这篇文章主要为大家展示了“Java如何实现经典游戏复杂迷宫”,内容简而易懂,条理清晰,希望能够帮助大家解决疑惑,下面让小编带领大家一起研究并学习一下“Java如何实现经典游戏复杂迷宫”这篇文章吧。
前言
人类建造迷宫已有5000年的历史。在世界的不同文化发展时期,这些奇特的建筑物始终吸引人们沿着弯弯曲曲、困难重重的小路吃力地行走,寻找真相。迷宫类小游戏应运而生。在游戏中,迷宫被表现为冒险舞台里,藏有各式各样奇妙与谜题或宝藏的危险区域。型态有洞窟、人工建筑物、怪物巢穴、密林或山路等。迷宫内有恶徒或凶猛的生物(真实存在或想像物体都有)徘徊,其中可能会有陷阱、不明设施、遗迹等。
《复杂迷宫》游戏是用java语言实现,采用了swing技术进行了界面化处理,设计思路用了面向对象思想。
主要需求
方向键控制移动,角色走出迷宫,游戏胜利。增加游戏难度和增加随机地图。
主要设计
构建游戏地图面板
设定迷宫地图,包含可走的通道,不可走的墙体,还有出口位置
键盘的上下左右按键,来控制角色的移动
角色移动的算法,通道可走,遇到墙体不可走
走到终点,有成功通关的提示。
增加游戏的难度选择,难度1,难度2和难度3
每次生成的地图是随机的
地图大小可选择,迷宫的长在10-45之间,宽在10-90之间
增加撞墙的音乐效果
功能截图
游戏开始页面
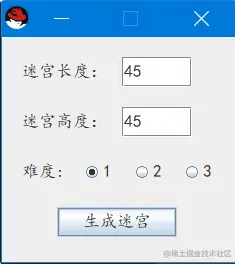
生成难度1,10*10的迷宫地图
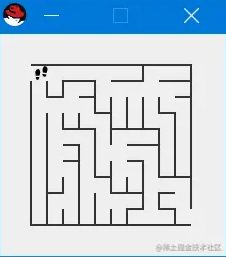
随机地图:生成难度1,10*10的迷宫地图
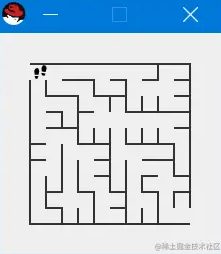
生成难度2,30*30的迷宫地图
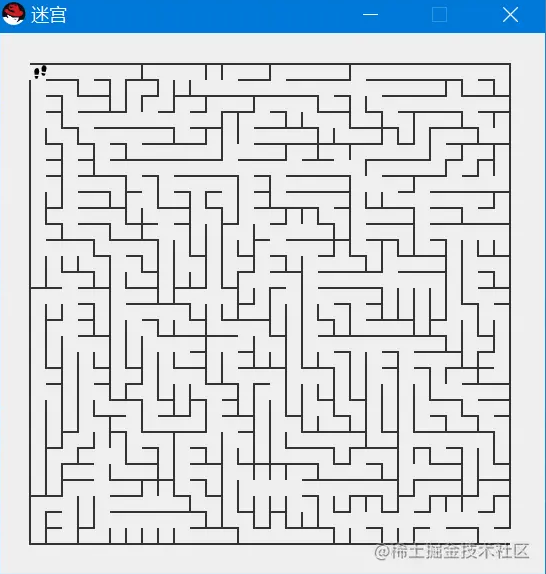
生成难度3,90*45的迷宫地图
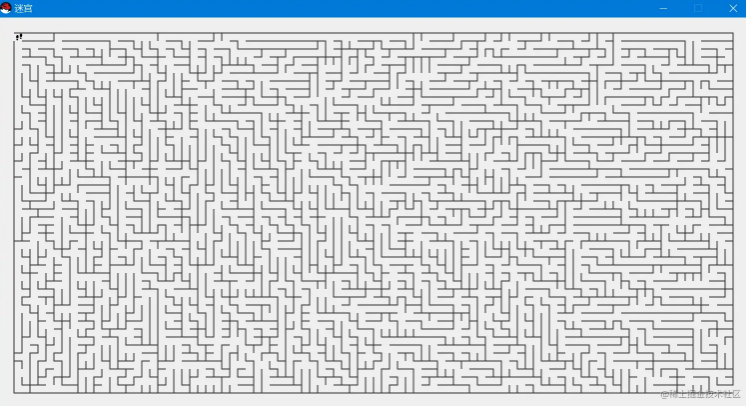
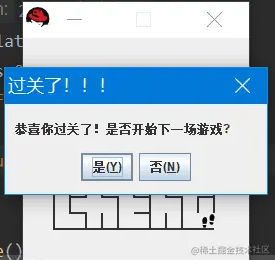
成功过关-效果
代码实现
窗口布局
public class StartView extends JFrame { public StartView() { this.setTitle("复杂迷宫"); this.setSize(240, 265); this.setLocationRelativeTo(null); this.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE); this.setResizable(false); initialize(); this.setVisible(true); } private void initialize() { JPanel contentPane = new JPanel(); this.setContentPane(contentPane); contentPane.setLayout(null); JLabel widthLabel = new JLabel("迷宫长度:"); JLabel heightLabel = new JLabel("迷宫高度:"); JLabel levelLabel = new JLabel("难度:"); JTextField widthText = new JTextField(); JTextField heightText = new JTextField(); JRadioButton level1 = new JRadioButton("1"); JRadioButton level2 = new JRadioButton("2"); JRadioButton level3 = new JRadioButton("3"); ButtonGroup levelGroup = new ButtonGroup(); levelGroup.add(level1); levelGroup.add(level2); levelGroup.add(level3); JButton run = new JButton("生成迷宫"); // 设定标签位置 widthLabel.setBounds(20, 20, 100, 30); heightLabel.setBounds(20, 70, 110, 30); widthText.setBounds(120, 20, 70, 30); heightText.setBounds(120, 70, 70, 30); levelLabel.setBounds(20, 120, 60, 30); level1.setBounds(80, 120, 50, 30); level2.setBounds(130, 120, 50, 30); level3.setBounds(180, 120, 50, 30); run.setBounds(55, 170, 120, 30); // 限制输入框只接收数字 widthText.setDocument(new NumberTextField()); heightText.setDocument(new NumberTextField()); // 改变字体 Font font = new Font("楷体", Font.PLAIN, 17); widthLabel.setFont(font); heightLabel.setFont(font); widthText.setFont(font); heightText.setFont(font); levelLabel.setFont(font); level1.setFont(font); level2.setFont(font); level3.setFont(font); run.setFont(font); // 取消按钮选中边框 level1.setFocusPainted(false); level2.setFocusPainted(false); level3.setFocusPainted(false); // 默认选择难度3 