IdleHandler的简单理解和使用
1、IdleHandler 是什么
IdleHandler 说白了,就是 Handler 机制提供的一种,可以在 Looper 事件循环的过程中,当出现空闲的时候,允许我们执行任务的一种机制。
IdleHandler 被定义在 MessageQueue 中,它是一个接口。
public final class MessageQueue { public static interface IdleHandler { boolean queueIdle(); }}- 返回值为 false,即只会执行一次;
- 返回值为 true,即每次当消息队列内没有需要立即执行的消息时,都会触发该方法。
基本使用方法
Looper.myQueue().addIdleHandler(new MessageQueue.IdleHandler() { @Override public boolean queueIdle() { Log.v(TAG, "#looper message has worked out"); return false; } }); }2、IdleHandler 使用方式
2.1、添加和删除
在MessageQueue中:
private final ArrayList<IdleHandler> mIdleHandlers = new ArrayList<>();public void addIdleHandler(@NonNull IdleHandler handler) { if (handler == null) { throw new NullPointerException("Can't add a null IdleHandler"); } synchronized (this) { mIdleHandlers.add(handler); }}public void removeIdleHandler(@NonNull IdleHandler handler) { synchronized (this) { mIdleHandlers.remove(handler); }}通过一个全局变量mIdleHandlers管理所有IdleHandler
2.2、执行
既然 IdleHandler 主要是在 MessageQueue 出现空闲的时候被执行,那么何时出现空闲?
MessageQueue 是一个基于消息触发时间的优先级链表,所以出现空闲存在两种场景。
- MessageQueue 为空,
没有消息; - MessageQueue 中最近需要处理的消息,是一个
延迟消息(when>currentTime),需要滞后执行;
这两个场景,都会尝试执行 IdleHandler。
处理 IdleHandler 的场景,就在 Message.next() 这个获取消息队列下一个待执行消息的方法中,我们跟一下具体的逻辑。
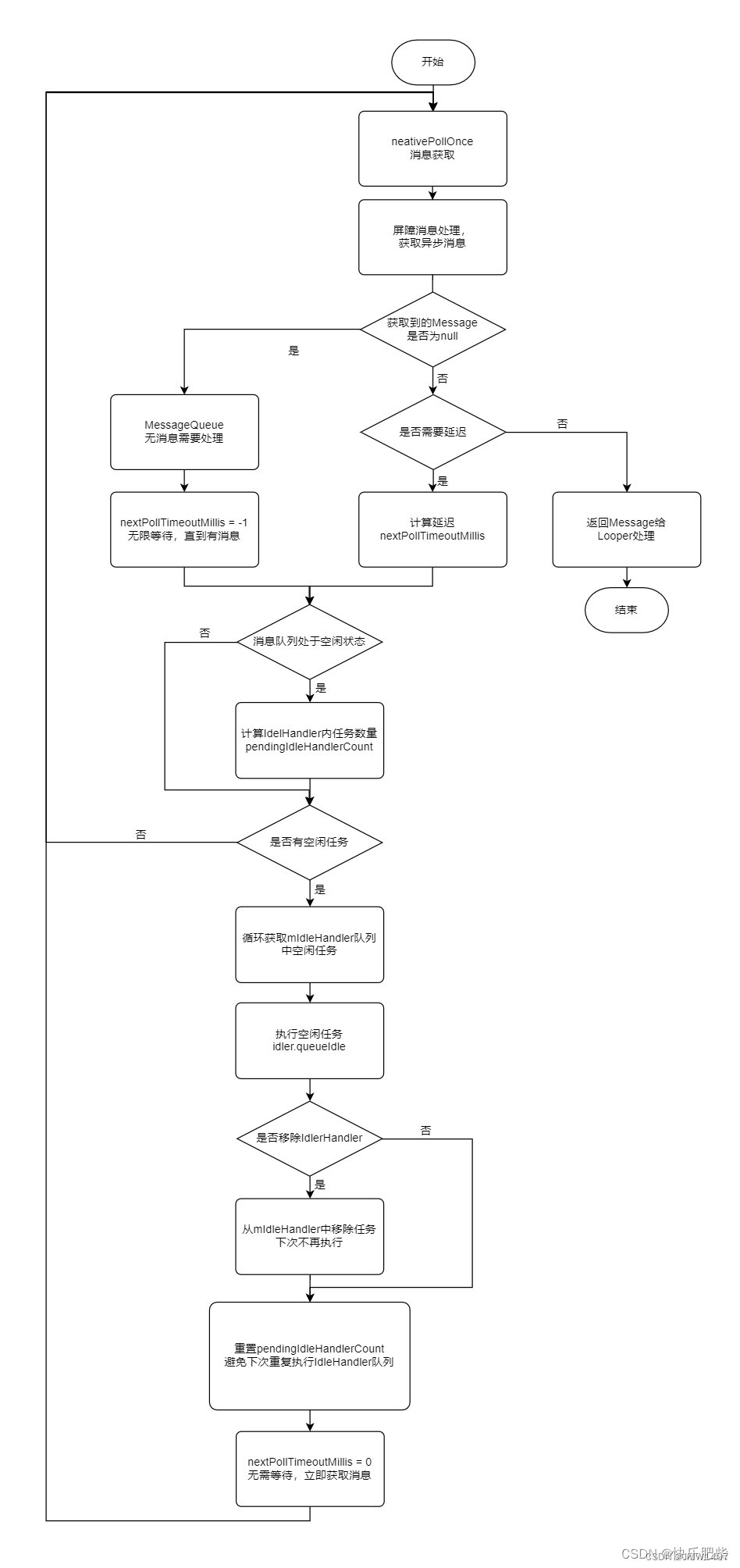
@UnsupportedAppUsage Message next() { // ... int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iteration int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0; for (;;) { if (nextPollTimeoutMillis != 0) { Binder.flushPendingCommands(); } nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis); synchronized (this) { // Try to retrieve the next message. Return if found. final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); Message prevMsg = null; Message msg = mMessages; // 注释1 屏障消息处理,获取异步消息 if (msg != null && msg.target == null) { // Stalled by a barrier. Find the next asynchronous message in the queue. do { prevMsg = msg; msg = msg.next; } while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous()); } // 注释2 获取到Message不为null,则说明存在需要处理的Message if (msg != null) { if (now < msg.when) { // Next message is not ready. Set a timeout to wake up when it is ready. nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(msg.when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE); } else { // Got a message. mBlocked = false; if (prevMsg != null) {prevMsg.next = msg.next; } else {mMessages = msg.next; } msg.next = null; if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Returning message: " + msg); msg.markInUse(); return msg; } } else { // No more messages. // MessageQueue无消息,设置延迟为-1,nativePollOnce无限等待,直到有消息 nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1; } // 注释3 执行到此处,说明没有需要执行的Message(MessageQueue为空,或者存在延迟Message) // Process the quit message now that all pending messages have been handled. if (mQuitting) { dispose(); return null; } // If first time idle, then get the number of idlers to run. // Idle handles only run if the queue is empty or if the first message // in the queue (possibly a barrier) is due to be handled in the future. if (pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0 && (mMessages == null || now < mMessages.when)) { pendingIdleHandlerCount = mIdleHandlers.size(); } // 注释4 IdleHandler队列为空,不执行,进入下一个循环,此后不再会执行IdleHandler判断,除非下次进入next方法 if (pendingIdleHandlerCount <= 0) { // No idle handlers to run. Loop and wait some more. mBlocked = true; continue; } if (mPendingIdleHandlers == null) { mPendingIdleHandlers = new IdleHandler[Math.max(pendingIdleHandlerCount, 4)]; } // 注释5 mIdleHandlers数组赋值给 mPendingIdleHandlers mPendingIdleHandlers = mIdleHandlers.toArray(mPendingIdleHandlers); } // 注释6 执行IdleHandler队列中的空闲任务 for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) { final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i]; mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null; // release the reference to the handler boolean keep = false; try { // 注释7 执行任务逻辑,并返回任务释放移除 keep = idler.queueIdle(); } catch (Throwable t) { Log.wtf(TAG, "IdleHandler threw exception", t); } if (!keep) { synchronized (this) { // 注释8 移除任务,下次不再执行 mIdleHandlers.remove(idler); } } } // 注释9 重置IdleHandler的Count为0,避免下次重复执行IdleHandler队列 pendingIdleHandlerCount = 0; // While calling an idle handler, a new message could have been delivered // so go back and look again for a pending message without waiting. nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0; } }如果本次循环拿到的Message为空,或者这个Message是一个延时的消息(now < mMessages.when)而且还没到指定的触发时间,那么,就认定当前的队列为空闲状态,(此时nextPollTimeoutMillis为-1)。
遍历mPendingIdleHandlers数组(这个数组里面的元素每次都会到mIdleHandlers中去拿)来调用每一个IdleHandler实例的queueIdle方法。
- 当
pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0时,根据mIdleHandlers.size()赋值给
pendingIdleHandlerCount,它是后期循环的基础; - 将
mIdleHandlers中的IdleHandler拷贝到mPendingIdleHandlers数组中,这个数组是临时的,之后进入 for 循环; - 循环中从数组中取出
IdleHandler,并调用其queueIdle()记录返回值存到keep中;
如果这个方法返回false的话,那么这个实例就会从 mIdleHandlers 中移除,也就是当下次队列空闲的时候,不会继续回调它的 queueIdle 方法了。
处理完 IdleHandler 后会将 nextPollTimeoutMillis 设置为0,也就是不阻塞消息队列,当然要注意这里执行的代码同样不能太耗时,因为它是同步执行的,如果太耗时肯定会影响后面的 message 执行。
