这篇文章主要介绍Canvas事件绑定的示例分析,文中介绍的非常详细,具有一定的参考价值,感兴趣的小伙伴们一定要看完!
我先来讲下实现原理:其实就是canvas绑定相关事件,在通过记录图片所在canvas的坐标,判断事件作用于哪个图片中。这样讲是不是感觉跟事件代理有点相似咧。不过实现起来还是有稍许复杂的。
ps:下面的代码我是用ts写的,大家当es6看就好了,稍有不同的可以查看
typescript的文档 (typescript真的很好用,建议大家多多了解)。
1、建立图片和canvas之间的联系(这里我用色块来代替图片)
这里要色块和canvas建立一定的联系,而不是单纯的渲染。还要记录色块所在坐标、宽高。我们先一步一步来实现
首先写基本的html页面创建一个canvas:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>canvas事件</title> <style> html, body { height: 100%; background: #eee; } canvas { background: #fff; display: block; margin: 0 auto; } </style></head><body> <canvas width="500" height="500" id="canvas"></canvas></body>下一步,我们要定一个Canvas的类,这个类应该要有些什么功能呢?
要有对应的canvas。
装色块数据的容器。
有添加色块的方法。
渲染色块的方法。
渲染所有色块的方法。
因为色块也有自己的一些参数,为了方便拓展,我们也为色块定一个类,这类需要的功能有:
宽、高、颜色、坐标(x,y),还有Canvas实例;初步就定这几个吧
ok开始写
// Canvas类class Canvas { blockList: Block[] ctx: any canvas: any createBlock (option) { option.Canvas = this this.blockList.push(new Block(option)) this.painting() } rendering (block) { // 渲染色块函数 this.ctx.fillStyle = block.color this.ctx.fillRect(block.x, block.y, block.w, block.h) } painting () { // 将容器里的色块全部渲染到canvas // 清空画布(渲染之前应该将老的清空) this.ctx.fillStyle = '#fff' this.ctx.fillRect(0, 0, this.canvas.width, this.canvas.height) this.blockList.forEach(ele => { this.rendering(ele) }) } constructor (ele) { // 初始化函数(输入的是canvas) // 设置canvas this.canvas = ele this.ctx = this.canvas.getContext('2d') // 色块容器 this.blockList = [] }}class Block { w: number h: number x: number y: number color: string Canvas: Canvas hierarchy: number constructor ({ w, h, x, y, color, Canvas }) { // 初始化设置色块相关属性 this.w = w this.h = h this.x = x this.y = y this.color = color this.Canvas = Canvas }}下面运行一波试试
// 创建Canvas实例,并添加蓝色个宽高100px,位置(100,100)、(300,100)红色和蓝色的色块 var canvas = new Canvas(document.getElementById('canvas')) canvas.createBlock({ // 红色 x: 100, y: 100, w: 100, h: 100, color: '#f00' }) canvas.createBlock({ // 蓝色 x: 100, y: 100, w: 300, h: 100, color: '#00f' })运行结果如下:

2、给色块添加点击事件
这里并不能直接给色块添加点击事件的,所以要通过坐标的方式判断目前点击的是哪个色块。
先给canvas添加点击事件。
判断色块区域。
执行相应事件。
class Block { // ...省略部分代码 checkBoundary (x, y) { // 判断边界方法 return x > this.x && x < (this.x + this.w) && y > this.y && y < (this.y + this.h) } mousedownEvent () { // 点击事件 console.log(`点击了颜色为${this.color}的色块`) }}class Canvas { // ...省略部分代码 constructor (ele) { this.canvas = ele this.ctx = this.canvas.getContext('2d') this.blockList = [] // 事件绑定(这里有一个要注意的,我这里用了bind方法,是为了将“mousedownEvent”方法内的this指向切换到Canvas) this.canvas.addEventListener('click', this.mousedownEvent.bind(this)) // 点击事件 } mousedownEvent () { // 点击事件 const x = e.offsetX const y = e.offsetY // 这里将点击的坐标传给所有色块,根据边界判断方法判断是否在点击在内部。是的话执行色块的事件方法。 this.blockList.forEach(ele => { if (ele.checkBoundary(x, y)) ele.mousedownEvent(e) }) }}
