本文小编为大家详细介绍“C++继承中的对象构造与析构和赋值重载实例分析”,内容详细,步骤清晰,细节处理妥当,希望这篇“C++继承中的对象构造与析构和赋值重载实例分析”文章能帮助大家解决疑惑,下面跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来学习新知识吧。
一、构造/析构顺序及继承性
class A{private:int _a;public:A(int a = 0): _a(a){cout << "A()" << this << endl;}~A(){cout << "~A()"<< this <<endl;}};class B : public A{private:int _b;public:B(int b): _b(b), A(){cout << "B()" << this << endl;}~B(){cout << "~B()"<< this <<endl;}};
结论:
构造顺序:先构造基类,后构造派生类
析构顺序:先析构派生类,后析构基类
二、拷贝构造的继承性
class A{private:int _a;public:A(int a = 0): _a(a){cout << "A()" << this << endl;}A(const A& src): _a(src._a){cout << "A(const A& src)"<< this << endl;}~A(){cout << "~A()"<< this <<endl;}};class B : public A{private:int _b;public:B(int b): _b(b), A(){cout << "B()" << this << endl;}B(const B& src): _b(src._b){cout << "B(const B& src)" << this << endl;}~B(){cout << "~B()"<< this <<endl;}};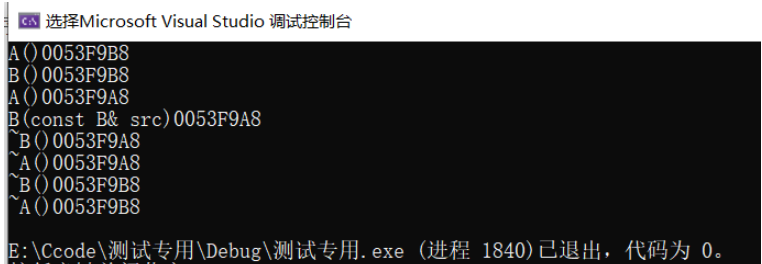
结论:
先调用基类缺省的构造函数,后调用派生类的拷贝构造函数
若派生类没有缺省构造函数A(),就会报错
疑惑:如何去调用基类的拷贝构造而不是缺省构造
#include<iostream>using namespace std;class A{private:int _a;public:A(int a = 0) : _a(a){cout << "A()" << this << endl;}A(const A& src) : _a(src._a){cout << "A(const A& src)" << this << endl;}~A(){cout << "~A()" << this << endl;}};class B : public A{private:int _b;public:B(int b) : _b(b), A(){cout << "B()" << this << endl;}B(const B& src) : _b(src._b), A(src)//发生赋值兼容规则(切片){cout << "B(const B& src)" << this << endl;}~B(){cout << "~B()" << this << endl;}};int main(){B b(10);B b1(b);return 0;}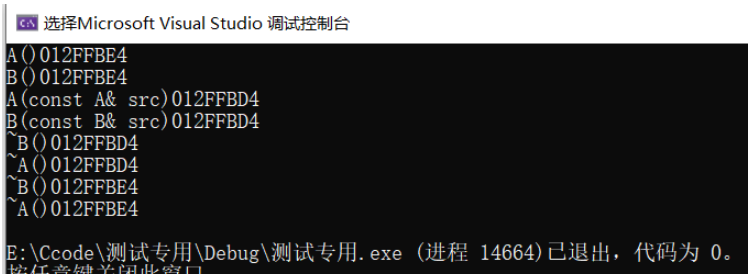
结果:
将B类型src传递给A类型的A(const A& src)拷贝构造函数,发生了赋值兼容规则(切片现象)
三、赋值重载不具有继承性
#include<iostream>using namespace std;class A{private:int _a;public:A(int a = 0) : _a(a){cout << "A()" << this << endl;}A(const A& src) : _a(src._a){cout << "A(const A& src)" << this << endl;}A& operator=(const A& src){if(this != &src){_a = src._a;cout << "A& operator=(const A& src)" << endl;}}~A(){cout << "~A()" << this << endl;}};class B : public A{private:int _b;public:B(int b) : _b(b), A(){cout << "B()" << this << endl;}B(const B& src) : _b(src._b), A(src)//发生赋值兼容规则(切片){cout << "B(const B& src)" << this << endl;}B& operator=(const B& src){if(this != &src){_b = src._b;cout << "B& operator=(const B& src)" << endl;}}~B(){cout << "~B()" << this << endl;}};int main(){B b1(10);B b2(20);b1 = b2;return 0;}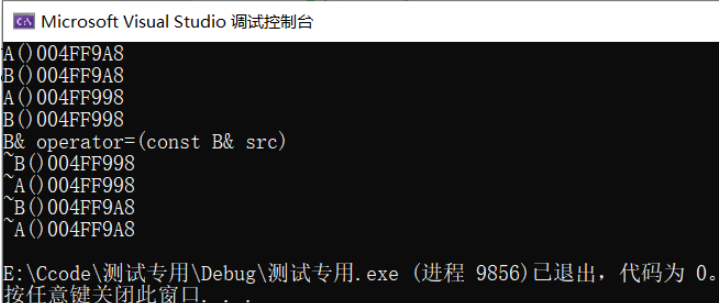
结论:默认情况下仅仅调用了派生类的对象的赋值重载,并未调用基类的赋值重载。
解决方案:
#include<iostream>using namespace std;class A{private:int _a;public:A(int a = 0) : _a(a){cout << "A()" << this << endl;}A(const A& src) : _a(src._a){cout << "A(const A& src)" << this << endl;}A& operator=(const A& src){if(this != &src){_a = src._a;cout << "A& operator=(const A& src)" << endl;}}~A(){cout << "~A()" << this << endl;}};class B : public A{private:int _b;public:B(int b) : _b(b), A(){cout << "B()" << this << endl;}B(const B& src) : _b(src._b), A(src)//发生赋值兼容规则(切片){cout << "B(const B& src)" << this << endl;}B& operator=(const B& src){if(this != &src){*(A*)this = src;//将调用基类赋值重载_b = src._b;cout << "B& operator=(const B& src)" << endl;}}~B(){cout << "~B()" << this << endl;}};int main(){B b1(10);B b2(20);b1 = b2;return 0;}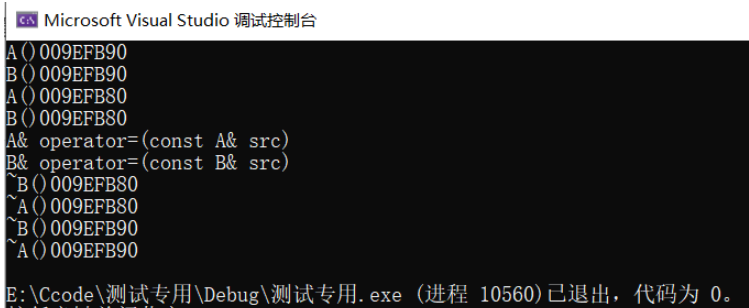
读到这里,这篇“C++继承中的对象构造与析构和赋值重载实例分析”文章已经介绍完毕,想要掌握这篇文章的知识点还需要大家自己动手实践使用过才能领会,如果想了解更多相关内容的文章,欢迎关注编程网行业资讯频道。