3、常见问题和使用场景
3.1、使用场景
根据IdleHandler的特性,其使用场景遵循一个基本原则:在不影响其他任务,在消息队列空闲状态下执行。
例如:Android Framework层的GC场景就使用了这个机制,只有当cpu空闲的时候才会去GC:
在ApplicationThread收到GC_WHEN_IDLE消息后,会触发scheduleGcIdler方法:
class H extends Handler { ...... public static final int GC_WHEN_IDLE = 120; ...... public void handleMessage(Message msg) { switch (msg.what) { ...... case GC_WHEN_IDLE: scheduleGcIdler(); ...... } }}在ActivityThread的scheduleGcIdler方法中(ApplicationThread是ActivityThread的非静态内部类,所以可以直接调用对应方法):
// 添加垃圾回收的IdleHandlervoid scheduleGcIdler() { if (!mGcIdlerScheduled) { mGcIdlerScheduled = true; Looper.myQueue().addIdleHandler(mGcIdler); } mH.removeMessages(H.GC_WHEN_IDLE);}// 移除垃圾回收的IdleHandlervoid unscheduleGcIdler() { if (mGcIdlerScheduled) { mGcIdlerScheduled = false; Looper.myQueue().removeIdleHandler(mGcIdler); } mH.removeMessages(H.GC_WHEN_IDLE);}final GcIdler mGcIdler = new GcIdler();final class GcIdler implements MessageQueue.IdleHandler { @Override public final boolean queueIdle() { doGcIfNeeded(); return false; }}void doGcIfNeeded() { mGcIdlerScheduled = false; final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); if ((BinderInternal.getLastGcTime()+MIN_TIME_BETWEEN_GCS) < now) { // 执行垃圾回收 BinderInternal.forceGc("bg"); }}这里通过一个自定义的IdleHandler进行GC的调用,在线程空闲的时候会调用mGcIdler,最终通过BinderInternal.forceGc("bg")方法触发GC,这个GC的最小间隔是5秒(MIN_TIME_BETWEEN_GCS的值)。并且注意了,mGcIdler的queueIdle返回的是false,所以这个mGcIdler会长期存在于主线程的MessageQueue中。
其他常见场景:IdleHandler基本使用及应用案例分析
3.2、常见问题
Q:IdleHandler 主要是在 MessageQueue 出现空闲的时候被执行,那么何时出现空闲?
MessageQueue 是一个基于消息触发时间的优先级队列,所以队列出现空闲存在两种场景。
MessageQueue 为空,没有消息;MessageQueue 中最近需要处理的消息,是一个延迟消息(when>currentTime),需要滞后执行;Q:IdleHandler 有什么用?
IdleHandler 是 Handler 提供的一种在消息队列空闲时,执行任务的时机;当 MessageQueue 当前没有立即需要处理的消息时,会执行 IdleHandler;Q:MessageQueue 提供了 add/remove IdleHandler 的方法,是否需要成对使用?
不是必须;IdleHandler.queueIdle() 的返回值,可以移除加入 MessageQueue 的 IdleHandler;Q:当 mIdleHanders 一直不为空时,为什么不会进入死循环?
只有在 pendingIdleHandlerCount 为 -1 时,才会尝试执行 mIdleHander;pendingIdlehanderCount 在 next() 中初始时为 -1,执行一遍后被置为 0,所以不会重复执行;Q:是否可以将一些不重要的启动服务,搬移到 IdleHandler 中去处理?
不建议;IdleHandler 的处理时机不可控,如果 MessageQueue 一直有待处理的消息,那么 IdleHander 的执行时机会很靠后;Q:IdleHandler 的 queueIdle() 运行在那个线程?
陷进问题,queueIdle() 运行的线程,只和当前 MessageQueue 的 Looper 所在的线程有关;子线程一样可以构造 Looper,并添加 IdleHandler;参考
1 、面试官:“看你简历上写熟悉 Handler 机制,那聊聊 IdleHandler 吧?”
2、深入浅出Handler(七) IdleHandler的巧用
3、关于空闲任务IdleHandler的那些事
4、源码阅读#Handler(下)同步屏障与IdleHandler
来源地址:https://blog.csdn.net/JMW1407/article/details/129133416