到这里为止已经实现了对不同canvas内不同色块绑定对应的点击事件。不过这个点击事件是不完美的,因为目前为止我们还没有引入层级的概念,就是说两个色块重叠部分点击的话,全部都会触发。所以我们还要给色块加入层级的属性。实现一个点击某一个色块改色块的层级就会提升到最高。
class Block { // ...省略部分代码 constructor ({ w, h, x, y, color, Canvas, hierarchy }) { // 初始化设置色块相关属性 this.w = w this.h = h this.x = x this.y = y this.color = color this.Canvas = Canvas this.hierarchy = 0 }}class Canvas { // ...省略部分代码 constructor (ele) { this.canvas = ele this.ctx = this.canvas.getContext('2d') this.blockList = [] // 事件绑定(这里有一个要注意的,我这里用了bind方法,是为了将“mousedownEvent”方法内的this指向切换到Canvas) this.canvas.addEventListener('click', this.mousedownEvent.bind(this)) // 点击事件 this.nowBlock = null // 当前选中的色块 } createBlock (option) { // 创建色块函数(这里的Block是色块的类) option.Canvas = this // 创建最新的色块的层级应该是最高的 option.hierarchy = this.blockList.length this.blockList.push(new Block(option)) this.rendering() } mousedownEvent (e) { // 点击事件 const x = e.offsetX const y = e.offsetY // 获取点中里层级最高的色块 this.nowBlock = (this.blockList.filter(ele => ele.checkBoundary(x, y))).pop() // 如果没有捕获的色块直接退出 if (!this.nowBlock) return // 将点击到的色块层级提高到最高 this.nowBlock.hierarchy = this.blockList.length // 重新排序(从小到大) this.blockList.sort((a, b) => a.hierarchy - b.hierarchy) // 在重新从0开始分配层级 this.blockList.forEach((ele, idx) => ele.hierarchy = idx) // 重新倒序排序后再重新渲染。 this.painting() this.nowBlock.mousedownEvent(e) // 只触发选中的色块的事件 }}// 这里我们还得加入第三块色块与红色色块重叠的色块canvas.createBlock({ x: 150, y: 150, w: 100, h: 100, color: '#0f0'})
Canvas中“mousedownEvent”方法内的代码是有点复杂的,主要是有点绕。
首先是this.nowBlock = (this.blockList.filter(ele => ele.checkBoundary(x, y))).pop()这段代码是怎么获取到点击到的色块中层级最高的色块。这里因为我们每次添加色块都是设置了最高层级的,所以“blockList”内的色块都是按层级从小到大排序的。所以我们取最后一个就可以了。
第二步就是将拿到的色块的层级提升到最高。
第三步就是从小到大重新排列色块。
因为第二步的时候我们修改了选中色块的层级,导致所有色块的层级不是连续的,为了避免层级不可控,我们还得重新定义层级。
重新渲染色块到canvas中,因为“blockList”内的色块是排好序的,所以按顺序渲染即可。
运行后的效果就是下面这样了:
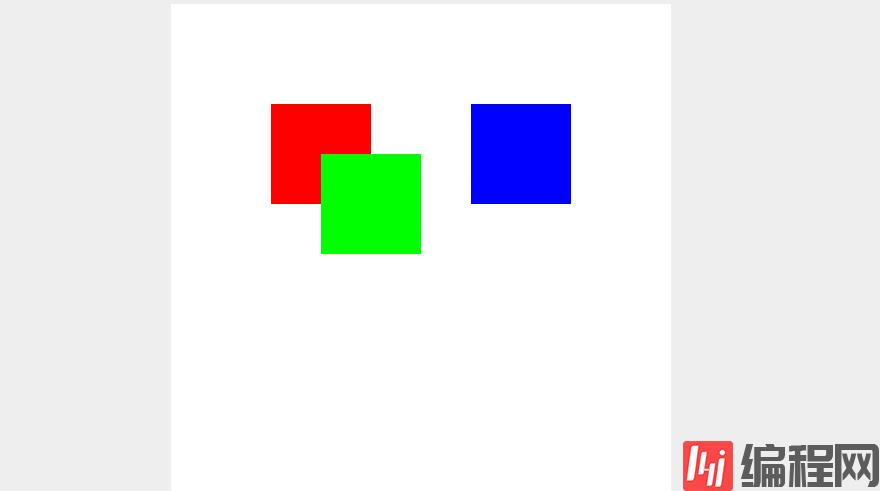
3、实现对不同色块进行拖拽
在上面我们已经实现了获取不同的色块,并修改它的层级。下面我们要实现色块的拖拽,主要就是获取鼠标移动过程中和一开始点击下去时位置坐标的变化。这个原理和普通的dom拖拽实现原理一样。
获取点击色块的点,距离色块左边和上边的距离(disX, disY)。
鼠标移动时,用鼠标当前距离canvas左边和上边的距离减去(disX, disY)这里就是色块的x,y坐标了。
