目录
一、强化学习的主要构成

强化学习主要由两部分组成:智能体(agent)和环境(env)。在强化学习过程中,智能体与环境一直在交互。智能体在环境里面获取某个状态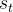 后,它会利用该状态输出一个动作(action)
后,它会利用该状态输出一个动作(action)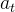 。然后这个动作会在环境之中被执行,环境会根据智能体采取的动作,输出下一个状态
。然后这个动作会在环境之中被执行,环境会根据智能体采取的动作,输出下一个状态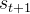 以及当前这个动作带来的奖励
以及当前这个动作带来的奖励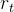 。智能体的目的就是尽可能多地从环境中获取奖励。
。智能体的目的就是尽可能多地从环境中获取奖励。
二、基于python的强化学习框架
基于python的强化学习框架有很多种,具体可以见这个博主的博客:(7条消息) 【强化学习/gym】(二)一些强化学习的框架或代码_o0o_-_的博客-CSDN博客_可解释性的强化学习框架代码 本次我使用到的框架是pytorch,因为DQN算法的实现包含了部分的神经网络,这部分对我来说使用pytorch会更顺手,所以就选择了这个。
三、gym
gym 定义了一套接口,用于描述强化学习中的环境这一概念,同时在其官方库中,包含了一些已实现的环境。
四、DQN算法
传统的强化学习算法使用的是Q表格存储状态价值函数或者动作价值函数,但是实际应用时,问题在的环境可能有很多种状态,甚至数不清,所以这种情况下使用离散的Q表格存储价值函数会非常不合理,所以DQN(Deep Q-learning)算法,使用神经网络拟合动作价值函数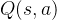 。
。
通常DQN算法只能处理动作离散,状态连续的情况,使用神经网络拟合出动作价值函数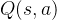 , 然后针对动作价值函数,选择出当状态state固定的Q值最大的动作a。
, 然后针对动作价值函数,选择出当状态state固定的Q值最大的动作a。