level3.setSelected(true); contentPane.add(widthLabel); contentPane.add(heightLabel); contentPane.add(widthText); contentPane.add(heightText); contentPane.add(levelLabel); contentPane.add(level1); contentPane.add(level2); contentPane.add(level3); contentPane.add(run); // 生成迷宫监听器 run.addActionListener(e -> { // 建议宽在10-90,长在10-45之间 if (widthText.getText().equals("")) { JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "长度不能为空!", "提示", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE); } else if (heightText.getText().equals("")) { JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "高度不能为空!", "提示", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE); } else { int width = Integer.parseInt(widthText.getText()); int height = Integer.parseInt(heightText.getText()); if (width >= 10 && width <= 90 && height >= 10 && height <= 45) { int level = level1.isSelected() ? 1 : level2.isSelected() ? 2 : 3; MazeModel maze = new MazeModel(width, height, level); this.dispose(); maze.draw(); } else { JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "迷宫的长必须在10-45之间,宽必须在10-90之间,请检查输入是否有误!", "错误输入", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE); } } }); // 添加回车键入监听器 KeyAdapter enterAdapter = new KeyAdapter() { @Override public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) { if (e.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.VK_ENTER) { run.doClick(); // 回车即生成迷宫 } } }; widthText.addKeyListener(enterAdapter); heightText.addKeyListener(enterAdapter); } public static void main(String[] args) { new StartView(); }}迷宫的数学模型
public class MazeModel { private int width; private int height; private ArrayList<MazePoint> mazePoints; public MazeModel(int width, int height, int level) { super(); this.width = width; this.height = height; switch (level) { case 1 : this.mazePoints = recursiveDivision(); case 2 : this.mazePoints = recursiveBacktracker(); case 3 : this.mazePoints = prim(); } } private ArrayList<MazePoint> recursiveBacktracker() { ArrayList<MazePoint> maze = new ArrayList<>(); // 初始化所以单元格都被强包围 for (int h = 0; h < height; h++) { for (int w = 0; w < width; w++) { MazePoint point = new MazePoint(w, h, true); maze.add(point); } } // 建立一个存放操作单元格的栈 Stack<MazePoint> stack = new Stack<>(); // 选择(0,0)点作为起始点,开始打通迷宫 stack.push(maze.get(0)); maze.get(0).visited = true; Random random = new Random(); int x; // 操作单元格的横坐标 int y; // 操作单元格的纵坐标 int direction; // 方向 while (!stack.empty()) { // 选择栈顶元素作为当前操作数 MazePoint operatingPoint = stack.peek(); x = operatingPoint.getX(); y = operatingPoint.getY(); direction = random.nextInt(4); MazePoint adjacency; switch (direction) { case 0: // 左边 if ((x - 1) >= 0) { // 判断左边是否为边缘 adjacency = maze.get(x - 1 + y * width); // 判断左边单元格是否被访问过 if (!adjacency.visited) { operatingPoint.setLeft(0); // 打通操作单元格的左墙,和左边单元格的右墙 adjacency.setRight(0); stack.push(adjacency); // 将左墙入栈,作为下次循环的操作单元格 adjacency.visited = true; // 将左边的单元格设置为访问过了 x--; // 改变操作单元格的坐标,方便后面判断当前单元格四周是否都访问过 } } break; case 1: // 右边 // 注释参照case0 if ((x + 1) < width) { adjacency = maze.get(x + 1 + y * width); if (!adjacency.visited) { operatingPoint.setRight(0); adjacency.setLeft(0); stack.push(adjacency); adjacency.visited = true; x++; } } break; case 2: // 上边 // 注释参照case0 if ((y - 1) >= 0) { adjacency = maze.get(x + (y - 1) * width); if (!adjacency.visited) { operatingPoint.setUp(0); adjacency.setDown(0); stack.push(adjacency); adjacency.visited = true; y--; } } break; case 3: // 下边 // 注释参照case0 if ((y + 1) < height) { adjacency = maze.get(x + (y + 1) * width); if (!adjacency.visited) { operatingPoint.setDown(0); adjacency.setUp(0); stack.push(adjacency); adjacency.visited = true; y++; } } break; } // 若操作单元格四周都被访问过,将该单元格出栈。 if ((x - 1 < 0 || maze.get(x - 1 + y * width).visited) && (x + 1 >= width || maze.get(x + 1 + y * width).visited) && (y - 1 < 0 || maze.get(x + (y - 1) * width).visited) && (y + 1 >= height || maze.get(x + (y + 1) * width).visited)) { stack.pop(); } } maze.get(0).setLeft(0); // 左上角开墙作为入口 maze.get(width * height - 1).setRight(0); // 右下角开墙作为出口 return maze; } private void divide(ArrayList<MazePoint> maze, int left, int right, int top, int down) { if (right - left > 0 && top - down > 0) { // 在区域中心”十“字筑墙 for (int x = left, y = (top - down) / 2 + down; x <= right; x++) { maze.get(x + y * this.width).setDown(1); maze.get(x + (y + 1) * this.width).setUp(1); } for (int x = (right - left) / 2 + left, y = down; y <= top; y++) { maze.get(x + y * this.width).setRight(1); maze.get(x + 1 + y * this.width).setLeft(1); } // 在“十”字墙中选其中三个方向拆一面墙 Random random = new Random(); int direction = random.nextInt(4); int x = (right - left) / 2 + left; int y = (top - down) / 2 + down; int tempX; int tempY; if (direction != 0) { // 打通一面左边的墙 if (x - left > left) { tempX = random.nextInt(x - left + 1) + left; } else { tempX = left; } tempY = y; maze.get(tempX + tempY * this.width).setDown(0); maze.get(tempX + (tempY + 1) * this.width).setUp(0); } if (direction != 1) { // 打通一面右边的墙 if (right - (x + 1) > x + 1) { tempX = random.nextInt(right - (x + 1) + 1) + x + 1; } else { tempX = x + 1; } tempY = y; maze.get(tempX + tempY * this.width).setDown(0); maze.get(tempX + (tempY + 1) * this.width).setUp(0); } if (direction != 2) { // 打通一面上面的墙 tempX = x; if (y - down > down) { tempY = random.nextInt(y - down + 1) + down; } else { tempY = down; } maze.get(tempX + tempY * this.width).setRight(0); maze.get(tempX + 1 + tempY * this.width).setLeft(0); } if (direction != 3) { // 打通一面下面的墙 tempX = x; if (top - (y + 1) > y + 1) { tempY = random.nextInt(top - (y + 1) + 1) + y + 1; } else { tempY = y + 1; } maze.get(tempX + tempY * this.width).setRight(0); maze.get(tempX + 1 + tempY * this.width).setLeft(0); } maze.stream().limit(this.width).forEach(m -> m.setUp(1)); maze.stream().skip((this.height - 1) * this.width).forEach(m -> m.setDown(1)); maze.stream().filter(m -> m.getX() == 0).forEach(m -> m.setLeft(1)); maze.stream().filter(m -> m.getX() == width - 1).forEach(m -> m.setRight(1)); divide(maze, left, (right - left) / 2 + left, (top - down) / 2 + down, down); divide(maze, left, (right - left) / 2 + left, top, (top - down) / 2 + down + 1); divide(maze, (right - left) / 2 + left + 1, right, (top - down) / 2 + down, down); divide(maze, (right - left) / 2 + left + 1, right, top, (top - down) / 2 + down + 1); } } private ArrayList<MazePoint> recursiveDivision() { // 初始化迷宫的所有单元格 ArrayList<MazePoint> maze = new ArrayList<>(); for (int h = 0; h < height; h++) { for (int w = 0; w < width; w++) { MazePoint point = new MazePoint(w, h); maze.add(point); } } divide(maze, 0, width - 1, height - 1, 0); // 递归分割迷宫 maze.get(0).setLeft(0); // 左上角开墙作为入口 maze.get(width * height - 1).setRight(0); // 右下角开墙作为出口 return maze; } private ArrayList<MazePoint> prim() { ArrayList<MazePoint> mazePoints = new ArrayList<>(); PrimMaze primMaze = new PrimMaze(width * 2 + 1, height * 2 + 1); int[][] tempMaze = primMaze.getMaze(); for (int i = 0; i < tempMaze.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < tempMaze[i].length; j++) { if (i % 2 != 0 && j % 2 != 0) { MazePoint mazePoint = new MazePoint(i / 2, j / 2); if (tempMaze[i - 1][j] == 10) { mazePoint.setLeft(1); } if (tempMaze[i + 1][j] == 10) { mazePoint.setRight(1); } if (tempMaze[i][j - 1] == 11) { mazePoint.setUp(1); } if (tempMaze[i][j + 1] == 11) { mazePoint.setDown(1); } mazePoints.add(mazePoint); } } } mazePoints.get(0).setLeft(0); // 左上角开墙作为入口 mazePoints.get(width * height - 1).setRight(0); // 右下角开墙作为出口 return mazePoints; } public void draw() { new PlayView(mazePoints); }}普里姆算法
class PrimMaze { private int[][] maze; public int[][] getMaze() { return maze; } PrimMaze(int row, int column) { int row1 = row / 2; int column1 = column / 2; maze = new int[row1 * 2 + 1][column1 * 2 + 1]; for (int x = 0; x < row1 * 2 + 1; x++) //初始化迷宫 { for (int y = 0; y < column1 * 2 + 1; y++) { if (x == 0 || x == row1 * 2) { maze[x][y] = -1; } if (y == 0 || y == column1 * 2) { maze[x][y] = -1; } } } for (int x = 1; x < row1 * 2; x++) { for (int y = 1; y < column1 * 2; y++) { if (x % 2 == 1 || y % 2 == 1) { maze[x][y] = 0; } if (x % 2 == 0 || y % 2 == 0) { maze[x][y] = 1; } } } ArrayList<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>(); //记录已连通的"路"的坐标的集合 int[] coordinate = new int[2]; //记录未访问的点坐标 int x = 1, y = 1; //设置起点位置 coordinate[0] = coordinate[1] = 1; list.add(coordinate); //将起点加入已经连通的路集合 //x,y表示当前访问坐标 while (list.size() < row1 * column1) //当所有点都已访问完时结束 { boolean flag1; //标识坐标是否已经被访问 int[] record = {-1, -1, -1, -1}; //用于记录四周未被访问的方位,0代表上,1代表下,2代表左,3代表右 if (x - 2 > 0) //判断当前位置上方是否有路 { int[] a = new int[2]; a[0] = x - 2; a[1] = y; flag1 = judge(a, list); //判断上方是否已经被访问 if (flag1) { record[0] = 0; } } if (x + 2 < row1 * 2) //判断当前位置下方是否有路 { int[] a = new int[2]; a[0] = x + 2; a[1] = y; flag1 = judge(a, list); //判断下方是否已经被访问 if (flag1) { record[1] = 1; } } if (y - 2 > 0) //判断当前位置左方是否有路 { int[] a = new int[2]; a[0] = x; a[1] = y - 2; flag1 = judge(a, list); //判断左方是否已经被访问 if (flag1) { record[2] = 2; } } if (y + 2 < column1 * 2) //判断当前位置右方是否有路 { int[] a = new int[2]; a[0] = x; a[1] = y + 2; flag1 = judge(a, list); //判断右方是否已经被访问 if (flag1) { record[3] = 3; } } boolean flag2 = false; //flag2标识四周是否有未访问过的路 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) //判断当前位置的四个方位是否有未访问过的路 { if (record[i] == i) { flag2 = true; //如果有未访问过的路,跳出循环 break; } } int r = new Random().nextInt(4); while (record[r] == r) { r = new Random().nextInt(4); } while (record[r] != r && flag2) //当方位标识错误且当前位置四周有未访问过的点时继续随机获取一个新的方位标识,直到标识正确 { r = new Random().nextInt(4); //随机选取一个可以符合条件的墙并将其敲碎 if (record[r] == r) //当标识正确时,敲碎两点之间的墙 { if (r == 0) { //当上方有未访问过的点时,敲碎上方的墙 maze[x - 1][y] = 0; } if (r == 1) { //当下方有未访问过的点时,敲碎下方的墙 maze[x + 1][y] = 0; } if (r == 2) { //当左方有未访问过的点时,敲碎左方的墙 maze[x][y - 1] = 0; } if (r == 3) { //当右方有未访问过的点时,敲碎右方的墙 maze[x][y + 1] = 0; } } } //将与当前坐标之间的墙被敲碎的路的坐标从未被访问的集合中移出 if (r == 0 && flag2) //如果敲碎的是上方的墙,则将上方的路加入到已连通的路集合 { int[] b = new int[2]; b[0] = x - 2; b[1] = y; if (judge(b, list)) { list.add(b); } } if (r == 1 && flag2) //如果敲碎的是下方的墙,则将下方的路加入到已连通的路集合 { int[] b = new int[2]; b[0] = x + 2; b[1] = y; if (judge(b, list)) { list.add(b); } } if (r == 2 && flag2) //如果敲碎的是左方的墙,则将左方的路加入到已连通的路集合 { int[] b = new int[2]; b[0] = x; b[1] = y - 2; if (judge(b, list)) { list.add(b); } } if (r == 3 && flag2) //如果敲碎的是右方的墙,则将右方的路加入到已连通的路集合 { int[] b = new int[2]; b[0] = x; b[1] = y + 2; if (judge(b, list)) { list.add(b); } } int i = new Random().nextInt(list.size()); //随机选取一个被连通的路坐标 x = list.get(i)[0]; //获取路坐标 y = list.get(i)[1]; } for (int r = 0; r < maze.length; r++)//将方格墙转为线条墙,10表示横,11表示竖 { for (int c = 0; c < maze[r].length; c++) { if (r % 2 == 0 && c % 2 == 1) { if (maze[r][c] != 0) { maze[r][c] = 10; } } if (r % 2 == 1 && c % 2 == 0) { if (maze[r][c] != 0) { maze[r][c] = 11; } } } } } boolean judge(int[] coordinate, ArrayList<int[]> list) //判断路是否已经加入通路集合,已加入则返回false { boolean flag = true; for (int[] ints : list) { if (coordinate[0] == ints[0] && coordinate[1] == ints[1]) //若已访问点集合中含有该位置的坐标,表示该位置已访问过,不用重复加入该位置的坐标 { flag = false; break; } } return flag; }}以上是“Java如何实现经典游戏复杂迷宫”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的内容对大家有所帮助,如果还想学习更多知识,欢迎关注编程网行业资讯频道!




