本文小编为大家详细介绍“Java怎么用递归实现树形结构的工具类”,内容详细,步骤清晰,细节处理妥当,希望这篇“Java怎么用递归实现树形结构的工具类”文章能帮助大家解决疑惑,下面跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来学习新知识吧。
需求描述
有时候,我们的数据是带有层级的,比如常见的省市区三级联动,就是一层套着一层,如下图:
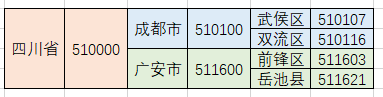
而我们在数据库存放数据的时候,往往是列表形式的,如下图:
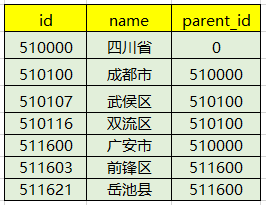
那么当我们从数据库查询出来,返回给前端的时候,前端又需要给出树形层级的时候,这个时候可能就需要递归处理为树形结构了,因此下面这个工具或许就可以用得上了。
使用示例
我们按照上面定义一个Place对象,打上工具注解:
@TreeKey 标识唯一
@TreeParentKey 标识父节点标识
@TreeChildren 标识子孙节点集合
@Data@Datapublic class Place { @TreeKey private String id; @TreeParentKey private String parentId; private String name; @TreeChildren private List<Place> children; public Place(String id, String name, String parentId) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.parentId = parentId; }}测试:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Place> places = new ArrayList<>(); places.add(new Place("510000", "四川省", "0")); places.add(new Place("510100", "成都市", "510000")); places.add(new Place("510107", "武侯区", "510100")); places.add(new Place("510116", "双流区", "510100")); places.add(new Place("511600", "广安市", "510000")); places.add(new Place("511603", "前锋区", "511600")); places.add(new Place("511621", "岳池县", "511600")); List<Place> treeList = TreeUtils.getTree(places, "0"); System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(treeList)); }}最终效果:

工具代码
@TreeKey
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;import java.lang.annotation.Retention;import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;import java.lang.annotation.Target;@Target(ElementType.FIELD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface TreeKey {}@TreeParentKey
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;import java.lang.annotation.Retention;import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;import java.lang.annotation.Target;@Target(ElementType.FIELD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface TreeParentKey {}@TreeChildren
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;import java.lang.annotation.Retention;import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;import java.lang.annotation.Target;@Target(ElementType.FIELD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface TreeChildren {}@TreeUtils
package com.csd.utils.tree;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.List;import java.util.Objects;public class TreeUtils { public static <T> List<T> getTree(List<T> list, Object highestParentKey) { if (Objects.isNull(list) || list.isEmpty()) { return Collections.emptyList(); } Field key = null; Field parentKey = null; Field children = null; Field[] fields = list.get(0).getClass().getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : fields) { if (Objects.isNull(key)) { TreeKey treeKey = field.getAnnotation(TreeKey.class); if (Objects.nonNull(treeKey)) { key = field; continue; } } if (Objects.isNull(parentKey)) { TreeParentKey treeParentKey = field.getAnnotation(TreeParentKey.class); if (Objects.nonNull(treeParentKey)) { parentKey = field; continue; } } if (Objects.isNull(children)) { TreeChildren treeChildren = field.getAnnotation(TreeChildren.class); if (Objects.nonNull(treeChildren)) { children = field; continue; } } } if (Objects.isNull(key) || Objects.isNull(parentKey) || Objects.isNull(children)) { return Collections.emptyList(); } key.setAccessible(true); parentKey.setAccessible(true); children.setAccessible(true); // 获取最高层数据 List<T> highs = new ArrayList<>(); try { for (T t : list) { Object pk = parentKey.get(t); if (getString(pk).equals(getString(highestParentKey))) { highs.add(t); } } // 获取最高层子孙节点 for (T t : highs) { setChildren(list, t, key, parentKey, children); } } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return highs; } private static <T> T setChildren(List<T> list, T parent, Field key, Field parentKey, Field children) throws IllegalAccessException { Object k = key.get(parent); List<T> tempList = new ArrayList<>(); for (T t : list) { Object pk = parentKey.get(t); if (getString(k).equals(getString(pk))) { tempList.add(setChildren(list, t, key, parentKey, children)); } } children.set(parent, tempList); return parent; } private static String getString(Object o) { return Objects.isNull(o) ? "" : o.toString(); }}读到这里,这篇“Java怎么用递归实现树形结构的工具类”文章已经介绍完毕,想要掌握这篇文章的知识点还需要大家自己动手实践使用过才能领会,如果想了解更多相关内容的文章,欢迎关注编程网行业资讯频道。




