这篇文章给大家分享的是有关怎么用C语言实现链式栈的内容。小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,一起跟随小编过来看看吧。
堆栈的基本概念
堆栈是只能在一端增删元素的表结构,该位置称为栈顶堆栈的基本运算是压入和弹出,前者相当于插入,而后者则是删除最后插入的元素,形成后进先出的运算规则最后插入的元素在被弹出之前可以作为栈顶被外界访问从空栈中弹出,或向满栈中压入,都被认为是一种错误
常见的栈有顺序栈和链式栈
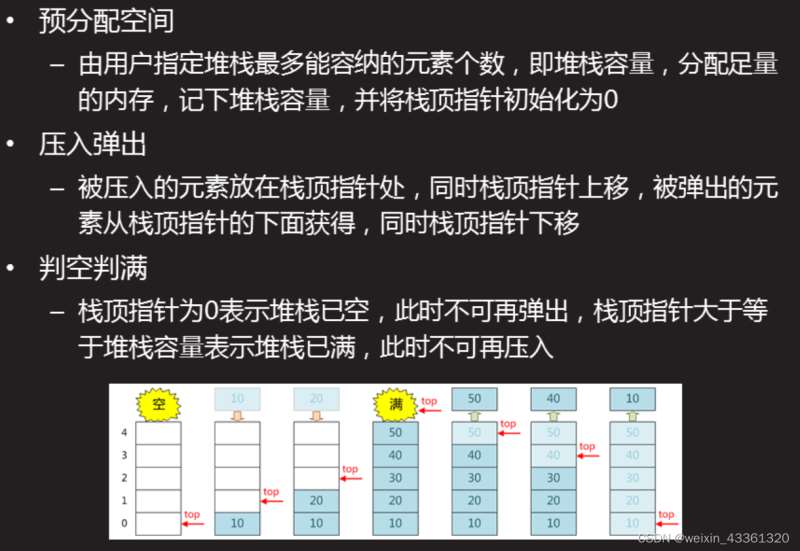
顺序栈
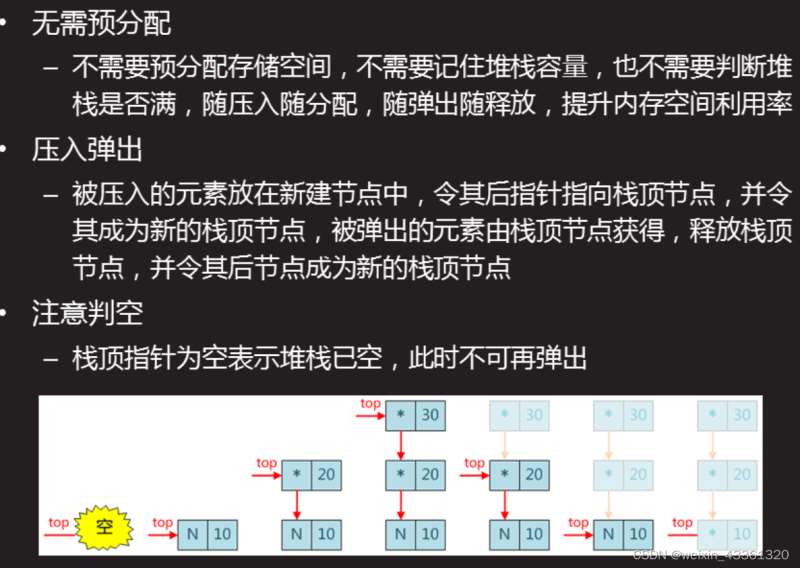
链式栈
- 链式栈的C代码实现
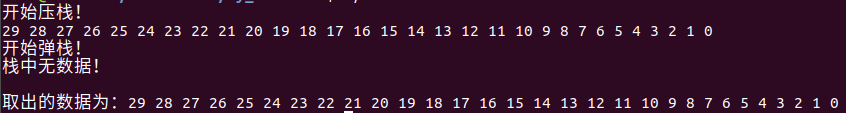
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>typedef struct node { struct node* pnode; int data;}node_t;typedef struct stack { struct node* top;//栈顶指针 int size;//栈中数据个数}stack_t;void stack_init(stack_t* stk){ stk->top = NULL; stk->size = 0;}void stack_push(stack_t* stk, int data){ node_t *node = malloc(sizeof(node_t)); node->data = data; node->pnode = stk->top; stk->top = node; stk->size++;}void stack_pop(stack_t* stk, int buf[], int size){ for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { if(stk->size == 0) { printf("栈中数据已弹净!\n"); break; } node_t* temp = stk->top; buf[i] = stk->top->data; stk->top = stk->top->pnode; stk->size--; free(temp); } }void stack_deinit(stack_t* stk){ while(stk->size || stk->top) { node_t* temp = stk->top; stk->top = stk->top->pnode; stk->size--; free(temp); } }void print_stack(stack_t* stk){ if(stk->size == 0) { printf("栈中无数据!\n"); } for(node_t* node = stk->top; node; node = node->pnode) { printf("%d ",node->data); } printf("\n");}#define N 30int main(void){ stack_t stack; int buf[N]; stack_init(&stack); printf("开始压栈!\n"); for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) { stack_push(&stack, i); } print_stack(&stack);//打印栈中数据 //stack_deinit(&stack); printf("开始弹栈!\n"); stack_pop(&stack, buf, N);//弹栈 print_stack(&stack); printf("取出的数据为:"); for(int i = 0; i < sizeof(buf) / sizeof(buf[0]); ++i) { printf("%d ", buf[i]); } printf("\n"); return 0;}代码运行效果
感谢各位的阅读!关于“怎么用C语言实现链式栈”这篇文章就分享到这里了,希望以上内容可以对大家有一定的帮助,让大家可以学到更多知识,如果觉得文章不错,可以把它分享出去让更多的人看到吧!