DQN算法有两个特点:
1.经验回放
每一次的样本都放到样本池中,所以可以多次反复的使用一个样本,重复利用。训练时一次随机抽取多个数据样本来进行训练。
2.目标网络
DQN算法的更新目标时让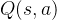 逼近
逼近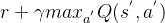 , 但是如果两个Q使用一个网络计算,那么Q的目标值也在不断改变, 容易造成神经网络训练的不稳定。DQN使用目标网络,训练时目标值Q使用目标网络来计算,目标网络的参数定时和训练网络的参数同步。
, 但是如果两个Q使用一个网络计算,那么Q的目标值也在不断改变, 容易造成神经网络训练的不稳定。DQN使用目标网络,训练时目标值Q使用目标网络来计算,目标网络的参数定时和训练网络的参数同步。
五、使用pytorch实现DQN算法
import timeimport randomimport torchfrom torch import nnfrom torch import optimimport gymimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom collections import deque, namedtuple # 队列类型from tqdm import tqdm # 绘制进度条用device = torch. Device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")Transition = namedtuple('Transition', ('state', 'action', 'reward', 'next_state', 'done'))1.replay memory
class ReplayMemory(object): def __init__(self, memory_size): self.memory = deque([], maxlen=memory_size) def sample(self, batch_size): batch_data = random.sample(self.memory, batch_size) state, action, reward, next_state, done = zip(*batch_data) return state, action, reward, next_state, done def push(self, *args): # *args: 把传进来的所有参数都打包起来生成元组形式 # self.push(1, 2, 3, 4, 5) # args = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) self.memory.append(Transition(*args)) def __len__(self): return len(self.memory)2.神经网络部分
class Qnet(nn.Module): def __init__(self, n_observations, n_actions): super(Qnet, self).__init__() self.model = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(n_observations, 128), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(128, n_actions) ) def forward(self, state): return self.model(state)3.Agent
class Agent(object): def __init__(self, observation_dim, action_dim, gamma, lr, epsilon, target_update): self.action_dim = action_dim self.q_net = Qnet(observation_dim, action_dim).to(device) self.target_q_net = Qnet(observation_dim, action_dim).to(device) self.gamma = gamma self.lr = lr self.epsilon = epsilon self.target_update = target_update self.count = 0 self.optimizer = optim.Adam(params=self.q_net.parameters(), lr=lr) self.loss = nn.MSELoss() def take_action(self, state): if np.random.uniform(0, 1) < 1 - self.epsilon: state = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float).to(device) action = torch.argmax(self.q_net(state)).item() else: action = np.random.choice(self.action_dim) return action def update(self, transition_dict): states = transition_dict.state actions = np.expand_dims(transition_dict.action, axis=-1) # 扩充维度 rewards = np.expand_dims(transition_dict.reward, axis=-1) # 扩充维度 next_states = transition_dict.next_state dones = np.expand_dims(transition_dict.done, axis=-1) # 扩充维度 states = torch.tensor(states, dtype=torch.float).to(device) actions = torch.tensor(actions, dtype=torch.int64).to(device) rewards = torch.tensor(rewards, dtype=torch.float).to(device) next_states = torch.tensor(next_states, dtype=torch.float).to(device) dones = torch.tensor(dones, dtype=torch.float).to(device) # update q_values # gather(1, acitons)意思是dim=1按行号索引, index=actions # actions=[[1, 2], [0, 1]] 意思是索引出[[第一行第2个元素, 第1行第3个元素],[第2行第1个元素, 第2行第2个元素]] # 相反,如果是这样 # gather(0, acitons)意思是dim=0按列号索引, index=actions # actions=[[1, 2], [0, 1]] 意思是索引出[[第一列第2个元素, 第2列第3个元素],[第1列第1个元素, 第2列第2个元素]] # states.shape(64, 4) actions.shape(64, 1), 每一行是一个样本,所以这里用dim=1很合适 predict_q_values = self.q_net(states).gather(1, actions) with torch.no_grad(): # max(1) 即 max(dim=1)在行向找最大值,这样的话shape(64, ), 所以再加一个view(-1, 1)扩增至(64, 1) max_next_q_values = self.target_q_net(next_states).max(1)[0].view(-1, 1) q_targets = rewards + self.gamma * max_next_q_values * (1 - dones) l = self.loss(predict_q_values, q_targets) self.optimizer.zero_grad() l.backward() self.optimizer.step() if self.count % self.target_update == 0: # copy model parameters self.target_q_net.load_state_dict(self.q_net.state_dict()) self.count += 14.模型训练函数
def run_episode(env, agent, repalymemory, batch_size): state = env.reset() reward_total = 0 while True: action = agent.take_action(state) next_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) # print(reward) repalymemory.push(state, action, reward, next_state, done) reward_total += reward if len(repalymemory) > batch_size: state_batch, action_batch, reward_batch, next_state_batch, done_batch = repalymemory.sample(batch_size) T_data = Transition(state_batch, action_batch, reward_batch, next_state_batch, done_batch) # print(T_data) agent.update(T_data) state = next_state if done: break return reward_totaldef episode_evaluate(env, agent, render): reward_list = [] for i in range(5): state = env.reset() reward_episode = 0 while True: action = agent.take_action(state) next_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) reward_episode += reward state = next_state if done: break if render: env.render() reward_list.append(reward_episode) return np.mean(reward_list).item()def test(env, agent, delay_time): state = env.reset() reward_episode = 0 while True: action = agent.take_action(state) next_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action) reward_episode += reward state = next_state if done: break env.render() time. Sleep(delay_time)5.训练模型
模型训练使用到的环境时gym提供的CartPole游戏(具体可以看这里:Cart Pole - Gym Documentation (gymlibrary.dev)),这个环境比较经典,小车运行结束的要求有三个:
(1)杆子的角度超过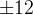 度
度
(2)小车位置大于 ±2.4(小车中心到达显示屏边缘)
(3)小车移动步数超过200(v1是500)
小车每走一步奖励就会+1,所以在v0版本环境中,小车一次episode的最大奖励为200。

if __name__ == "__main__": # print("prepare for RL") env = gym.make("CartPole-v0") env_name = "CartPole-v0" observation_n, action_n = env.observation_space.shape[0], env.action_space.n # print(observation_n, action_n) agent = Agent(observation_n, action_n, gamma=0.98, lr=2e-3, epsilon=0.01, target_update=10) replaymemory = ReplayMemory(memory_size=10000) batch_size = 64 num_episodes = 200 reward_list = [] # print("start to train model") # 显示10个进度条 for i in range(10): with tqdm(total=int(num_episodes/10), desc="Iteration %d" % i) as pbar: for episode in range(int(num_episodes / 10)): reward_episode = run_episode(env, agent, replaymemory, batch_size) reward_list.append(reward_episode) if (episode+1) % 10 == 0: test_reward = episode_evaluate(env, agent, False) # print("Episode %d, total reward: %.3f" % (episode, test_reward)) pbar.set_postfix({ 'episode': '%d' % (num_episodes / 10 * i + episode + 1), 'return' : '%.3f' % (test_reward) }) pbar.update(1) # 更新进度条 test(env, agent, 0.5) # 最后用动画观看一下效果 episodes_list = list(range(len(reward_list))) plt.plot(episodes_list, reward_list) plt.xlabel('Episodes') plt.ylabel('Returns') plt.title('Double DQN on {}'.format(env_name)) plt.show()训练结果如图所示:

参考资料:
来源地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Er_Studying_Bai/article/details/128462002







