今天小编给大家分享一下怎么用Python获取和存储时间序列数据的相关知识点,内容详细,逻辑清晰,相信大部分人都还太了解这方面的知识,所以分享这篇文章给大家参考一下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后有所收获,下面我们一起来了解一下吧。
要求
本教程在通过Homebrew已安装Python 3的macOS系统上完成。建议安装额外的工具,比如virtualenv、pyenv或conda-env,以简化Python和Client的安装。完整的要求在这里:
txtinfluxdb-client=1.30.0pandas=1.4.3requests>=2.27.1本教程还假设您已经创建Free Tier InfluxDB云帐户或正在使用InfluxDB OSS,您也已经:
创建了存储桶。您可以将存储桶视为数据库或InfluxDB中最高层次的数据组织。
创建了令牌。
最后,该教程要求您已经使用OpenWeatherMap创建了一个帐户,并已创建了令牌。
请求天气数据
首先,我们需要请求数据。我们将使用请求库,通过OpenWeatherMap API从指定的经度和纬度返回每小时的天气数据。
# Get time series data from OpenWeatherMap APIparams = {'lat':openWeatherMap_lat, 'lon':openWeatherMap_lon, 'exclude': "minutely,daily", 'appid':openWeatherMap_token}r = requests.get(openWeather_url, params = params).json()hourly = r['hourly']将数据转换成Pandas DataFrame
接下来,将JSON数据转换成Pandas DataFrame。我们还将时间戳从秒精度的Unix时间戳转换成日期时间对象。之所以进行这种转换,是由于InfluxDB写入方法要求时间戳为日期时间对象格式。接下来,我们将使用这种方法,将数据写入到InfluxDB。我们还删除了不想写入到InfluxDB的列。
python# Convert data to Pandas DataFrame and convert timestamp to datetime objectdf = pd.json_normalize(hourly)df = df.drop(columns=['weather', 'pop'])df['dt'] = pd.to_datetime(df['dt'], unit='s')print(df.head)将Pandas DataFrame写入到InfluxDB
现在为InfluxDB Python客户端库创建实例,并将DataFrame写入到InfluxDB。我们指定了测量名称。测量含有存储桶中的数据。您可以将其视为InfluxDB的数据组织中仅次于存储桶的第二高层次结构。
您还可以使用data_frame__tag_columns参数指定将哪些列转换成标签。
由于我们没有将任何列指定为标签,我们的所有列都将转换成InfluxDB中的字段。标签用于写入有关您的时间序列数据的元数据,可用于更有效地查询数据子集。字段是您在 InfluxDB中存储实际时间序列数据的位置。
on# Write data to InfluxDBwith InfluxDBClient(url=url, token=token, org=org) as client:df = dfclient.write_api(write_options=SYNCHRONOUS).write(bucket=bucket,record=df,data_frame_measurement_name="weather",data_frame_timestamp_column="dt")完整脚本
回顾一下,不妨看看完整的脚本。 我们采取以下步骤:
导入库。
收集以下内容:
InfluxDB存储桶
InfluxDB组织
InfluxDB令牌
InfluxDB URL
OpenWeatherMap URL
OpenWeatherMap 令牌
创建请求。
将JSON响应转换成Pandas DataFrame。
删除您不想写入到InfluxDB的任何列。
