); } } try { SocketUtil.sendInfo("[客户端]发送一个数据包,大小" + sb.toString().getBytes().length + "B"); // 发送chunk的长度 outputStream.write(SocketUtil.intToStr(sb.toString().getBytes().length).getBytes()); // 发送chunk块 outputStream.write(sb.toString().getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // 最后发送000表示结束 try { outputStream.write("000".getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); }}public class SocketServer { private final int PORT = 50055; private ServerSocket serverSocket = null; public SocketServer() { // 启动服务端监听 start(); while(serverSocket == null) {} SocketUtil.sendInfo("服务端启动..."); } // 启动服务端监听程序 private void start() { new Thread(()->{ try { serverSocket = new ServerSocket(PORT); Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream(); while(true) { byte[] type = new byte[1]; inputStream.read(type); String typeinfo = new String(type, 0, 1); if(typeinfo.equals("2")) { byte[] file = SocketUtil.readBytes(inputStream, "服务端"); String filetxt = new String(file, 0, file.length); String info = "[服务端]接收完文件,大小" + file.length + "B" + "\n"; info = info + "[服务端]具体内容如下:" + "\n" + filetxt; SocketUtil.sendInfo(info); // 给客户端发送一个响应信息表示接收成功 String typetxt = "1"; outputStream.write(typetxt.getBytes()); String successinfo = "文件接收成功"; String lentxt = SocketUtil.intToStr(successinfo.getBytes().length); outputStream.write(lentxt.getBytes()); outputStream.write(successinfo.getBytes()); outputStream.write("000".getBytes()); } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); }}上述代码中,服务端只负责接收二进制流,客户端只负责发送二进流,并且服务端在接收完二进制流数据后,会给服务端返回一个表示接收成功的文字信息。

到此,相信大家对“Android怎么使用socket进行二进制流数据传输”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是编程网网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!