class Block { // ...省略部分代码 mousedownEvent (e: MouseEvent) { const disX = e.offsetX - this.x // 点击时距离色块左边的距离 const disY = e.offsetY - this.y // 点击时距离色块上边的距离 // 绑定鼠标滑动事件;这里mouseEvent.offsetX同样是鼠标距离canvas左侧的距离,mouseEvent.offsetX - disX就是色块的x坐标了。同理y也是这样算的。最后在重新渲染就好了。 document.onmousemove = (mouseEvent) => { this.x = mouseEvent.offsetX - disX this.y = mouseEvent.offsetY - disY this.Canvas.painting() } // 鼠标松开则清空所有事件 document.onmouseup = () => { document.onmousemove = document.onmousedown = null } // console.log(`点击了颜色为${this.color}的色块22`) }}效果如下:
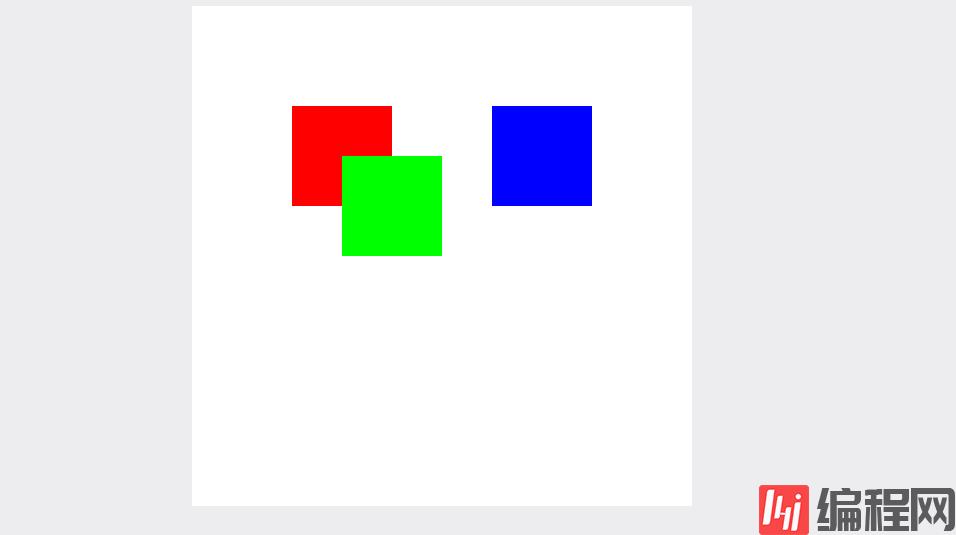
下面贴上完整的代码(html和调用的方法就不放了)这个例子只是简单实现给canvas内的内容绑定事件,大家可以实现复杂一点的,例如把色块换成图片,除了拖拽还以给图片缩放,旋转,删除等等。
class Canvas { blockList: Block[] ctx: any canvas: any nowBlock: Block createBlock (option) { option.hierarchy = this.blockList.length option.Canvas = this this.blockList.push(new Block(option)) this.painting() } rendering (block) { this.ctx.fillStyle = block.color this.ctx.fillRect(block.x, block.y, block.w, block.h) } painting () { // 清空画布 this.ctx.fillStyle = '#fff' this.ctx.fillRect(0, 0, this.canvas.width, this.canvas.height) this.blockList.forEach(ele => { this.rendering(ele) }) } mousedownEvent (e: MouseEvent) { // 点击事件 const x = e.offsetX const y = e.offsetY // 获取点中里层级最高的色块 this.nowBlock = (this.blockList.filter(ele => ele.checkBoundary(x, y))).pop() // 如果没有捕获的色块直接退出 if (!this.nowBlock) return // 将点击到的色块层级提高到最高 this.nowBlock.hierarchy = this.blockList.length // 重新排序(从小到大) this.blockList.sort((a, b) => a.hierarchy - b.hierarchy) // 在重新从0开始分配层级 this.blockList.forEach((ele, idx) => ele.hierarchy = idx) // 重新倒序排序后再重新渲染。 this.painting() this.nowBlock.mousedownEvent(e) // this.blockList.forEach(ele => { // if (ele.checkBoundary(x, y)) ele.clickEvent(e) // }) } constructor (ele) { this.canvas = ele this.ctx = this.canvas.getContext('2d') this.blockList = [] // 事件绑定 this.canvas.addEventListener('mousedown', this.mousedownEvent.bind(this)) }}class Block { w: number h: number x: number y: number color: string Canvas: Canvas hierarchy: number constructor ({ w, h, x, y, color, Canvas, hierarchy }) { this.w = w this.h = h this.x = x this.y = y this.color = color this.Canvas = Canvas this.hierarchy = hierarchy } checkBoundary (x, y) { return x > this.x && x < (this.x + this.w) && y > this.y && y < (this.y + this.h) } mousedownEvent (e: MouseEvent) { const disX = e.offsetX - this.x const disY = e.offsetY - this.y document.onmousemove = (mouseEvent) => { this.x = mouseEvent.offsetX - disX this.y = mouseEvent.offsetY - disY this.Canvas.painting() } document.onmouseup = () => { document.onmousemove = document.onmousedown = null } // console.log(`点击了颜色为${this.color}的色块22`) }}以上是“Canvas事件绑定的示例分析”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!希望分享的内容对大家有帮助,更多相关知识,欢迎关注编程网行业资讯频道!