将时间戳列从Unix时间转换成Pandas日期时间对象。
为InfluxDB Python Client库创建实例。
编写DataFrame,并指定测量名称和时间戳列。
pythonimport requestsimport influxdb_clientimport pandas as pdfrom influxdb_client import InfluxDBClientfrom influxdb_client.client.write_api import SYNCHRONOUSbucket = "OpenWeather"org = "" # or email you used to create your Free Tier InfluxDB Cloud accounttoken = " url = "" # for example, https://us-west-2-1.aws.cloud2.influxdata.com/openWeatherMap_token = ""openWeatherMap_lat = "33.44"openWeatherMap_lon = "-94.04"openWeather_url = "https://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/onecall"# Get time series data from OpenWeatherMap APIparams = {'lat':openWeatherMap_lat, 'lon':openWeatherMap_lon, 'exclude': "minutely,daily", 'appid':openWeatherMap_token}r = requests.get(openWeather_url, params = params).json()hourly = r['hourly']# Convert data to Pandas DataFrame and convert timestamp to datetime objectdf = pd.json_normalize(hourly)df = df.drop(columns=['weather', 'pop'])df['dt'] = pd.to_datetime(df['dt'], unit='s')print(df.head)# Write data to InfluxDBwith InfluxDBClient(url=url, token=token, org=org) as client:df = dfclient.write_api(write_options=SYNCHRONOUS).write(bucket=bucket,record=df,data_frame_measurement_name="weather",data_frame_timestamp_column="dt")查询数据
现在,我们已经将数据写入到InfluxDB,可以使用InfluxDB UI来查询数据了。导航到数据资源管理器(从左侧导航栏中)。使用Query Builder(查询构建器),选择想要可视化的数据和想要为之可视化的范围,然后点击“提交”。
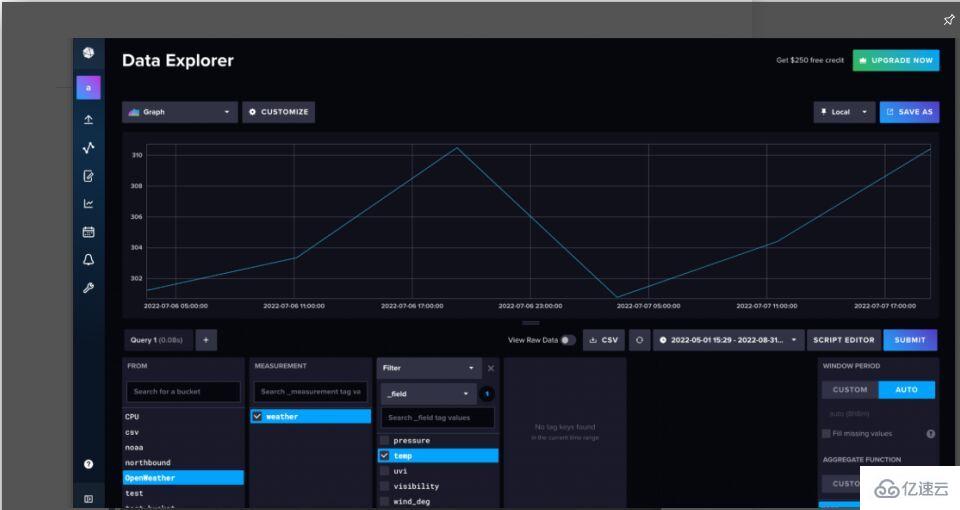
图1. 天气数据的默认物化视图。InfluxDB自动聚合时间序列数据,这样新用户就不会意外查询太多数据而导致超时
专业提示:当您使用查询构建器查询数据时,InfluxDB自动对数据进行下采样。要查询原始数据,导航到Script Editor(脚本编辑器)以查看底层Flux查询。Flux是面向InfluxDB的原生查询和脚本语言,可用于使用您的时间序列数据来分析和创建预测。使用aggregateWindow()函数取消行注释或删除行,以查看原始数据。
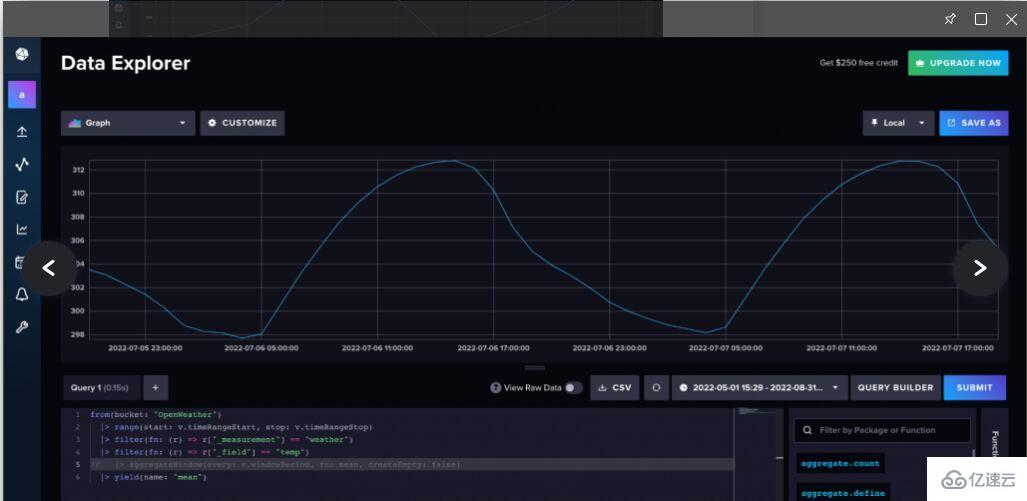
图2. 导航到脚本编辑器,并取消注释或删除aggregateWindow()函数,以查看原始天气数据
以上就是“怎么用Python获取和存储时间序列数据”这篇文章的所有内容,感谢各位的阅读!相信大家阅读完这篇文章都有很大的收获,小编每天都会为大家更新不同的知识,如果还想学习更多的知识,请关注编程网行业资讯频道。












