这期内容当中小编将会给大家带来有关Mybatis批量更新实体对象的方式是什么,文章内容丰富且以专业的角度为大家分析和叙述,阅读完这篇文章希望大家可以有所收获。
Mybatis批量更新实体对象
(1)Dao层接口
void batchUpdatePlan(List<PubPurchasePlan> plans);(2)Mapper.xml 文件
<sql id="batchUpdatePlanCondition"> <where> <foreach collection="list" item="item" open="( " separator=") or (" close=" )"> comId = #{item.comId} AND id = #{item.id} </foreach> </where></sql><update id="batchUpdatePlan" parameterType="list"> UPDATE pub_purchase_plan <trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=","> <trim prefix="warehouseId=case" suffix="end,"> <foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index"> WHEN comId = #{item.comId} AND id = #{item.id} THEN #{item.warehouseId} </foreach> </trim> <trim prefix="productId=case" suffix="end,"> <foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index"> WHEN comId = #{item.comId} AND id = #{item.id} THEN #{item.productId} </foreach> </trim> <trim prefix="amount=case" suffix="end,"> <foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index"> WHEN comId = #{item.comId} AND id = #{item.id} THEN #{item.amount} </foreach> </trim> <trim prefix="deleted=case" suffix="end,"> <foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index"> WHEN comId = #{item.comId} AND id = #{item.id} THEN #{item.deleted} </foreach> </trim> <trim prefix="price=case" suffix="end,"> <foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index"> WHEN comId = #{item.comId} AND id = #{item.id} THEN #{item.price} </foreach> </trim> <trim prefix="type=case" suffix="end,"> <foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index"> WHEN comId = #{item.comId} AND id = #{item.id} THEN #{item.type} </foreach> </trim> </trim> <include refid="batchUpdatePlanCondition"/></update>Mybatis批量更新数据三种方法效率对比
探讨批量更新数据三种写法的效率问题
实现方式有三种
用for循环通过循环传过来的参数集合,循环出N条sql
用mysql的case when 条件判断变相的进行批量更新
用ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE进行批量更新
下面进行实现。
注意第一种方法要想成功,需要在db链接url后面带一个参数 &allowMultiQueries=true
即: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mysqlTest?characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true
其实这种东西写过来写过去就是差不多一样的代码,不做重复的赘述,直接上代码。
<!-- 批量更新第一种方法,通过接收传进来的参数list进行循环着组装sql --> <update id="updateBatch" parameterType="java.util.List" > <foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" open="" close="" separator=";"> update standard_relation <set > <if test="item.standardFromUuid != null" > standard_from_uuid = #{item.standardFromUuid,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, </if> <if test="item.standardToUuid != null" > standard_to_uuid = #{item.standardToUuid,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, </if> <if test="item.gmtModified != null" > gmt_modified = #{item.gmtModified,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP}, </if> </set> where id = #{item.id,jdbcType=BIGINT} </foreach> </update> <!-- 批量更新第二种方法,通过 case when语句变相的进行批量更新 --> <update id="updateBatch" parameterType="java.util.List" > update standard_relation <trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=","> <trim prefix="standard_from_uuid =case" suffix="end,"> <foreach collection="list" item="i" index="index"> <if test="i.standardFromUuid!=null"> when id=#{i.id} then #{i.standardFromUuid} </if> </foreach> </trim> <trim prefix="standard_to_uuid =case" suffix="end,"> <foreach collection="list" item="i" index="index"> <if test="i.standardToUuid!=null"> when id=#{i.id} then #{i.standardToUuid} </if> </foreach> </trim> <trim prefix="gmt_modified =case" suffix="end,"> <foreach collection="list" item="i" index="index"> <if test="i.gmtModified!=null"> when id=#{i.id} then #{i.gmtModified} </if> </foreach> </trim> </trim> where <foreach collection="list" separator="or" item="i" index="index" > id=#{i.id} </foreach> </update>批量更新第三种方法,用ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE <insert id="updateBatch" parameterType="java.util.List"> insert into standard_relation(id,relation_type, standard_from_uuid, standard_to_uuid, relation_score, stat, last_process_id, is_deleted, gmt_created, gmt_modified,relation_desc)VALUES <foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" separator=","> (#{item.id,jdbcType=BIGINT},#{item.relationType,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{item.standardFromUuid,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{item.standardToUuid,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{item.relationScore,jdbcType=DECIMAL}, #{item.stat,jdbcType=TINYINT}, #{item.lastProcessId,jdbcType=BIGINT}, #{item.isDeleted,jdbcType=TINYINT}, #{item.gmtCreated,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP}, #{item.gmtModified,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},#{item.relationDesc,jdbcType=VARCHAR}) </foreach> ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE id=VALUES(id),relation_type = VALUES(relation_type),standard_from_uuid = VALUES(standard_from_uuid),standard_to_uuid = VALUES(standard_to_uuid), relation_score = VALUES(relation_score),stat = VALUES(stat),last_process_id = VALUES(last_process_id), is_deleted = VALUES(is_deleted),gmt_created = VALUES(gmt_created), gmt_modified = VALUES(gmt_modified),relation_desc = VALUES(relation_desc) </insert> @Override public void updateStandardRelations() { List<StandardRelation> list=standardRelationMapper.selectByStandardUuid("xiemingjieupdate"); for(StandardRelation tmp:list){ tmp.setStandardFromUuid(tmp.getStandardFromUuid()+"update"); tmp.setStandardToUuid(tmp.getStandardToUuid()+"update"); } long begin=System.currentTimeMillis(); standardRelationManager.updateBatch(list); long end=System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.print("当前的批量更新的方法用时"+(end-begin)+"ms"); }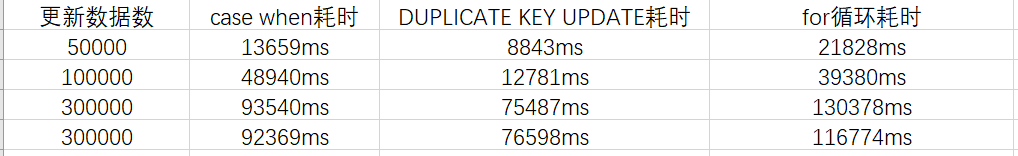
sql语句for循环效率其实相当高的,因为它仅仅有一个循环体,只不过最后update语句比较多,量大了就有可能造成sql阻塞。
case when虽然最后只会有一条更新语句,但是xml中的循环体有点多,每一个case when 都要循环一遍list集合,所以大批量拼sql的时候会比较慢,所以效率问题严重。使用的时候建议分批插入。
duplicate key update可以看出来是最快的,但是一般大公司都禁用,公司一般都禁止使用replace into和INSERT INTO … ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE,这种sql有可能会造成数据丢失和主从上表的自增id值不一致。而且用这个更新时,记得一定要加上id,而且values()括号里面放的是数据库字段,不是java对象的属性字段。

根据效率,安全方面综合考虑,选择适合的很重要。
上述就是小编为大家分享的Mybatis批量更新实体对象的方式是什么了,如果刚好有类似的疑惑,不妨参照上述分析进行理解。如果想知道更多相关知识,欢迎关注编程网行业资讯频道。







